Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (4): 572-581.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2023.04.010
• Physiology and Ecology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Lei XU, Xiao XU, Qinsong LIU( )
)
Received:2023-01-16
Online:2023-07-20
Published:2023-07-03
Contact:
Qinsong LIU
E-mail:qinsongliu@126.com
About author:XU Lei(1997—),male,master candidate,mainly engaged in plant molecular biology research.
Supported by:CLC Number:
Lei XU, Xiao XU, Qinsong LIU. Effects of Exogenous Salicylic Acid on Antioxidant System and Gene Expression of Davidia involucrata Seedlings under Salt Stress[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(4): 572-581.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://bbr.nefu.edu.cn/EN/10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2023.04.010
Table 1
Primer sequences for qRT-PCR
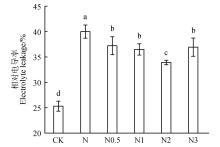
Fig.1
Effects of SA at different concentrations on relative electrolyte leakage of D. involucrata leaves under salt stress.CK.Water with no salt;N.Water with salt;N0.5. 0.5 mmol·L-1 SA with salt;N1. 1.0 mmol·L-1 SA with salt;N2. 2.0 mmol·L-1 SA with salt;N3. 3.0 mmol·L-1 SA with salt;Different letters indicated significant differences(P<0.05);the same as below
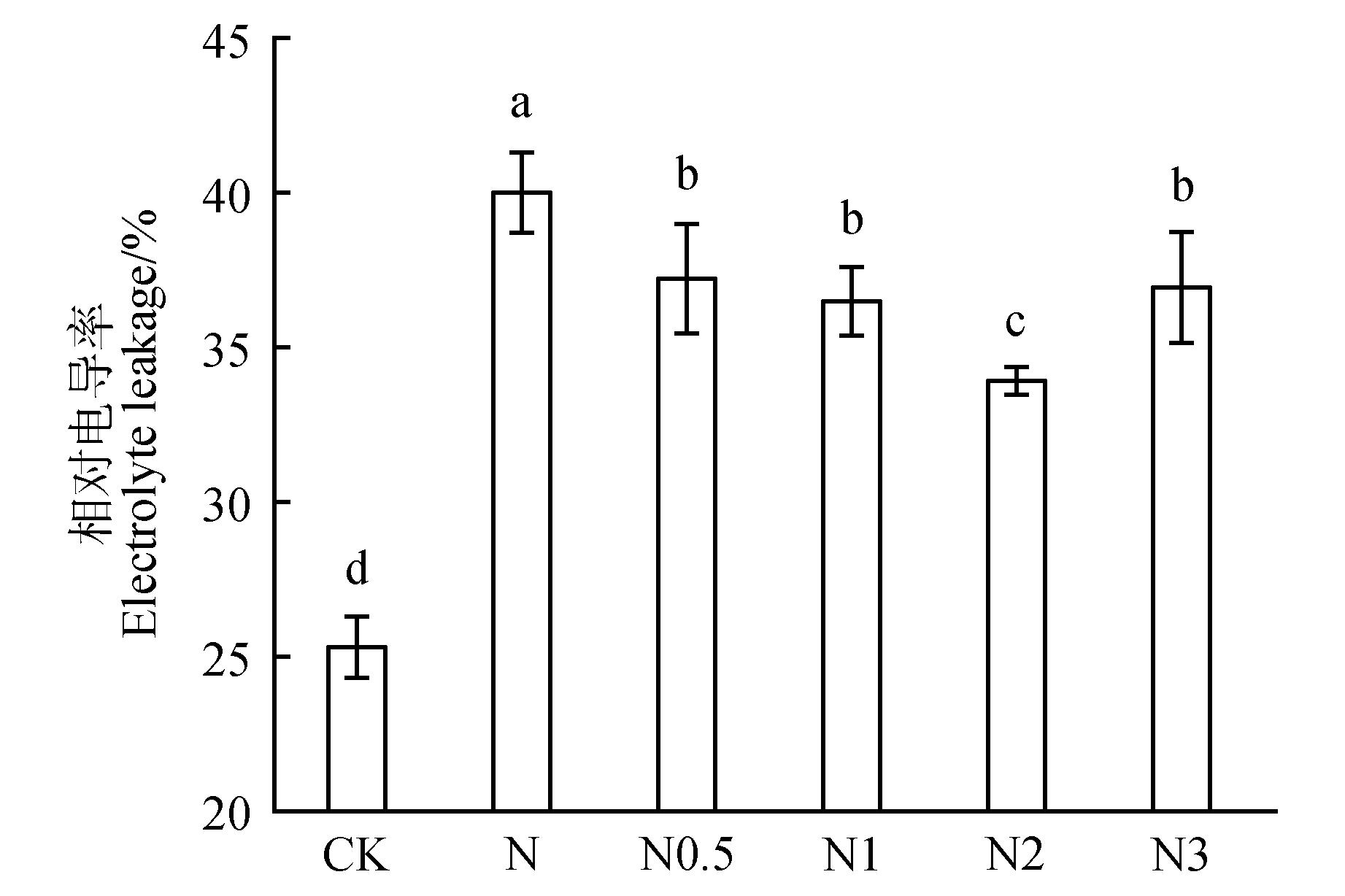
Table 2
Evaluation of transcriptome sequencing data
样品名称 Sample | 原始读长 Raw reads | 过滤读长 Clean reads | 质量值 Q30/% | GC含量 GC content/% | 总比对 Total mapped | 多重比对 Multiple mapped | 唯一比对 Uniquely mapped |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Table 3
KEGG analysis of DEGs
| 1.86×10-12 | ||||
| 4.75×10-7 | ||||
| 1.22×10-6 | ||||
| 0.000 616 | ||||
| 0.001 230 | ||||
| 0.001 399 | ||||
| 0.001 453 | ||||
| 0.001 561 | ||||
| 0.002 448 |
Table 4
DEGs annotated to phenylpropanoid biosynthetic pathways
基因ID Gene ID | 基因功能 Gene function | 调控 Regulation | log2FoldChange | padj padj value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dinv31309 | 苯丙氨酸解氨酶 Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase | 上调Up | 2.351 835 618 | 7.60×10-91 |
| Dinv42363 | 苯丙氨酸解氨酶 Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase | 上调Up | 2.262 196 592 | 8.18×10-34 |
| Dinv37296 | 苯丙氨酸解氨酶2 Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase 2 | 上调Up | 1.087 079 283 | 0.002 635 67 |
