Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (3): 349-360.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2024.03.004
• Genetic and Breeding • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xiaoqian WU, Xu HE, Jinghui GAO, Shuang LI( )
)
Received:2024-01-19
Online:2024-05-20
Published:2024-05-14
Contact:
Shuang LI
E-mail:shuangli@nefu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Xiaoqian WU, Xu HE, Jinghui GAO, Shuang LI. Germplasm Innovation and Characteristic Analysis of Transgenic PsnNAC007Populus simonii×P. nigra with High Drought Tolerance[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(3): 349-360.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://bbr.nefu.edu.cn/EN/10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2024.03.004
Table 1
Primer sequences
引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′→3′) Sequences(5′→3′) | 用途 Application |
|---|---|---|
| PsnNAC007-F | CACCATGAAAGGAAATAGATCAGCAG | PsnNAC007基因克隆 PsnNAC007 gene cloning |
| PsnNAC007-R | GCACACATCAAGAACCCTATT | |
| PsnNAC007-XbaⅠ-F | CTAGTCTAGAATGAAAGGAAATAGATCAGCAG | pBI121-35S-PsnNAC007载体构建 pBI121-35S-PsnNAC007 vector construction |
| PsnNAC007-SacⅠ-R | CTAGGAGCTCGCACACATCAAGAACCCTATT | |
| 35S-F | CCCACTATCCTTCGCAAGACC | 转基因鉴定 Transgenic identification |
| PsnNAC007-middle-R | CGACCAATGGGTTTATCTGCTC | |
| RT-PsnActin-F | GGATATTCAGCCCCTTGTCTG- | 相对表达量检测引物 Relative expression level detection primers |
| RT-PsnActin-R | TCGTCACCAACATAAGCATCC | |
| RT-PsnNAC007-F | ATGAAAGGAAATAGATCAGCAGAT | |
| RT-PsnNAC007-R | ATTGGCCTCCACATTTCTTAAGC |
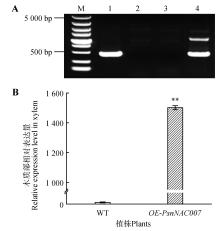
Fig.2
Identification of OE-PsnNAC007 transgenic plantsA.PCR identification of transgenic plants(M. 5 000 bp Marker;1.Positive control with pBI121-35S-PsnNAC007 plasmid;2,3.Negative control with wild-type leaf DNA as PCR template;4.DNA of kanamycin-resistance plant leaf as PCR template);B.Relative expression level identification of transgenic plants(WT.Stands for P. simonii×P. nigra wild-type;OE-PsnNAC007.PsnNAC007 overexpression plants); error bars indicated one SE of three biological replicates;asterisks indicated *P<0.05,**P<0.01(Student’s t-test);the same as below.
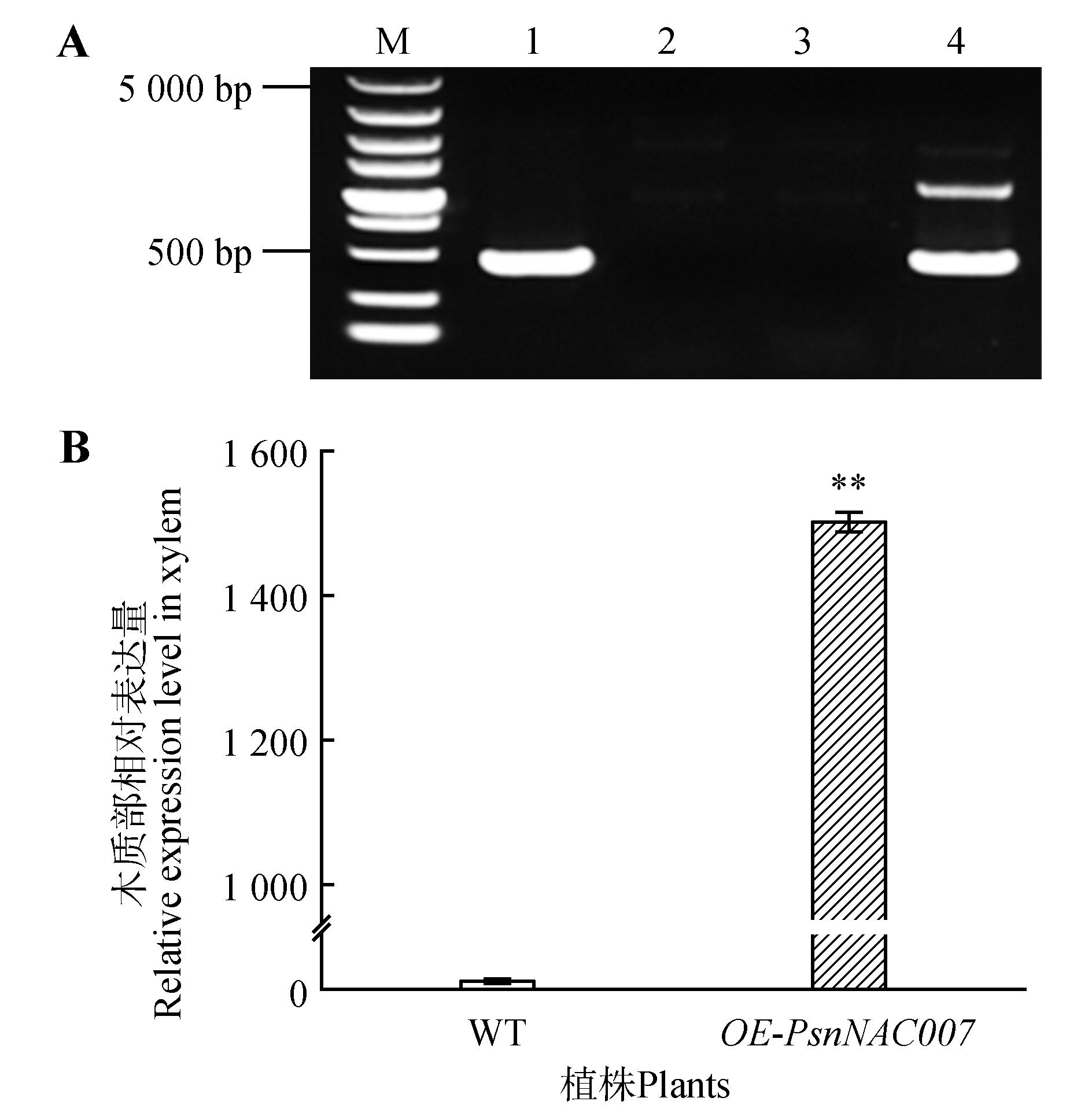
Table 2
Wood component analysis of wild type and PsnNAC007 overexpressed plants
参数 Parameter | 野生型 Wild-type/% | PsnNAC007过表达植株 OE-PsnNAC007/% |
|---|---|---|
不可溶性木质素 Acid-insoluble lignin | 20.32±0.23 | 22.43±0.28** |
可溶性木质素 Acid-soluble lignin | 2.96±0.07 | 2.64±0.03** |
| 总木质素Total lignin | 23.29±0.29 | 25.07±0.30** |
| 葡萄糖Glucose | 53.37±0.17 | 53.63±0.19 |
| 木糖Xylose | 11.39±0.26 | 11.59±0.40 |
