Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (5): 821-829.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2022.05.013
• Molecular biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Denggao LI, Rui LIN, Qinghui MU, Na ZHOU, Yanru ZHANG, Wei BAI( )
)
Received:2022-03-15
Online:2022-09-20
Published:2022-09-15
Contact:
Wei BAI
E-mail:baiwei@imau.edu.cn
About author:LI Denggao(1990—),male,doctor,mainly engaged in research of molecular biology of plant stress resistance.
Supported by:CLC Number:
Denggao LI, Rui LIN, Qinghui MU, Na ZHOU, Yanru ZHANG, Wei BAI. Cloning and Functional Analysis of StNPR4 gene in Solanum tuberosum[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(5): 821-829.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://bbr.nefu.edu.cn/EN/10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2022.05.013
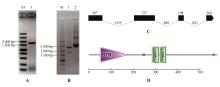
Fig.2
PCR amplification,enzyme digestion and structure prediction of StNPR4A.PCR amplification of StNPR4 CDS(M.DNA Marker;1.StNPR4 CDSfragments);B.Enzyme digestion of StNPR4 cloning vector(M.DNA Marker; 1.Double digestion of StNPR4-pMD19-T vector;2.StNPR4-pMD19-T vector);C.StNPR4 gene structure;D.StNPR4 protein structural domains
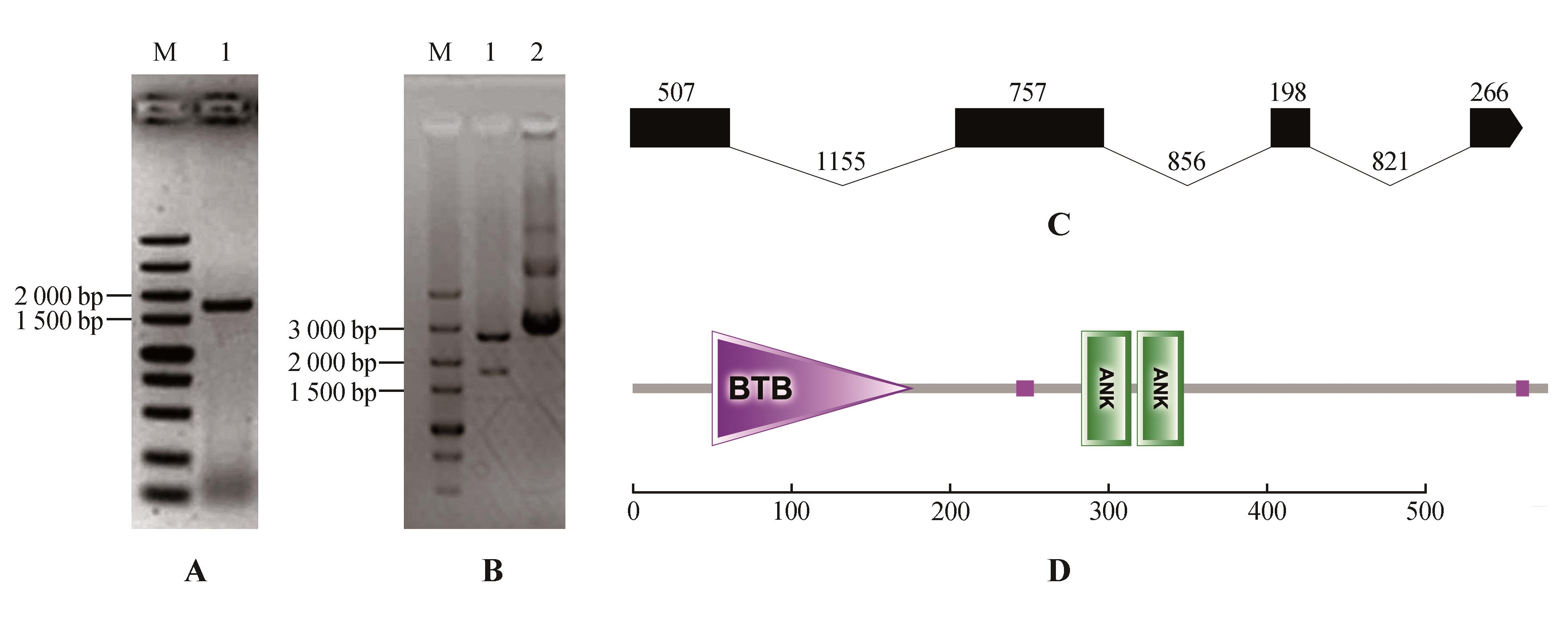
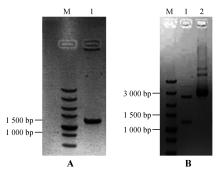
Fig.5
PCR amplification of StNPR4 promoter and enzyme digestion of the vectorA.PCR amplification of the StNPR4 promoter(M.DNA Marker;1.StPRONPR4 fragments at 1 246 bp;B.Enzyme digestion identification of StNPR4 cloning vector(M.DNA Marker;1.StPRONPR4 fragments at 1 246 bp;2.StproNPR4 -pENTR L16 vector)
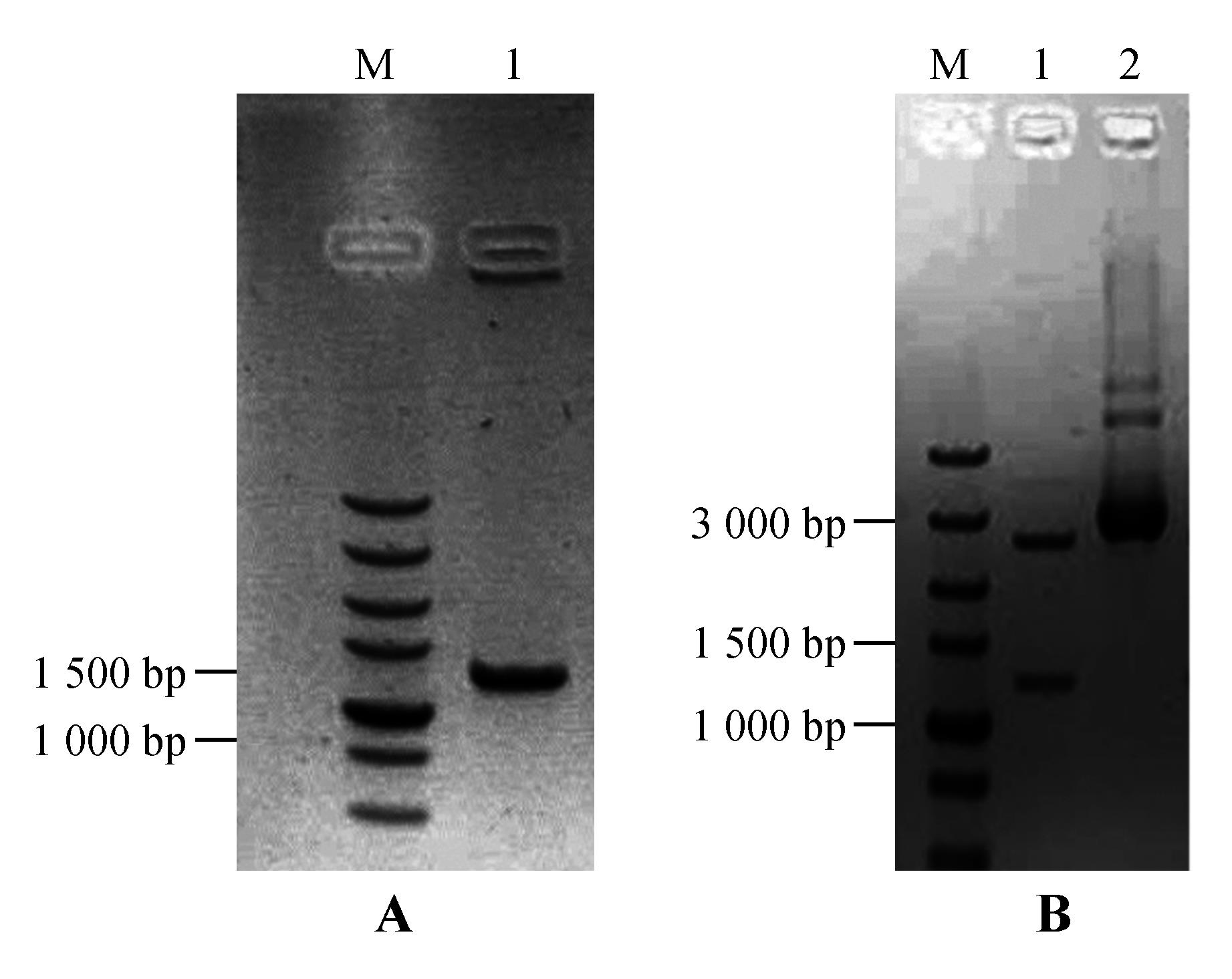
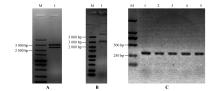
Fig.6