| Dinv13688 | 4-香豆酸-辅酶A连接酶2 4-coumarate--CoA ligase 2 | 上调Up | 1.109 700 195 | 2.86×10-23 |
| Dinv28733 | 反肉桂酸4-单加氧酶 Trans-cinnamate 4-monooxygenase | 下调Down | -1.530 300 677 | 1.74×10-23 |
| Dinv28734 | 反肉桂酸4-单加氧酶 Trans-cinnamate 4-monooxygenase | 下调Down | -1.541 750 51 | 6.44×10-39 |
| Dinv23273 | 莽草酸羟基肉桂酰基转移酶 Shikimate O-hydroxycinnamoyltransferase | 上调Up | 1.188 252 729 | 5.25×10-8 |
| novel.386 | 咖啡酰辅酶A-O-甲基转移酶 Caffeoyl-CoA O-methyltransferase | 上调Up | 1.675 679 415 | 3.25×10-69 |
| Dinv17295 | 咖啡酸3-O-甲基转移酶 Caffeic acid 3-O-methyltransferase | 上调Up | 1.287 852 331 | 1.27×10-54 |
| Dinv28242 | 咖啡酸3-O-甲基转移酶 Caffeic acid 3-O-methyltransferase | 上调Up | 1.438 655 657 | 3.08×10-12 |
| Dinv34261 | 咖啡酸3-O-甲基转移酶 Caffeic acid 3-O-methyltransferase | 下调Down | -1.031 352 199 | 0.015 344 14 |
| Dinv11989 | 金黄紫堇碱-9-O-甲基转移酶 (S)-scoulerine 9-O-methyltransferase | 上调Up | 1.261 821 713 | 1.31×10-6 |
| Dinv32208 | 金黄紫堇碱-9-O-甲基转移酶 (S)-scoulerine 9-O-methyltransferase | 上调Up | 1.298 036 084 | 0.007 392 16 |
| Dinv01483 | 细胞色素P450 CYP736A12 Cytochrome P450 CYP736A12 | 上调Up | 1.811 961 135 | 0.003 220 73 |
| Dinv07345 | 细胞色素P450 CYP736A12 Cytochrome P450 CYP736A12 | 上调Up | 2.860 017 242 | 3.14×10-6 |
| Dinv09818 | 细胞色素P450 CYP736A12 Cytochrome P450 CYP736A12 | 上调Up | 2.177 280 915 | 0.002 024 71 |
| Dinv25301 | 阳离子过氧化酶1 Cationic peroxidase 1 | 上调Up | 2.235 343 16 | 5.63×10-120 |
| Dinv11392 | 阳离子过氧化酶1 Cationic peroxidase 1 | 上调Up | 2.440 567 688 | 2.70×10-28 |
| Dinv12259 | 过氧化物酶4 Peroxidase 4 | 上调Up | 1.573 980 32 | 9.56×10-47 |
| Dinv25889 | 过氧化物酶12 Peroxidase 12 | 上调Up | 1.286 981 443 | 2.20×10-47 |
| Dinv17837 | 过氧化物酶27 Peroxidase 27 | 上调Up | 1.895 642 79 | 1.41×10-18 |
| Dinv12377 | 过氧化物酶52 Peroxidase 52 | 上调Up | 1.911 382 699 | 0.001 561 24 |
| Dinv13222 | 过氧化物酶17 Peroxidase 17 | 下调Down | -1.004 666 156 | 0.002 319 32 |
| Dinv36329 | 过氧化物酶N Peroxidase N | 下调Down | -1.888 094 821 | 5.04×10-6 |
| Dinv06626 | 木质素形成阴离子过氧化酶 Lignin-forming anionic peroxidase | 上调Up | 2.568 700 798 | 0.010 706 1 |
| Dinv39392 | 花青素3-O-葡糖基转移酶5 Anthocyanidin 3-O-glucosyltransferase 5 | 上调Up | 1.051 221 111 | 6.76×10-9 |
| Dinv23882 | 阿魏酰辅酶A正羟基化酶2 Feruloyl CoA ortho-hydroxylase 2 | 上调Up | 3.220 236 762 | 1.02×10-31 |
