Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (1): 76-89.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2023.01.009
• Physiology and Ecology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jianxin LIU( ), Ruirui LIU, Xiuli LIU, Xiaobin OU, Haiyan JIA, Ting BU, Na LI
), Ruirui LIU, Xiuli LIU, Xiaobin OU, Haiyan JIA, Ting BU, Na LI
Received:2022-02-17
Online:2023-01-20
Published:2022-12-23
Contact:
Jianxin LIU
E-mail:liujx1964@163.com
About author:LIU Jianxin(1964—),male,professor,mainly engaged in the study of plant stress physiology.E-mail:liujx1964@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
Jianxin LIU, Ruirui LIU, Xiuli LIU, Xiaobin OU, Haiyan JIA, Ting BU, Na LI. Effects of Exogenous Hydrogen Sulfide on Contents of Organic Acids and Hormones in Leaves of Avena nuda under Saline-Alkali Stress[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(1): 76-89.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://bbr.nefu.edu.cn/EN/10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2023.01.009
Table 1
Effects of exogenous hydrogen sulfide on the content of organic acids in leaves of naked oat under saline-alkali stress
有机酸 Organic acid | 有机酸质量分数 Content of organic acids /(μg·g-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | SA | SA+NaHS | NaHS | |
| 琥珀酸Succinic acid | 75.88±11.33bc | 88.33±4.46a | 83.06±9.55ab | 73.29±7.60c |
| 丁烯二酸Butenedioic acid | 32.44±5.28b | 40.36±7.71a | 44.44±6.70a | 38.66±2.83ab |
| 苹果酸Malic acid | 1 086.15±63.20b | 1 168.84±90.54a | 1 166.64±95.38a | 1 094.94±47.00ab |
| 柠檬酸Citric acid | 1 861.49±464.71a | 2 320.79±531.62a | 2 166.66±446.02a | 2 150.29±389.79a |
| 丙二酸Malonic acid | 26.94±5.00a | 31.88±6.41a | 28.43±5.20a | 31.47±3.81a |
| 葡萄糖醛酸Glucuronic acid | 30.95±6.21c | 59.70±12.39a | 45.45±6.80b | 45.72±6.43b |
| 泛酸Pantothenic acid | 1 014.42±102.74a | 1 093.14±195.54a | 1 069.82±84.66a | 1 134.46±103.36a |
| 烟酸Nicotinic acid | 2.96±0.62ab | 3.00±0.46ab | 2.52±0.24b | 3.23±0.57a |
| 焦谷氨酸Pyroglutamic acid | 15.99±1.49b | 12.53±2.00c | 11.45±2.21c | 19.10±4.65a |
| 辛二酸Suberic acid | 0.38±0.02b | 0.38±0.07b | 0.33±0.04b | 0.55±0.09a |
| 3-羟基-3-甲基谷氨酸3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaric acid | 5.73±0.70ab | 5.38±0.39b | 6.15±0.49a | 6.02±0.92ab |
| 苯丙酮酸Phenylpyruvic acid | 2.62±0.33a | 3.06±0.64a | 3.12±0.44a | 2.85±0.50a |
| 总有机酸Total organic acids | 4 155.94±551.75b | 4 827.40±753.16a | 4 628.07±535.33ab | 4 600.58±441.97ab |

Fig.1
PLS-DA score plot of organic acids in naked oat leaves under different treatments(A) and 200 permutation test of the model(B)CK.Spraying water under no salt-alkali stress; SA.Spraying water under salt-alkali stress; SA+NaHS.Spraying NaHS under salt-alkali stress; NaHS.Spraying NaHS under no salt-alkali stress;The same as below
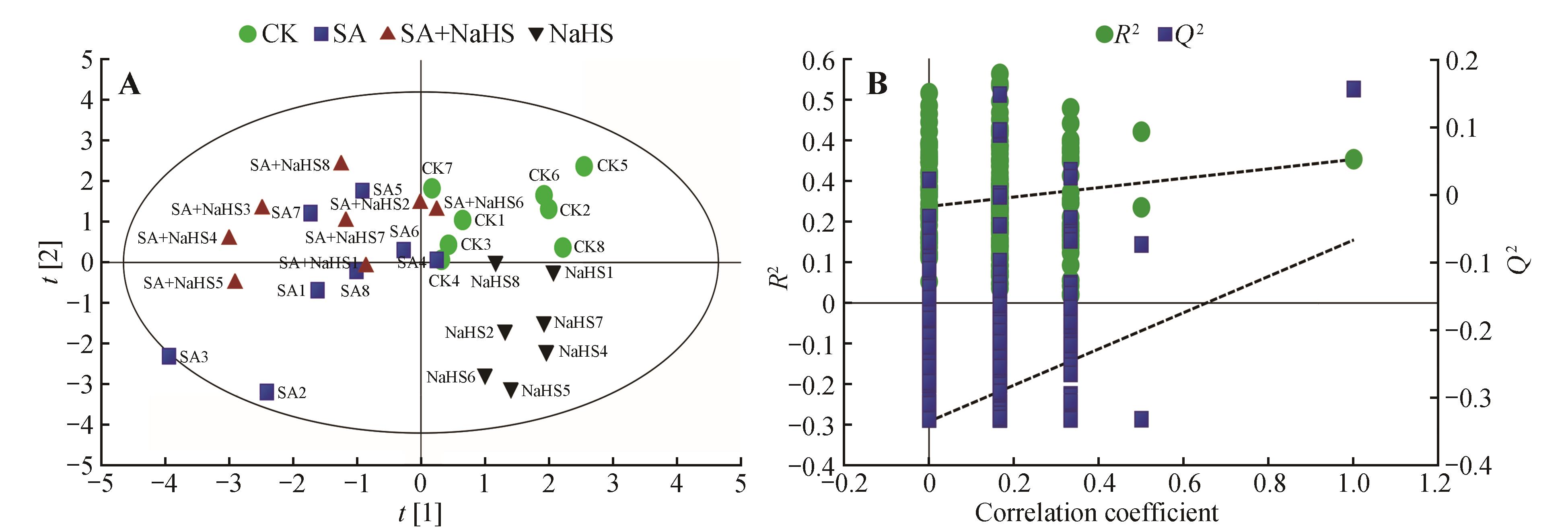
Fig.2