| 半乳糖Galactose | 1.34±0.05 | 1.28±0.03 |
| 阿拉伯糖Arabinose | 2.30±0.13 | 2.29±0.05 |
总碳水化合物 Total carbohydrate | 68.41±0.38 | 68.79±0.48 |
| 1 | 山仑,邓西平,康绍忠.我国半干旱地区农业用水现状及发展方向[J].水利学报,2022(9):27-31. |
| SHAN L, DENG X P, KANG S Z.Current situation and perspective of agricultural water used in semiarid area of China[J].Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2022(9):27-31. | |
| 2 | 许恩银,聂影,芮晓东.基于森林资源清查数据的林地利用效率变化研究[J].南京林业大学学报(自然科学版),2022,46(5):213-220. |
| XU E Y, NIE Y, RUI X D.Analysis on the forest land use efficiency changes based on forest resource inventory data[J].Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition),2022,46(5):213-220. | |
| 3 | BANDURSKA H.Drought stress responses:coping strategy and resistance[J].Plants,2022,11(7):922. |
| 4 | BRÉDA N,HUC R, GRANIER A,et al.Temperate forest trees and stands under severe drought:a review of ecophysiological responses,adaptation processes and long-term consequences[J].Annals of Forest Science,2006,63(6):625-644. |
| 5 | FICHOT R, LAURANS F, MONCLUS R,et al.Xylem anatomy correlates with gas exchange,water-use efficiency and growth performance under contrasting water regimes:evidence from Populus deltoides × Populus nigra hybrids[J].Tree Physiology,2009,29(12):1537-1549. |
| 6 | LIMOUSIN J M, LONGEPIERRE D,HUC R,et al.Change in hydraulic traits of mediterranean Quercus ilex subjected to long-term throughfall exclusion[J].Tree Physiology,2010,30(8):1026-1036. |
| 7 | VENTURAS M D, SPERRY J S, HACKE U G.Plant xylem hydraulics:What we understand,current research,and future challenges[J].Journal of Integrative Plant Biology,2017,59(6):356-389. |
| 8 | TONG S F, WANG Y B, CHEN N N,et al.Ptonf-yc9-srmt-ptord26 module regulates the high saline tolerance of a triploid poplar[J].Genome Biology,2022,23(1):148. |
| 9 | LI S, LIN Y C J, WANG P Y. et al.The AREB1 transcription factor influences histone acetylation to regulate drought responses and tolerance in Populus trichocarpa [J].The Plant Cell,2019,31(3):663-686. |
| 10 | 杜兆伟,郑唐春,李爽,等.小黑杨快繁与再生体系的优化[J].植物研究,2015,35(6):904-907. |
| DU Z W, ZHENG T C, LI S,et al.Rapid propagation and regeneration system of Populus simonii×Populus nigra [J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2015,35(6):904-907. | |
| 11 | 李晶,王福森,李树森,等.几个杨树新品系抗寒性测定试验[J].防护林科技,2012(1):59-61. |
| LI J, WANG F S, LI S S,et al.Cold-resistance determination for several new strains of poplar[J].Protection Forest Science and Technology,2012(1):59-61. | |
| 12 | 何旭,高源,张群野,等.白城小黑杨遗传转化体系建立及其应用[J].植物研究,2023,43(5):667-678. |