| Dinv23884 | 阿魏酰辅酶A正羟基化酶2 Feruloyl CoA ortho-hydroxylase 2 | 上调Up | 3.605 091 407 | 8.94×10-11 |
| Dinv13044 | β-葡萄糖苷酶11 Beta-glucosidase 11 | 上调Up | 2.002 038 447 | 9.03×10-5 |
| novel.1358 | β-葡萄糖苷酶12 Beta-glucosidase 12 | 上调Up | 2.001 540 708 | 0.002 155 38 |
| Dinv15038 | β-葡萄糖苷酶12 Beta-glucosidase 12 | 上调Up | 1.099 056 6 | 0.004 863 62 |
| Dinv43480 | β-葡萄糖苷酶12 Beta-glucosidase 12 | 上调Up | 1.754 417 253 | 0.026 302 63 |
| Dinv43482 | β-葡萄糖苷酶13 Beta-glucosidase 13 | 上调Up | 1.040 292 995 | 1.74×10-9 |
| Dinv00375 | β-葡萄糖苷酶 BoGH3BBeta-glucosidase BoGH3B | 上调Up | 2.531 914 008 | 0.004 682 7 |
| Dinv11980 | β-葡萄糖苷酶 BoGH3BBeta-glucosidase BoGH3B | 上调Up | 4.713 211 126 | 3.63×10-5 |
| Dinv25096 | β-葡萄糖苷酶 BoGH3BBeta-glucosidase BoGH3B | 上调Up | 1.824 354 237 | 1.81×10-19 |
| Dinv32836 | β-葡萄糖苷酶 BoGH3BBeta-glucosidase BoGH3B | 上调Up | 1.009 153 603 | 0.000 118 01 |
| Dinv13045 | 萝卡辛糖苷酶 Raucaffricine-O-beta-D-glucosidase | 上调Up | 3.172 249 014 | 6.02×10-7 |
| Dinv42534 | 萝卡辛糖苷酶 Raucaffricine-O-beta-D-glucosidase | 上调Up | 4.657 804 191 | 1.35×10-33 |
| Dinv13427 | 萝卡辛糖苷酶 Raucaffricine-O-beta-D-glucosidase | 下调Down | -1.429 541 93 | 9.70×10-5 |
| novel.1554 | β-葡萄糖苷酶12 Beta-glucosidase 12 | 下调Down | -1.136 799 964 | 0.001 879 18 |
| Dinv36313 | β-葡萄糖苷酶12 Beta-glucosidase 12 | 下调Down | -1.758 193 | 6.50×10-7 |
| Dinv34083 | β-葡萄糖苷酶40 Beta-glucosidase 40 | 下调Down | -1.053 398 192 | 0.005 758 |
Table 5
KEGG analysis of up-regulated DEGs
通路 Pathway | 上调基因数量 Number of up-regulated DEGs | P P value |
|---|---|---|
| 苯丙烷类生物合成Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis | 34 | 1.13×10-14 |
| 二萜生物合成Diterpenoid biosynthesis | 9 | 2.61×10-6 |
| 氰基氨基酸代谢Cyanoamino acid metabolism | 12 | 6.64×10-6 |
| 光合作用-天线蛋白Photosynthesis-antenna proteins | 7 | 3.33×10-5 |
| α-亚麻酸代谢alpha-Linolenic acid metabolism | 9 | 0.000 323 |
| 淀粉和蔗糖代谢Starch and sucrose metabolism | 19 | 0.000 332 |
| 油菜素甾醇生物合成Brassinosteroid biosynthesis | 5 | 0.000 564 |
| 苯丙氨酸代谢Phenylalanine metabolism | 8 | 0.000 982 |
| 角质、木栓质和蜡生物合成Cutin, suberine and wax biosynthesis | 5 | 0.003 323 |
| 植物-病原互作Plant-pathogen interaction | 19 | 0.003 603 |
| 1 | 蒋雪梅,胥晓,戚文华,等.盐胁迫下外施脯氨酸和磷肥对青杨雌雄幼苗生长及生理特性的影响[J].热带亚热带植物学报,2016,24(6):696-702. |