OPLS-DA score plot(A,C,E) and S-plot(B,D,F) of organic acids in naked oat leaves under different treatmentA-B.CK vs. SA;. C-D.SA vs. SA+NaHS; E-F.CK vs. NaHS;Succi.Succinic acid; Butene.Butenedioic acid; Malic.Malic acid; Citric.Citric acid; Malonic.Malonic acid; Glucu.Glucuronic acid; Panto.Pantothenic acid; Nicotinic.Nicotinic acid; Pyrog.Pyroglutamic acid; Suberic.Suberic acid; HMA. 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaric acid; Phenyl.Phenylpyruvic acid
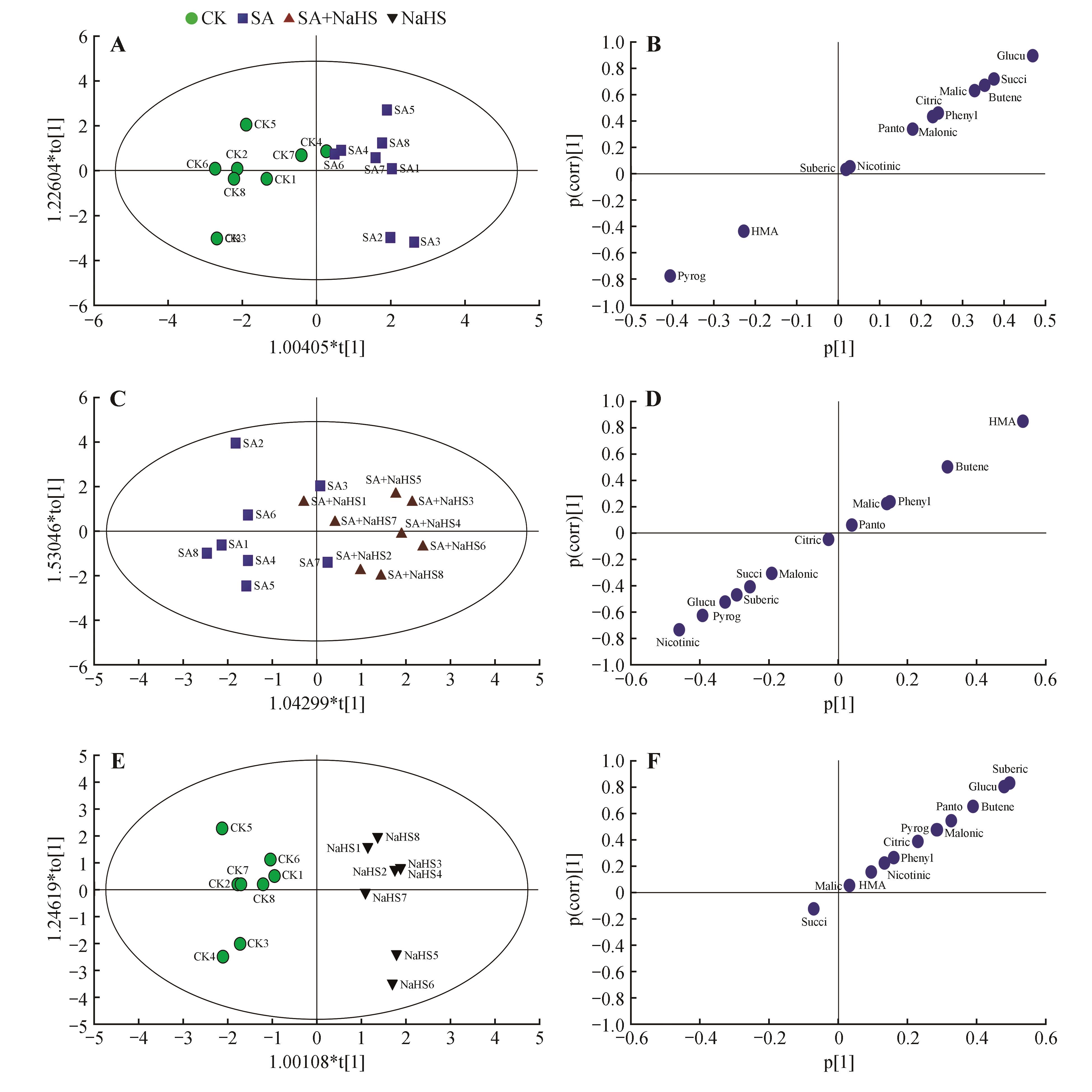
Table 2
Effects of exogenous hydrogen sulfide on the content of hormone in leaves of naked oat under saline-alkali stress
激素 Hormone | 激素质量分数 Content of hormone /(ng·g-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | SA | SA+NaHS | NaHS | |
| 吲哚乙酸 Indole-3-acetic acid(IAA) | 1.471±0.240b | 1.651±0.198b | 1.866±0.177a | 1.788±0.314a |
| 赤霉素 A1 Gibberellin A1(GA1) | 0.068±0.010b | 0.079±0.009 b | 0.093±0.018b | 0.125±0.051a |
| 赤霉素 A3 Gibberellin A3(GA3) | 0.339±0.083bc | 0.404±0.080ab | 0.267±0.126c | 0.484±0.142a |
| 赤霉素 A4 Gibberellin A4(GA4) | 0.021±0.007ab | 0.034±0.023a | 0.009±0.007b | 0.009±0.005b |
| 赤霉素 A7 Gibberellin A7(GA7) | 0.009±0.004c | 0.012±0.004bc | 0.018±0.005a | 0.014±0.003ab |
| 茉莉酸 Jasmonic acid(JA) | 2.413±0.738ab | 2.509±0.907ab | 1.675±0.590b | 3.004±1.475a |
| 茉莉酸-异亮氨酸 Jasmonoyl-isoleucine(JA-Ile) | 1.850±0.542a | 1.447±0.320b | 1.423±0.254b | 2.212±0.570a |
| 茉莉酸甲酯 Methyl Jasmonate(MJA) | 0.589±0.204b | 0.887±0.176b | 1.258±0.348a | 1.237±0.407a |
| 脱落酸 Abscisic acid(ABA) | 7.699±1.220b | 6.695±0.626b | 6.211±1.106b | 9.760±2.070a |
| 反式-玉米素 Trans-Zeatin(tZ) | 0.318±0.038ab | 0.209±0.047c | 0.257±0.062bc | 0.385±0.098a |
| 反式-玉米素核苷 Trans-Zeatin-riboside(tZR) | 0.009±0.003a | 0.008±0.001ab | 0.004±0.006b | 0.011±0.004a |
| N6-(Δ2-异戊烯)腺嘌呤 N6-(Δ2-Isopentenyl) adenine(iP) | 0.049±0.013a | 0.041±0.014b | 0.045±0.010a | 0.031±0.004b |
| N6-(Δ2-异戊烯基)腺苷 N6-(Δ2-Isopentenyl) adenosine(iPA) | 0.068±0.017a | 0.079±0.021a | 0.060±0.027a | 0.078±0.013a |
| 油菜素内酯 Brassinolide | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 1-氨基环丙烷羧酸 1-Aminocyclopropanecarboxylic acid(ACC) | 0.147±0.024b | 0.162±0.030ab | 0.109±0.030c | 0.183±0.038a |
Fig.4
OPLS-DA score plot(A,C,E) and S-plot(B,D,F) of hormones in naked oat leaves under different treatmentA-B. CK vs. SA; C-D. SA vs. SA+NaHS; E-F. CK vs. NaHS;IAA.Indole-3-acetic acid; GA1.Gibberellin A1; GA3.Gibberellin A3; GA4.Gibberellin A4; GA7.Gibberellin A7; JA.Jasmonic acid; JA-Ile.Jasmonoyl-isoleucine; MJA.Methyl Jasmonate; ABA.Abscisic acid; tZ.Trans-zeatin; tZR.Trans-zeatin-riboside; iP. N6-(Δ2-Isopentenyl) adenine; iPA. N6-(Δ2-Isopentenyl) adenosine; ACC. 1-Aminocyclopropanecarboxylic acid
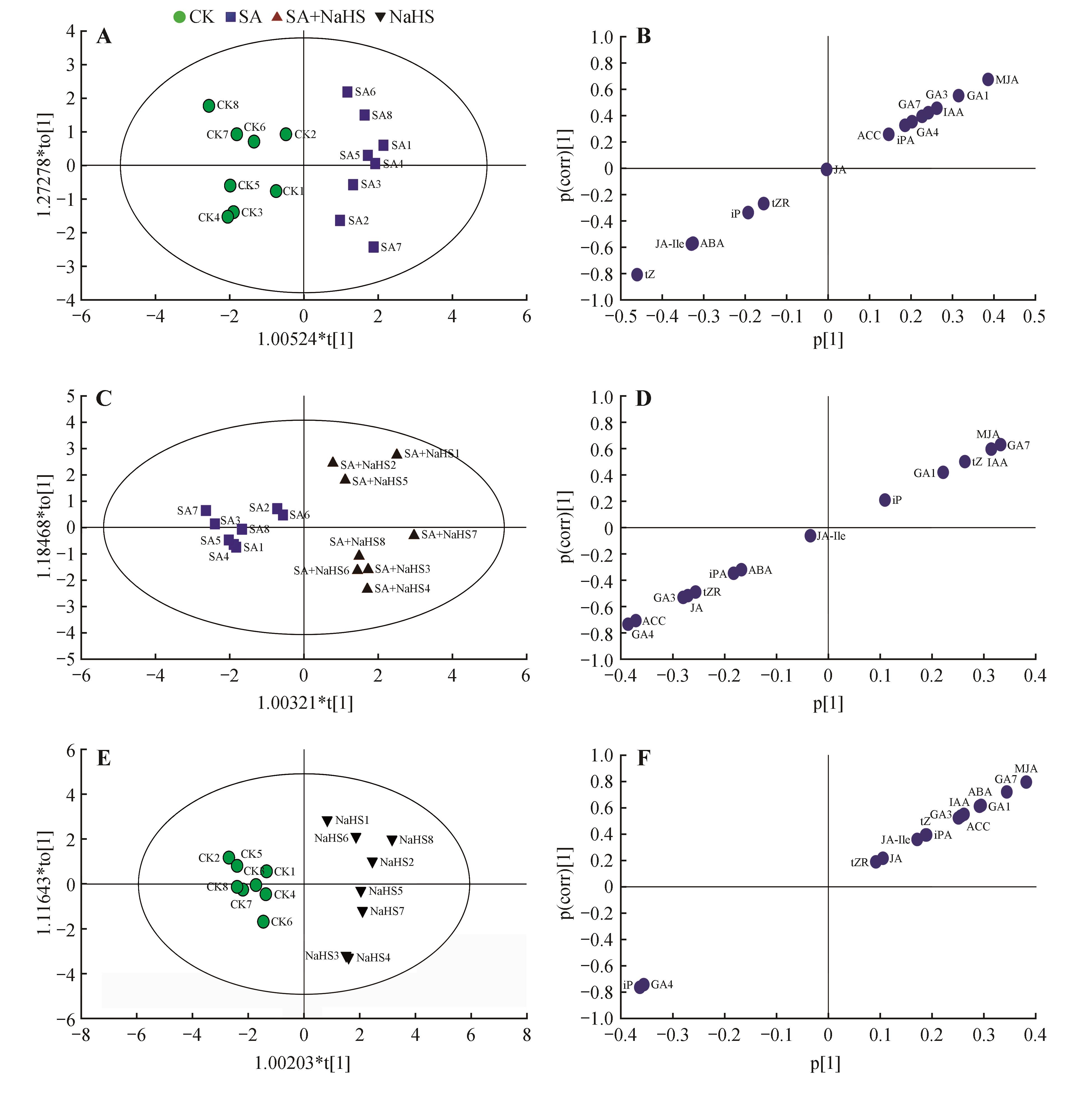
Table 3
Effects of exogenous hydrogen sulfide on the total amount of different hormones and the ratio of total hormone amount in leaves of naked oat under saline-alkali stress