| HE X, GAO Y, ZHANG Q Y,et al.Establishment and application of genetic transformation system for Populus simonii×P.nigra ‘Baicheng’[J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2023,43(5):667-678. | |
| 13 | ILYAS M, NISAR M, KHAN N,et al.Drought tolerance strategies in plants:a mechanistic approach[J].Journal of Plant Growth Regulation,2020,40(3):926-944. |
| 14 | PASCUAL M B, DE LA TORRE F, CAÑAS R A,et al.NAC transcription factors in woody plants[J].Progress in Botany,2018,80:195-222. |
| 15 | HAN K J, ZHAO Y, SUN Y H,et al.NACs,generalist in plant life[J].Plant Biotechnology Journal,2023,21(12):2433-2457. |
| 16 | NURUZZAMAN M, MANIMEKALAI R, SHARONI A M,et al.Genome-wide analysis of NAC transcription factor family in rice[J].Gene,2010,465(1/2):30-44. |
| 17 | JEONG J S, KIM Y S, BAEK K H,et al.Root-specific expression of OsNAC10 improves drought tolerance and grain yield in rice under field drought conditions[J].Plant Physiology,2010,153(1):185-197. |
| 18 | CHEN D D, CHAI S C, MCINTYRE C L,et al.Overexpression of a predominantly root-expressed NAC transcription factor in wheat roots enhances root length,biomass and drought tolerance[J].Plant Cell Reports,2018,37(2):225-237. |
| 19 | YANG C F, HUANG Y Z, LV W H,et al. GmNAC8 acts as a positive regulator in soybean drought stress[J].Plant Science,2020,293:110442. |
| 20 | WANG H L, YANG Q, TAN S Y,et al.Regulation of cytokinin biosynthesis using PtRD26pro-IPT module improves drought tolerance through PtARR10-PtYUC4/5-mediated reactive oxygen species removal in Populus [J].Journal of Integrative Plant Biology,2022,64(3):771-786. |
| 21 | CHEN Z H, PENG Z X, LIU S Q,et al.Overexpression of PeNAC122 gene promotes wood formation and tolerance to osmotic stress in poplars[J].Physiologia Plantarum,2022,174(4):e13751. |
| 22 | 李开隆,杨传平,刘桂丰.黑龙江省杨树遗传育种研究进展[J].东北林业大学学报,2003,31(4):45-48. |
| LI K L, YANG C P, LIU G F.Research Progresses of genetics and breeding of Populus in Heilongjiang province[J].Journal of Northeast Forestry University,2003,31(4):45-48. | |
| 23 | 吴丽丽,高福玲,王雷,等.杨树幼茎特异表达基因及PsnLAC基因的克隆[J].东北林业大学学报,2011,39(4):5-7. |
| WU L L, GAO F L, WANG L,et al.Specific gene expression in stem of Populus simonii×P.nigra and cloning of PsnLAC gene[J].Journal of Northeast Forestry University,2011,39(4):5-7. | |
| 24 | 王遂,刘梦然,黄海娇,等.转TaLEA基因小黑杨抗寒株系的筛选[J].东北林业大学学报,2011,39(9):5-7. |
| WANG S, LIU M R, HUANG H J,et al.Selection of cold resistant strains from TaLEA gene transferred Populus simonii×P.nigra [J].Journal of Northeast Forestry University,2011,39(9):5-7. | |
| 25 | WANG S J, FAN Y, DU S H. et al.PtaERF194 inhibits plant growth and enhances drought tolerance in poplar[J].Tree Physiology,2022,42(8):1678-1692. |