Enzyme digestion identification of vectors and PCR identification of transgenic plantsA.Identification of StPRONPR4-StNPR4 pENTR L16 cloning vector by enzymatic digestion;M.DNA Marker;1.StPRONPR4-StNPR4 fragments at 3 021 bp;B.Identification of StPRONPR4-StNPR4 pORE O4 binary expression vector by enzymatic digestion;M.DNA Marker;1.StPRONPR4-StNPR4 fragments at 3 021 bp;C.PCR identification of different StNPR4 transgenic lines;M.DNA Marker;1-5.Different StNPR4 transgenic lines
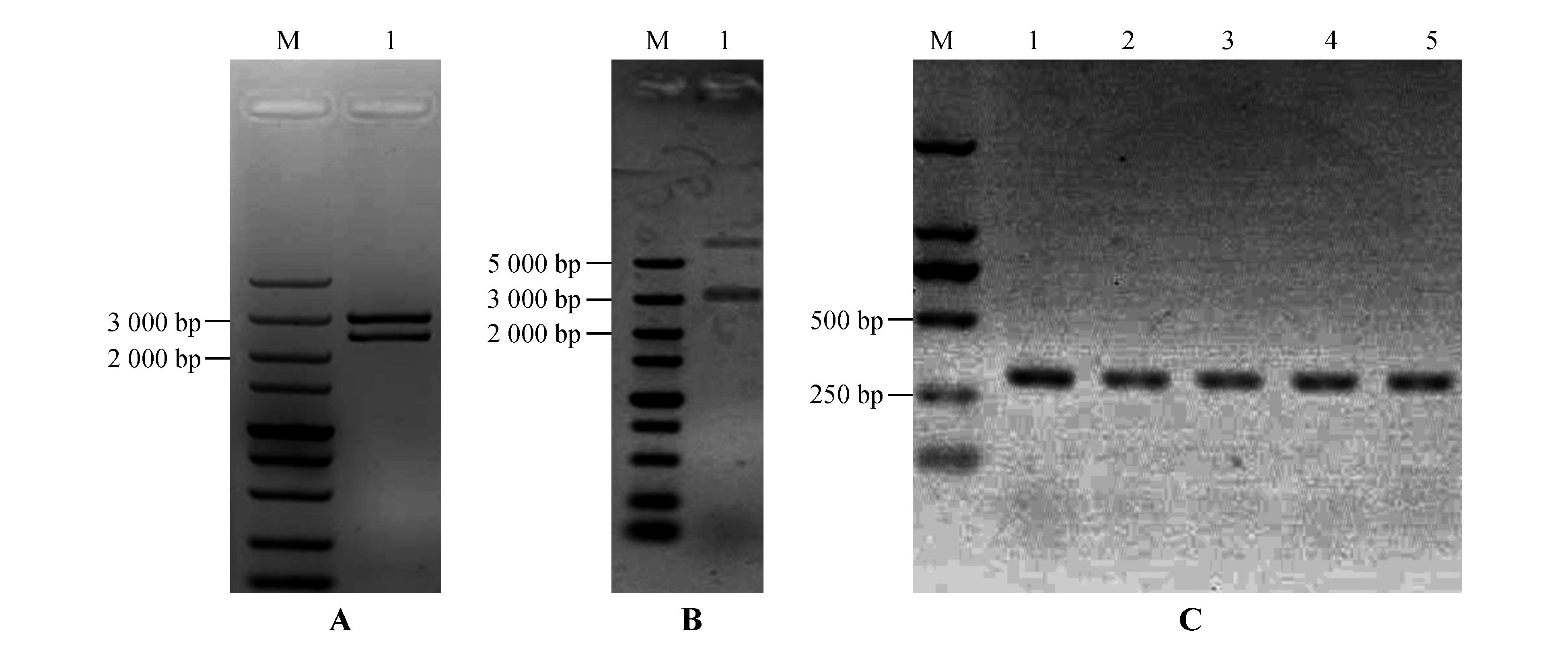
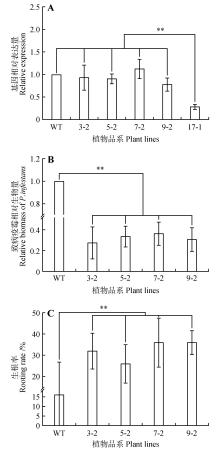
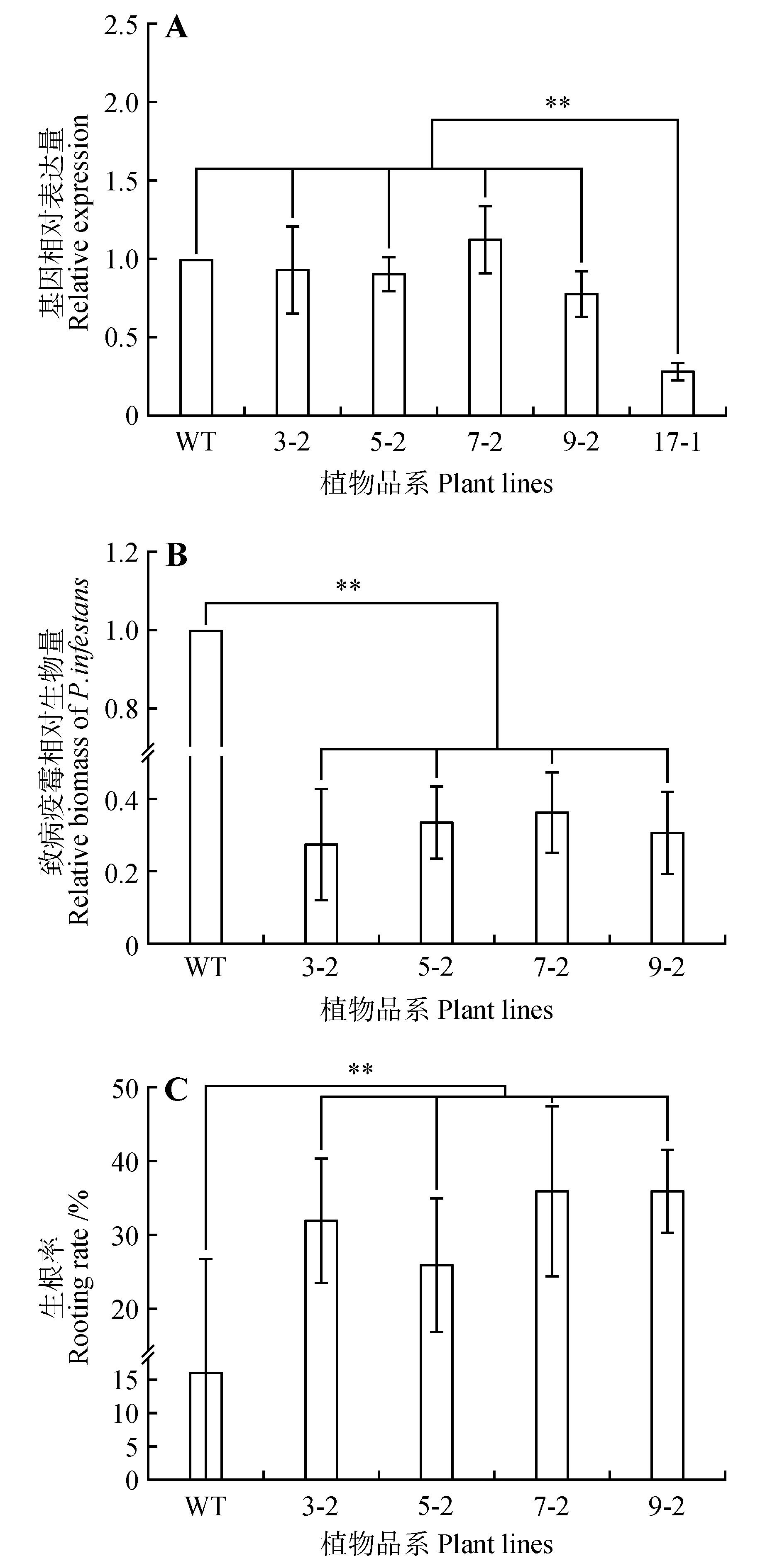
Fig.7
Functional analysis of StNPR4 transgenic plantsA.StNPR4 expression level in transgenic lines;B.Relative biomass of pathogens after inoculation of transgenic lines with phytophthora infestans;C.Rooting rates of transgenic lines after treatment with 150 mmol·L-1 NaCl;* represents P<0.05,** represents P<0.01,and equal variance t-test was used to analyze each experimental group and the control group at the same time point,the same as below
| 1 | CAO H, BOWLING S A, GORDON A S,et al.Characterization of an Arabidopsis mutant that is nonresponsive to inducers of systemic acquired resistance[J].The Plant Cell,1994,6(11):1583-1592. |
| 2 | PIETERSE C M J, S C MVAN WEES, AVAN PELT J,et al.A novel signaling pathway controlling induced systemic resistance in Arabidopsis [J].The Plant Cell,1998,10(9):1571-1580. |
| 3 | SPOEL S H, KOORNNEEF A, CLAESSENS S M C,et al.NPR1 modulates cross-talk between salicylate-and jasmonate-dependent defense pathways through a novel function in the cytosol[J].The Plant Cell,2003,15(3):760-770. |
| 4 | MOU Z L, FAN W H, DONG X N.Inducers of plant systemic acquired resistance regulate NPR1 function through redox changes[J].Cell,2003,113(7):935-944. |
| 5 | ZHANG Y L, TESSARO M J, LASSNER M,et al.Knockout analysis of Arabidopsis transcription factors TGA2,TGA5,and TGA6 reveals their redundant and essential roles in systemic acquired resistance[J].The Plant Cell,2003,15(11):2647-2653. |