激素 Hormone | CK | SA | SA+NaHS | NaHS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 吲哚乙酸 Indole-3-acetic acid(IAA) /(ng·g-1) | 1.471±0.240b | 1.651±0.198b | 1.866±0.177a | 1.788±0.314a |
| 赤霉素类 Gibberellins(GAs) /(ng·g-1) | 0.438±0.088bc | 0.529±0.072ab | 0.387±0.123c | 0.632±0.115a |
| 茉莉酸类 Jasmonic acids (JAs) /(ng·g-1) | 4.853±0.950b | 4.843±0.866b | 4.356±0.894b | 6.453±1.930a |
| 脱落酸 Abscisic acid (ABA) /(ng·g-1) | 7.699±1.220b | 6.695±0.626b | 6.211±1.106b | 9.760±2.070a |
| 细胞分裂素 Cytokinin(CTK) /(ng·g-1) | 0.444±0.040ab | 0.337±0.052c | 0.374±0.071bc | 0.505±0.106 a |
| 1-氨基环丙烷羧酸 1-Aminocyclopropanecarboxylic acid(ACC) /(ng·g-1) | 0.147±0.024b | 0.162±0.030ab | 0.109±0.030c | 0.183±0.038a |
| IAA/ABA | 0.196±0.047b | 0.249±0.038b | 0.309±0.065a | 0.193±0.060b |
| GAs/ABA | 0.058±0.015a | 0.080±0.017a | 0.064±0.024a | 0.070±0.028a |
| JAs/ABA | 0.635±0.118a | 0.729±0.148a | 0.714±0.150a | 0.717±0.351a |
| CTK/ABA | 0.060±0.014a | 0.051±0.013a | 0.062±0.013a | 0.056±0.023a |
| ACC/ABA | 0.020±0.006ab | 0.024±0.005a | 0.018±0.004b | 0.020±0.006ab |
Table 4
Effects of exogenous hydrogen sulfide on yield components of naked oat under saline-alkaline stress
处理 Treatment | 穗数量 /(穗) Spike number | 穗铃数量 /(铃) Spike boll number | 穗粒数量 /(粒) Spike grain number | 千粒质量 1 000 grains weigh /g | 籽粒产量 Grain yield /g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 158.4±12.2a | 2234.2±771.9a | 2834.0±861.7a | 15.62±0.76a | 44.70±9.99a |
| SA | 146.4±35.2a | 1910.0±502.3a | 1574.4±454.6b | 15.22±2.16a | 25.23±4.64b |
| SA+NaHS | 149.6±27.1a | 2095.2±524.6a | 2544.2±704.4a | 14.32±0.52a | 38.56±9.56a |
| NaHS | 161.0±42.4a | 2638.0±391.5a | 3620.0±1093.6a | 13.76±1.15a | 47.79±4.63a |
Table 5
Correlation coefficient and order between organic acid and hormone content and yield traits of naked oat
指标 Index | 关联度 Correlation coefficient | 关联序 Correlation order | 指标 Index | 关联度 Correlation coefficient | 关联序 Correlation order |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 琥珀酸 Succinic acid | 0.660 | 26 | 赤霉素A1 Gibberellin A1 | 0.727 | 10 |
| 丁烯二酸 Butenedioic acid | 0.685 | 22 | 赤霉素A3 Gibberellin A3 | 0.715 | 13 |
| 苹果酸 Malic acid | 0.710 | 15 | 赤霉素A4 Gibberellin A4 | 0.703 | 16 |
| 柠檬酸 Citric acid | 0.695 | 20 | 赤霉素A7 Gibberellin A7 | 0.679 | 23 |
| 丙二酸 Malonic acid | 0.736 | 7 | 茉莉酸 Jasmonic acid | 0.728 | 9 |
| 葡萄糖醛酸 Glucuronic acid | 0.670 | 25 | 茉莉酸-异亮氨酸 Jasmonoyl-isoleucine | 0.739 | 5 |
| 泛酸 Pantothenic acid | 0.723 | 12 | 茉莉酸甲酯 Methyl Jasmonate | 0.698 | 17 |
| 烟酸 Nicotinic acid | 0.741 | 4 | 脱落酸 Abscisic acid | 0.747 | 3 |
| 焦谷氨酸 Pyroglutamic acid | 0.776 | 1 | 反式-玉米素 Trans-Zeatin | 0.770 | 2 |
| 辛二酸 Suberic acid | 0.737 | 6 | 反式-玉米素核苷 Trans-Zeatin-riboside | 0.733 | 8 |
3-羟基-3-甲基谷氨酸 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaric acid | 0.723 | 11 | N6-(Δ2-异戊烯)腺嘌呤 N6-(Δ2-Isopentenyl) adenine | 0.672 | 24 |