| JIANG X M, XU X, QI W H,et al.Effects of exogenous proline and phosphate fertilizer on growth and physiological traits of female and male Populus cathayana seedlings under salt stress[J].Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany,2016,24(6):696-702. | |
| 2 | LUO L M, ZHANG P P, ZHU R H,et al.Autophagy is rapidly induced by salt stress and is required for salt tolerance in Arabidopsis [J].Frontiers in Plant Science,2017,8:1459. |
| 3 | LIU Q S, VETUKURI R R, XU W J,et al.Transcriptomic responses of dove tree(Davidia involucrata Baill.) to heat stress at the seedling stage[J].Forests,2019,10(8):656. |
| 4 | LIU Q S, FENG Z Q, XU W J,et al.Exogenous melatonin-stimulated transcriptomic alterations of Davidia involucrata seedlings under drought stress[J].Trees,2021,35:1025-1038. |
| 5 | 徐云飞,刘沁松,徐文娟,等.天然珙桐种群结构与动态特征在高低纬度地区的差异[J].植物研究,2020,40(6):855-866. |
| XU Y F, LIU Q S, XU W J,et al.Differences in population structure and dynamic characteristics of Davidia involucrata Baill. between high and low latitude regions[J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2020,40(6):855-866. | |
| 6 | 牛文娟,张涛,邓东周,等.珙桐繁殖技术及生长发育研究进展[J].植物生理学报,2013,49(10):1018-1022. |
| NIU W J, ZHANG T, DENG D Z,et al.A review on reproductive technology and growing of Davidia involucrata Baill.[J].Plant Physiology Journal,2013,49(10):1018-1022. | |
| 7 | VEKEMANS D, VIAENE T, CARIS P,et al.Transference of function shapes organ identity in the dove tree inflorescence[J].New Phytologist,2012,193(1):216-228. |
| 8 | 孙贵佳,杨艳,刘西典,等.Na2CO3和NaCl胁迫对珙桐叶片光合特性影响的比较[J].西南师范大学学报(自然科学版),2014,39(11):66-70. |
| SUN G J, YANG Y, LIU X D,et al.On comparison of stress from Na2CO3 and NaCl on photosynthetic characteristics of Davidia involucrata Baill.[J].Journal of Southwest China Normal University(Natural Science Edition),2014,39(11):66-70. | |
| 9 | 李润枝,靳晴,李召虎,等.水杨酸提高甘草种子萌发和幼苗生长对盐胁迫耐性的效应[J].作物学报,2020,46(11):1810-1816. |
| LI R Z, JIN Q, LI Z H,et al.Salicylic acid improved salinity tolerance of Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch during seed germination and seedling growth stages[J].Acta Agronomica Sinica,2020,46(11):1810-1816. | |
| 10 | NADARAJAH K, ABDUL HAMID N W, ABDUL RAHMAN N S N.SA-mediated regulation and control of abiotic stress tolerance in rice[J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2021,22(11):5591. |