| 6 | JAYAKANNAN M, BOSE J, BABOURINA O,et al.Salicylic acid in plant salinity stress signalling and tolerance[J].Plant Growth Regulation,2015,76(1):25-40. |
| 7 | JAYAKANNAN M, BOSE J, BABOURINA O,et al.The NPR1-dependent salicylic acid signalling pathway is pivotal for enhanced salt and oxidative stress tolerance in Arabidopsis [J].Journal of Experimental Botany,2015,66(7):1865-1875. |
| 8 | SARISOY U, SECKIN DINLER B, TASCI E.The effects of NPR1 dependent salicylic acid change in increasing salt tolerance of soybean leaves by acclimation[J].Notulae Botanicae Horti Agrobotanici Cluj-Napoca,2018,46(2):356-364. |
| 9 | 刘晓东,李月,王若仲,等.过表达GH3-5提高拟南芥抗旱的分子机制[J].南京农业大学学报,2016,39(4):557-562. |
| LIU X D, LI Y, WANG R Z,et al.Molecular mechanism of drought tolerance conferred by overexpression of GH3-5[J].Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University,2016,39(4):557-562. | |
| 10 | OLATE E, JIMÉNEZ-GÓMEZ J M, HOLUIGUE L,et al.NPR1 mediates a novel regulatory pathway in cold acclimation by interacting with HSFA1 factors[J].Nature Plants,2018,4(10):811-823. |
| 11 | ZHOU M, WANG W, KARAPETYAN S,et al.Redox rhythm reinforces the circadian clock to gate immune response[J].Nature,2015,523(7561):472-476. |
| 12 | ZHANG Y L, CHENG Y T, QU N,et al.Negative regulation of defense responses in Arabidopsis by two NPR1 paralogs[J].The Plant Journal,2006,48(5):647-656. |
| 13 | DING Y L, SUN T J, AO K,et al.Opposite roles of salicylic acid receptors NPR1 and NPR3/NPR4 in transcriptional regulation of plant immunity[J].Cell,2018,173(6):1454-1467. |
| 14 | HEPWORTH S R, ZHANG Y L, MCKIM S,et al.BLADE-ON-PETIOLE-dependent signaling controls leaf and floral patterning in Arabidopsis [J].The Plant Cell,2005,17(5):1434-1448. |