| 苯丙酮酸 Phenylpyruvic acid | 0.714 | 14 | N6-(Δ2-异戊烯基)腺苷 N6-(Δ2-Isopentenyl) adenosine | 0.698 | 18 |
| 吲哚乙酸 Indole-3-acetic acid | 0.696 | 19 | 1-氨基环丙烷羧酸 1-Aminocyclopropanecarboxylic acid | 0.690 | 21 |
| 1 | 张毅,石玉,胡晓辉,等.外源Spd对盐碱胁迫下番茄幼苗氮代谢及主要矿质元素含量的影响[J].应用生态学报,2013,24(5):1401-1408. |
| ZHANG Y, SHI Y, HU X H,et al.Effects of exogenous spermidine on the nitrogen metabolism and main mineral elements contents of tomato seedlings under saline-alkali stress [J].Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2013,24(5):1401-1408. | |
| 2 | 付寅生,崔继哲,陈广东,等.盐碱胁迫下碱地肤Na+/H+逆向转运蛋白基因KsNHX1表达分析[J].应用生态学报,2012,23(6):1629-1634. |
| FU Y S, CUI J Z, CHEN G D,et al.Expression of Na+/H+ antiporter gene KsNHX1 in Kochia sieversiana under saline-alkali stress [J].Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2012,23(6):1629-1634. | |
| 3 | 闫永庆,王文杰,朱虹,等.混合盐碱胁迫对青山杨渗透调节物质及活性氧代谢的影响[J].应用生态学报,2009,20(9):2085-2091. |
| YAN Y Q, WANG W J, ZHU H,et al.Effects of salt-alkali stress on osmoregulation substance and active oxygen metabolism of Qingshan poplar(Populus pseudo-cathayana×P.deltoides)[J].Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2009,20(9):2085-2091. | |
| 4 | 刘建新,刘瑞瑞,贾海燕,等.外源H2S对盐碱胁迫下裸燕麦幼苗叶片渗透胁迫的调节作用[J].生态学杂志,2020,39(12):3989-3997. |
| LIU J X, LIU R R, JIA H Y,et al.Regulation of exogenous hydrogen sulfide on osmotic stress in leaves of naked oat seedlings under saline-alkali mixed stress[J].Chinese Journal of Ecology,2020,39(12):3989-3997. | |
| 5 | 杨国会.碱胁迫诱导小冰麦有机酸积累和分泌的研究[J].西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版),2010,38(7):77-84. |
| YANG G H.Study on organic acids accumulation and secretion of alkali stress induced in wheat-wheatgrass[J].Journal of Northwest A & F University(Natural Science Edition),2010,38(7):77-84. | |
| 6 | GUO L Q, SHI D C, WANG D L.The key physiological response to alkali stress by the alkali-resistant halophyte Puccinellia tenuiflorais the accumulation of large quantities of organic acids and into therhyzosphere[J].Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science,2010,196(2):123-135. |
| 7 | 胡妮,陈柯罕,李取生,等.盐胁迫下苋菜品种有机酸变化对Cd累积和耐盐性的影响[J].农业环境科学学报,2016,35(5):858-864. |
| HU N, CHEN K H, LI Q S,et al.Effects of salinity-inducted organic acid variation on Cd accumulation and salinity tolerance of edible amaranth[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science,2016,35(5):858-864. | |
| 8 | GONG B, WEN D,BLOSZIESS,et al.Comparative effects of NaCl and NaHCO3 stresses on respiratory metabolism,antioxidant system,nutritional status,and organic acid metabolism in tomato roots[J].Acta Physiologiae Plantarum,2014,36(8):2167-2181. |
| 9 | 郭立泉,陈建欣,崔景军,等.盐、碱胁迫下星星草有机酸代谢调节的比较研究[J].东北师大学报(自然科学版),2009,41(4):123-128. |
| GUO L Q, CHEN J X, CUI J J,et al.Comparative studies of metabolic regulation of organic acids in Puccinellia tenuiflora under salt and alkali stresses[J].Journal of Northeast Normal University(Natural Science Edition),2009,41(4):123-128. | |