| 26 | RODRIGUEZ-ZACCARO F D, GROOVER A.Wood and water:How trees modify wood development to cope with drought[J].Plants,People,Planet,2019,1(4):346-355. |
| 27 | ECKERT C, SHARMIN S, KOGEL A,et al.What makes the wood?Exploring the molecular mechanisms of xylem acclimation in hardwoods to an ever-changing environment[J].Forests,2019,10(4):358. |
| 28 | BARIGAH T S, CHARRIER O, DOURIS M,et al.Water stress-induced xylem hydraulic failure is a causal factor of tree mortality in beech and poplar[J].Annals of Botany,2013,112(7):1431-1437. |
| 29 | LAUDER J D.From the cell to the stand:trait-based approaches to understanding forest response to climate cha-nge[M].Merced:University of California,2020:101-113. |
| 30 | BANG S W, LEE D K, JUNG H,et al.Overexpression of OsTF1L,a rice HD-Zip transcription factor,promotes lignin biosynthesis and stomatal closure that improves drought tolerance[J].Plant Biotechnology Journal,2019,17(1):118-131. |
| 31 | MÉNARD D, BLASCHEK L, KRIECHBAUM K,et al.Plant biomechanics and resilience to environmental changes are controlled by specific lignin chemistries in each vascular cell type and morphotype[J].The Plant Cell,2022,34(12):4877-4896. |
| 32 | SAINI R, KAUR A, SAINI J K,et al.Trends in lignin biotransformations for bio-based products and energy applications[J].BioEnergy Research,2023,16(1):88-104. |
| 33 | ZAHRA N, HAFEEZ M B, KAUSAR A,et al.Plant photosynthetic responses under drought stress:effects and management[J].Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science,2023,209(5):651-672. |
| [1] | Dongyue WANG, Ruyue WANG, Maotong SUN, Cuishuang LIU, Jihong LI. Establishment of Genetic Transformation System for ‘Populus leucopyramidalis 1’ and Transformation of Insect Resistance Gene [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(3): 361-369. |
| [2] | Xu HE, Yuan GAO, Qunye ZHANG, Chenguang ZHOU, Wei LI, Shuang LI. Establishment and Application of Genetic Transformation System for Populus simonii×P. nigra ‘Baicheng’ [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(5): 667-678. |
| [3] | Yu SUN, Yiteng ZHANG, Huihui CHENG. The Function of Salt and Alkaline Tolerance of WRKY42 Gene in Amorpha fruticosa [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(4): 612-621. |
| [4] | Zhanmin ZHENG, Yubing SHANG, Guangbo ZHOU, Di XIAO, Yi LIU, Xiangling YOU. Genetic Transformation and Function Analysis of PsnHB13 and PsnHB15 of Populus simonii × Populus nigra [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(3): 340-350. |
| [5] | Shixian LIAO, Yuting WANG, Liben DONG, Yongmei GU, Fenglin JIA, Tingbo JIANG, Boru ZHOU. Function Analysis of the Transcription Factor PsnbZIP1 of Populus simonii×P. nigra in Response to Salt Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(2): 288-299. |