| 15 | SPOEL S H, MOU Z L, TADA Y,et al.Proteasome - mediated turnover of the transcription coactivator NPR1 plays dual roles in regulating plant immunity[J].Cell,2009,137(5):860-872. |
| 16 | LIU Y N, SUN T J, SUN Y L,et al.Diverse roles of the salicylic acid receptors NPR1 and NPR3/NPR4 in plant immunity[J].The Plant Cell,2020,32(12):4002-4016. |
| 17 | BACKER R, NAIDOO S,BERG NVAN DEN.The NONEXPRESSOR OF PATHOGENESIS-RELATED GENES1(NPR1) and related family:mechanistic insights in plant disease resistance[J].Frontiers in Plant Science,2019,10:102. |
| 18 | 王攀,蔡兆明,廖静静,等.大白菜NPR家族基因鉴定及表达模式分析[J].分子植物育种,2021,19(3):746-758. |
| WANG P, CAI Z M, LIAO J J,et al.Genome-wide identification and expression pattern analysis of histidine NPR family genes in Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis [J].Molecular Plant Breeding,2021,19(3):746-758. | |
| 19 | 李雅倩,王林,宋婧含,等.小麦NPR1基因家族鉴定及其表达分析[J].南方农业学报,2021,52(9):2339-2349. |
| LI Y Q, WANG L, SONG J H,et al.Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of wheat NPR1 gene family[J].Journal of Southern Agriculture,2021,52(9):2339-2349. | |
| 20 | 江慎秀,尚海,李涛,等.油桐NPR1家族全基因组鉴定及表达模式分析[J].植物遗传资源学报,2021,22(2):521-531. |
| JIANG S X, SHANG H, LI T,et al.Genome-wide identification and expression pattern analysis of NPR1 family in Vernicia fordii [J].Journal of Plant Genetic Resources,2021,22(2):521-531. | |
| 21 | ZHANG J K, JIAO P, ZHANG C,et al.Apple NPR1 homologs and their alternative splicing forms may contribute to SA and disease responses[J].Tree Genetics & Genomes,2016,12(5):92. |
| 22 | 淳俊,桑有顺,冯焱,等.四川省马铃薯晚疫病研究进展[J].中国农学通报,2018,34(30):136-139. |
| CHUN J, SANG Y S, FENG Y,et al.Potato late blight in Sichuan:research progress[J].Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin,2018,34(30):136-139. | |