| 10 | PATEL S,ADBHAIA, KARMAKAR N.Ionic balance of sugar beet(Beta vulgaris L.) under salinity stress with special reference to organic acids and antioxidant system[J].Indian Journal of Agricultural Biochemistry,2017,30(1):73-79. |
| 11 | 麻莹,郭立泉,张淑芳,等.盐碱胁迫下抗碱牧草碱地肤溶质积累、分布特点及有机酸的生理贡献[J].草业学报,2013,22(1):193-200. |
| MA Y, GUO L Q, ZHANG S F,et al.Solute accumulation and distribution traits of an alkali resistant forage plant Kochia sieversiana and physiological contribution of organic acid under salt and alkali stresses[J].Acta Prataculturae Sinica,2013,22(1):193-200. | |
| 12 | 郭志刚,李文芳,毛娟,等.钾肥施用对元帅苹果果实内源激素含量及酸代谢的影响[J].农业工程学报,2019,35(10):281-290. |
| GUO Z G, LI W F, MAO J,et al.Effects of potassium fertilizer on endogenous hormone content and acid metabolism in fruit of apple cv.‘Red Delicious’[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2019,35(10):281-290. | |
| 13 | 张敏,蔡瑞国,李慧芝,等.盐胁迫环境下不同抗盐性小麦品种幼苗长势和内源激素的变化[J].生态学报,2008,28(1):310-320. |
| ZHANG M, CAI R G, LI H Z,et al.Responses of seedling growth and endogenous hormone contents in different wheat cultivars to salt stress[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2008,28(1):310-320. | |
| 14 | TUNA A L, KAYA C, DIKILITAS M,et al.The combined effects of gibberellic acid and salinity on some antioxidant enzyme activities,plant growth parameters and nutritional status in maize plants[J].Environmental and Experimental Botany,2008,62(1):1-9. |
| 15 | 王鑫,刘丹,陈婧婷,等.外源BR对盐碱胁迫下甜菜内源激素含量及保护酶活性的影响[J].西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版),2021,49(7):20-30,41. |
| WANG X, LIU D, CHEN J T,et al.Effects of exogenous BR on endogenous hormone and protective enzyme activities in sugar beet under saline-alkali stress[J].Journal of Northwest A & F University(Natural Science Edition),2021,49(7):20-30,41. | |
| 16 | ZHANG J H, JIA W S, YANG J C,et al.Role of ABA in integrating plant responses to drought and salt stresses[J].Field Crops Research,2006,97(1):111-119. |
| 17 | CACHORRO P, MARTÍNEZ R, ORTIZ A,et al.Abscisic acid and osmotic relations in Phaseolus vulgaris L.shoots under salt stress[J].Journal of Plant Growth Regulation,1995,14(2):99-104. |
| 18 | FORMENTIN E, BARIZZA E, STEVANATO P,et al.Fast regulation of hormone metabolism contributes to salt tolerance in rice(Oryza sativa spp. japonica,L.) by inducing specific morpho-physiological responses[J].Plants-Basel,2018,7(3):75.. |
| 19 | JIN Z P, PEI Y X.Physiological implications of hydrogen sulfide in plants:pleasant exploration behind its unpleasant odour[J].Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity,2015,2015:397502. |
| 20 | MOSTOFA M G, SAEGUSA D, FUJITA M,et al.Hydrogen sulfide regulates salt tolerance in rice by maintaining Na+/K+ balance,mineral homeostasis and oxidative metabolism under excessive salt stress[J].Frontiers in Plant Science,2015,6:1055. |