| [6] | Senyao LIU, Fenglin JIA, Qing GUO, Gaofeng FAN, Boru ZHOU, Tingbo JIANG. Response Analysis of Transcription Factor PsnbHLH162 Gene in Populus simonii × P. nigra under Salt Stress and Low Temperature Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(2): 300-310. |
| [7] | Jinxia DU, Tingting SHEN, Haoran WANG, Yiping LIN, Huiyu LI, Lianfei ZHANG. Construction of Suppression Expression Vector and Genetic Transformation of BpSPL9 gene from Betula platyphylla [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(1): 30-35. |
| [8] | Ting QIAN, Fan ZHAO, Yujie ZHANG, Xueli LI, Kun SUN, Hui ZHANG. Study on Adaptive Differentiation of Transcription Factor bHLH94 Gene to Altitude in Hippophae neurocarpa and H.tibetana [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(6): 976-985. |
| [9] | Denggao LI, Rui LIN, Qinghui MU, Na ZHOU, Yanru ZHANG, Wei BAI. Cloning and Functional Analysis of StNPR4 gene in Solanum tuberosum [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(5): 821-829. |
| [10] | Sisi CHEN, Muhong XIE, Maokai CUI, Wenkai LI, Zhenggang XU, Caixia JIA, Guiyan YANG. Identification of Broussonetia papyrifera Transcription Factor BpbZIP1 and Analysis of Its Response to Cadmium Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(3): 394-402. |
| [11] | Bin WEI, Yi LI, Shiping SU. The Effect of Exogenous Proline on the Stomata of Nitraria tangutorum Leaves under Natural Drought [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(3): 492-501. |
| [12] | Qi Li, Siyu Yan, Su Chen. Genetic Transformation of BpERF98 Gene and Abiotic Stress Response of Transgenic Plant in Betula platyphylla [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(1): 93-103. |
| [13] | Lian-Bin HAN, Qing GUO, Kai ZHAO, Ting-Bo JIANG, Bo-Ru ZHOU, Li LI. Cloning and Expression Analysis of HD-Zip Transcription Factor PsnHB63 in Populus simonii × P. nigra [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(6): 1006-1014. |
| [14] | Feng HE, Hong-Yan DU, Pan-Feng LIU, Lu WANG, Jun QING, Lan-Ying DU. Effects of Drought Stress on Leaf Structure of Eucommia ulmoides [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(6): 947-956. |
| [15] | Shuang-Hui TIAN, He CHENG, Yang ZHANG, Cong LIU, De-An XIA, Zhi-Gang WEI. Genome-wide Identification and Expressional Analysis of Carotenoid Cleavage Dioxygenases(CCD) Gene Family in Populus trichocarpa under Drought and Salt Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(6): 993-1005. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||