| 23 | TIAN L X, YANG J Q, HOU W J,et al.Molecular cloning and characterization of a P-glycoprotein from the diamondback moth,Plutella xylostella(Lepidoptera:Plutellidae) [J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2013,14(11):22891-22905. |
| 24 | WITHERS J, DONG X N.Posttranslational modifications of NPR1:a single protein playing multiple roles in plant immunity and physiology[J].PLoS Pathogens,2016,12(8):e1005707. |
| 25 | BAI W, CHERN M, RUAN D L,et al.Enhanced disease resistance and hypersensitivity to BTH by introduction of an NH1/OsNPR1 paralog[J].Plant Biotechnology Journal,2011,9(2):205-215. |
| 26 | ZAVALIEV R, MOHAN R, CHEN T Y,et al.Formation of NPR1 condensates promotes cell survival during the plant immune response[J].Cell,2020,182(5):1093-1108. |
| 27 | SEO S Y, WI S J, PARK K Y.Functional switching of NPR1 between chloroplast and nucleus for adaptive response to salt stress[J].Scientific Reports,2020,10(1):4339. |
| 28 | DIVI U K, RAHMAN T, KRISHNA P.Brassinosteroid - mediated stress tolerance in Arabidopsis shows interactions with abscisic acid,ethylene and salicylic acid pathways[J].BMC Plant Biology,2010,10:151. |
| 29 | QUILIS J, PEÑAS G, MESSEGUER J,et al.The Arabidopsis AtNPR1 inversely modulates defense responses against fungal,bacterial,or viral pathogens while conferring hypersensitivity to abiotic stresses in transgenic rice[J].Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions,2008,21(9):1215-1231. |
| 30 | HAO L, ZHAO Y, JIN D D,et al.Salicylic acid - altering Arabidopsis mutants response to salt stress[J].Plant and Soil,2012,354(1/2):81-95. |
| 31 | XU Y Q, WANG H, QIN R L,et al.Characterization of NPR1 and NPR4 genes from mulberry(Morus multicaulis) and their roles in development and stress resistance[J].Physiologia Plantarum,2019,167(3):302-316. |