| 21 | CHEN J, WANG W H, WU F H,et al.Hydrogen sulfide enhances salt tolerance through nitric oxide-mediated maintenance of ion homeostasis in barley seedling roots[J].Scientific Reports,2015,5:12516. |
| 22 | 黄菡,郭莎莎,陈良超,等.外源硫化氢对盐胁迫下茶树抗氧化特性的影响[J].植物生理学报,2017,53(3):497-504. |
| HUANG H, GUO S S, CHEN L C,et al.Effects of exogenous hydrogen sulfide on the antioxidant characteristics of tea plant(Camellia sinensis) under salt stress[J].Plant Physiology Journal,2017,53(3):497-504. | |
| 23 | SHAN C, LIU H, ZHAO L,et al.Effects of exogenous hydrogen sulfide on the redox states of ascorbate and glutathione in maize leaves under salt stress[J].Biologia Plantarum,2014,58(1):169-173. |
| 24 | 刘建新,刘瑞瑞,刘秀丽,等.不同时期喷施NaHS对盐碱胁迫下裸燕麦叶片渗透调节物质和抗氧化活性的影响[J].生态学杂志,2021,40(11):3620-3632. |
| LIU J X, LIU R R, LIU X L,et al.Effects of spraying NaHS at different growth stages on osmotic adjustment substance and antioxidant activity in leaves of naked oat under saline-alkali stress[J].Chinese Journal of Ecology,2021,40(11):3620-3632. | |
| 25 | MICEK P, KULIG B, WOŹNICA P,et al.The nutritive value for ruminants of faba bean(Vicia faba) seeds and naked oat(Avena nuda) grain cultivated in an organic farming system[J].Journal of Animal and Feed Sciences,2012,21(4):773-786. |
| 26 | 张达斌,黄文凤,惠蕾,等.PEG胁迫下旱地油菜绿肥苗期抗旱性筛选和评价[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2022,28(1):168-180. |
| ZHANG D B, HUANG W F, HUI L,et al.Evaluation of drought resistance of Brassica green manure crops using seedling growth indices[J].Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers,2022,28(1):168-180. | |
| 27 | 贲蓓倍,徐维红,邹德玉,等.不同施肥条件下的小麦籽粒代谢组学研究[J].麦类作物学报,2021,41(2):212-219. |
| BEN B B, XU W H, ZOU D Y,et al.Study on metabonomics of wheat grain under different fertilization conditions[J].Journal of Triticeae Crops,2021,41(2):212-219. | |
| 28 | 高双红,李媛英,刘博文,等.H2S对弱光胁迫下高羊茅幼苗生理特性和内源激素的影响[J].草地学报,2021,29(10):2233–2239. |
| GAO S H, LI Y Y, LIU B W,et al.Effects of H2S on physiological characteristics and endogenous hormones in tall fescue seedlings under low-light stress[J].Acta Agrestia Sinica,2021,29(10):2233-2239. | |
| 29 | CHEN P, YANG W X, MIN X W,et al.Hydrogen sulfide alleviates salinity stress in Cyclocarya paliurus by maintaining chlorophyll fluorescence and regulating nitric oxide level and antioxidant capacity[J].Plant Physiology and Biochemistry,2021,167:738-747. |
| 30 | DING H N, MA D Y, HUANG X,et al.Exogenous hydrogen sulfide alleviates salt stress by improving antioxidant defenses and the salt overly sensitive pathway in wheat seedlings[J].Acta Physiologiae Plantarum,2019,41(7):1-11. |
| 31 | DENG Y Q, BAO J, YUAN F,et al.Exogenous hydrogen sulfide alleviates salt stress in wheat seedlings by decreasing Na+ content[J].Plant Growth Regulation,2016,79(3):391-399. |
| 32 | LI J S, JIA H L, WANG J,et al.Hydrogen sulfide is involved in maintaining ion homeostasis via regulating plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter system in the hydrogen peroxide-dependent manner in salt-stress Arabidopsis thaliana root[J].Protoplasma,2014,251(4):899-912. |
| 33 | MÜLLER R, SISLER E C, SEREK M.Stress induced ethylene production,ethylene binding,and the response to the ethylene action inhibitor 1-MCP in miniature roses[J].Scientia Horticulturae,2000,83(1):51-59. |
| 34 | ALI M S, BAEK K H.Jasmonic acid signaling pathway in response to abiotic stresses in plants[J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2020,21(2):621-639. |
| 35 | ZHOU H, CHEN Y, ZHAI F C,et al.Hydrogen sulfide promotes rice drought tolerance via reestablishing redox homeostasis and activation of ABA biosynthesis and signaling[J].Plant Physiology and Biochemistry,2020,155:213-220. |
| 36 | 姚曼红,刘琳,曾幼玲.五大类传统植物激素对植物响应盐胁迫的调控[J].生物技术通报,2011(11):1-5,25. |
| YAO M H, LIU L, ZENG Y L.Several kinds of phytohormone in plants responses to salt-stress[J].Biotechnology Bulletin,2011(11):1-5,25. | |
| 37 | CHANG C S, WANG B L, SHI L,et al.Alleviation of salt stress-induced inhibition of seed germination in cucumber(Cucumis sativus L.) by ethylene and glutamate[J].Journal of Plant Physiology,2010,167(14):1152-1156. |
| 38 | 刘海英,崔长海,赵倩,等.施用有机肥环境下盐胁迫小麦幼苗长势和内源激素的变化[J].生态学报,2011,31(15):4215-4224. |
| LIU H Y, CUI C H, ZHAO Q,et al.Effects of organic fertilizer on growth and endogenous hormone contents of wheat seedlings under salt stress[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2011,31(15):4215-4224. | |
| 39 | 张丽,贾志国,马庆华,等.盐碱胁迫对平欧杂种榛生长及叶片内源激素含量的影响[J].林业科学研究,2015,28(3):394-401. |
| ZHANG L, JIA Z G, MA Q H,et al.Effects of saline-alkali stresses on the growth and endogenous hormone contents in leaves of hybrid hazelnut Liaozhen 3[J].Forest Research,2015,28(3):394-401. | |
| 40 | ACHARD P, CHENG H, DE GRAUWE L,et al.Integration of plant responses to environmentally activated phytohormonal signals[J].Science,2006,311(5757):91-94. |
| 41 | ŠVEIKAUSKAS V, BAREIKIENÉ N, JANČYS Z.Energy-dependent auxin transport through the plasmalemma:the role of H+-ATPase[J].Biologija,2003,3:60-62. |
| [1] | Shuyao ZHUANG, Hengbo XU, Xiaoyu HU, Shang DAI, Yanni ZHANG. Effects of Saline-alkali Stress on Growth and Physiological Characteristics of Color Leaf Heuchera micrantha ‘Silver Fan’ Seedlings [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(4): 520-530. |
| [2] | Yuping QIU, Yichuan WANG, Hongwei GUO. Research Progress on the Regulatory Mechanism of Plant Root Hair Development [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(3): 321-332. |
| [3] | Chunjing JIAO, Mingyue LI, Peng ZHANG. Effects of Exogenous Hormones Soaking and Osmotic Treatment on Thermal Dormancy of Seeds of Fraxinus mandshurica [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(3): 370-378. |