| [1] | Xu HE, Yuan GAO, Qunye ZHANG, Chenguang ZHOU, Wei LI, Shuang LI. Establishment and Application of Genetic Transformation System for Populus simonii×P. nigra ‘Baicheng’ [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(5): 667-678. |
| [2] | Lei XU, Xiao XU, Qinsong LIU. Effects of Exogenous Salicylic Acid on Antioxidant System and Gene Expression of Davidia involucrata Seedlings under Salt Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(4): 572-581. |
| [3] | Haonan ZHANG, Shanshan CHEN, Jianmin XU, Ping LUO, Xiaoping WANG, Zhiru XU, Chunjie FAN. Cloning and Functional Analysis of EgrWAT1 Gene in Eucalyptus grandis [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(4): 601-611. |
| [4] | Li LI, Xin WANG, Yuejing ZHANG, Lingyun JIA, Hailong PANG, Hanqing FENG. Effects of Abiotic Stresses on the Intracellular and Extracellular ATP Levels of Tobacco Suspension Cells [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(2): 179-185. |
| [5] | Shixian LIAO, Yuting WANG, Liben DONG, Yongmei GU, Fenglin JIA, Tingbo JIANG, Boru ZHOU. Function Analysis of the Transcription Factor PsnbZIP1 of Populus simonii×P. nigra in Response to Salt Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(2): 288-299. |
| [6] | Senyao LIU, Fenglin JIA, Qing GUO, Gaofeng FAN, Boru ZHOU, Tingbo JIANG. Response Analysis of Transcription Factor PsnbHLH162 Gene in Populus simonii × P. nigra under Salt Stress and Low Temperature Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(2): 300-310. |
| [7] | Haiyun SONG, Tao ZHANG, Peng HE, Shufang ZHENG, Lifeng WANG, Wenlin WANG. Cloning and Expression Analysis of MibZIP1 from Macadamia integrifolia [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(1): 131-139. |