| [4] | Haiyun SONG, Tao ZHANG, Peng HE, Shufang ZHENG, Lifeng WANG, Wenlin WANG. Cloning and Expression Analysis of MibZIP1 from Macadamia integrifolia [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(1): 131-139. |
| [5] | Bi QIN, Xiaoxiao WANG, Yushuang YANG, Qiuhai NIE, Qiuhui CHEN, Shizhong LIU. Identification and Expression Pattern Analysis of TkAPC10 in Taraxacum kok-saghyz Rodin [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(5): 830-839. |
| [6] | Kun CHEN, Gonggui FANG, Huaizhi MU, Jing JIANG. Analysis of the Promoter Sequence and Response Characteristics of the BpPIN3 gene in Betula platyphylla [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(4): 592-601. |
| [7] | Liben PAN, Xue YAN, Jia LIU, Kexin WU, Yang LIU, Shaochong LIU. Physiological Characteristics of Early Spring Flowering Plants under Northeast Forest [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(4): 657-666. |
| [8] | Dongmei HUANG, Ying CHEN, Lu BAI, Di’an NI, Yiyang XU, Zhiguo ZHANG, Qiaoping QIN. Transcriptome Analysis of Hemerocallis fulva Leaves Respond to Low Temperature Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(3): 424-436. |
| [9] | Jianxin LIU, Ruirui LIU, Xiuli LIU, Haiyan JIA, Ting BU, Na LI. Effects of Spraying NaHS at Different Growth Stages on H2S Production and Reactive Oxygen Species Metabolism of Naked Oat Leaves under Saline-Alkali Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(3): 455-465. |
| [10] | Guobin Liu, Ting Liao, Ye Wang, Liqin Guo, Jinzhe Zhao, Yanwu Yao, Jun Cao. Regulation Mechanism of Endogenous Hormones in Adventitious Roots Formation of Platycladus orientalis ‘Beverleyensis’ [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(2): 278-288. |
| [11] | Yuqi Zhang, Xin Su, Zhiqiang You, Jinbo Fu, Yaguang Zhan, Jing Yin. [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(2): 289-298. |
| [12] | Jian-Xin LIU, Rui-Rui LIU, Xiu-Li LIU, Hai-Yan JIA, Ting BU, Na LI. Effect of Soaking Seeds with NaHS on Seed Germination Characteristics of Naked Oat under Saline-Alkali Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(6): 870-877. |
| [13] | Bo-Chao ZHANG, Jia-Lin WANG, Yuan YIN, Yi-Da CHE, Jun-Jie DENG, Rong-Shu ZHANG. Tissue Expression Patterns of PdPapWRKY51 in Shanxin Poplar (Populus davidiana × P. alba var. pyramidlis) under Stress Conditions [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(6): 911-920. |
| [14] | Si-Han WANG, Tao YANG, Jin-Zhu ZHANG, Jie DONG, Zhi-Ling KOU, Dai-Di CHE. Effects of Changes in Seed Cell Tissue Structure and Endogenous Hormones on Dormancy of Wild Rosa rugosa Fruit during Development [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(3): 387-394. |
| [15] | Wei LONG, Xiao-Hua YAO, Le-Yan LÜ. Dynamic Changes of Endogenous Hormones in Rootstocks and Scions within Nurse Seedling Graft in Camellia oleifera Under Wound [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(2): 232-242. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||