| [8] | Jinxia DU, Tingting SHEN, Haoran WANG, Yiping LIN, Huiyu LI, Lianfei ZHANG. Construction of Suppression Expression Vector and Genetic Transformation of BpSPL9 gene from Betula platyphylla [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(1): 30-35. |
| [9] | Na LI, Xiaonan WANG. Screening and Phenotypic Identification of Seed Coat Pigmentation Mutants in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(1): 59-68. |
| [10] | Denggao LI, Rui LIN, Qinghui MU, Na ZHOU, Yanru ZHANG, Wei BAI. Identification and Analysis of the Potato StCRKs Gene Family and Expression Patterns in Response to Stress Signals [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(6): 1033-1043. |
| [11] | Liran YUE, Yingjie LIU, Chenxu LIU, Yunwei ZHOU. Cloning and Functional Analysis of miR398a from Chrysanthemum× grandiflora in Response to Salt Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(6): 986-996. |
| [12] | Jiaorao CHEN, Xu XU, Zhangli HU, Shuang YANG. Recent Advances on Salt Stress Sensitivity and Related Calcium Signals in Plants [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(4): 713-720. |
| [13] | He CHENG, Shuanghui TIAN, Yang ZHANG, Cong LIU, De’an XIA, Zhigang WEI. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analysis of nsLTP Gene Family in Populus trichocarpa [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(3): 412-423. |
| [14] | Yuning Yang, Hao Dong, Shiwei Dong, Nairui Wang, Yue Song, Hanguo Zhang, Shujuan Li. Cloning and Expression Analysis of Transcription Factor LobHLH34 from Larix olgensis [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(1): 112-120. |
| [15] | Qiu-Jin TAN, Tao ZHANG, Yuan-Rong WEI, Shu-Fang ZHENG, Xiu-Hua TANG, Wen-Lin WANG. Cloning and Expression Vector Construction of a Flowering Related Gene MiMADS-box from Macadamia integrifolia [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(6): 888-895. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||