| 11 | 高俊凤.植物生理学实验指导[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2006:15-16. |
| GAO J F.Experimental guidance for plant physiology[M].Beijing:Higher Education Press,2006:15-16. | |
| 12 | CHEN Y, MA T, ZHANG L S,et al.Genomic analyses of a “living fossil”:The endangered dove-tree[J].Molecular Ecology Resources,2020,20(3):756-769. |
| 13 | MA J, WANG Y, WANG L Y,et al.Transcriptomic analysis reveals the mechanism of the alleviation of salt stress by salicylic acid in pepper(Capsicum annuum L.)[J].Molecular Biology Reports,2022,50(4):3593-3606. |
| 14 | 孙德智,韩晓日,彭靖,等.外源NO和SA对盐胁迫下番茄幼苗叶片膜脂过氧化及AsA-GSH循环的影响[J].植物科学学报,2018,36(4):612-622. |
| SUN D Z, HAN X R, PENG J,et al.Effects of exogenous nitric oxide and salicylic acid on membrane peroxidation and the ascorbate-glutathione cycle in leaves of Lycopersicon esculentum seedlings under NaCl stress[J].Plant Science Journal,2018,36(4):612-622. | |
| 15 | 刘庆,董元杰,刘双,等.外源水杨酸(SA)对NaCl胁迫下棉花幼苗生理生化特性的影响[J].水土保持学报,2014,28(2):165-168,174. |
| LIU Q, DONG Y J, LIU S,et al.Effects of exogenous salicylic acid on the physiological and biochemical characteristics of cotton seedlings under salt stress[J].Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2014,28(2):165-168,174. | |
| 16 | 付乃鑫,贺明荣,诸葛玉平,等.外源SA对盐胁迫下冬小麦幼苗生长的缓解效应及其机理[J].中国农业大学学报,2019,24(3):10-17. |
| FU N X, HE M R, ZHUGE Y P,et al.Effects and mechanisms of exogenous SA alleviating the growth of winter wheat seedlings under salt stress[J].Journal of China Agricultural University,2019,24(3):10-17. | |
| 17 | 周旋,申璐,肖霄,等.外源水杨酸对盐胁迫下茶树生长及抗氧化酶活性的影响[J].西北农业学报,2014,23(6):127-133. |
| ZHOU X, SHEN L, XIAO X,et al.Effects of exogenous salicylic acid on growth and antioxidant enzyme activities of tea plant(Camellia sinensis) under salt stress[J].Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica,2014,23(6):127-133. | |
| 18 | 赵宝泉,邢锦城,王静,等.水杨酸对盐胁迫下杭白菊幼苗生长和生理特性的影响[J].吉林农业大学学报,2020,42(4):370-379. |
| ZHAO B Q, XING J C, WANG J,et al.Effects of exogenous salicylic acid on growth and physiological properties of Chrysanthemum morifolium seedlings under salt stress[J].Journal of Jilin Agricultural University,2020,42(4):370-379. | |
| 19 | LI G Z, PENG X Q, WEI L T,et al.Salicylic acid increases the contents of glutathione and ascorbate and temporally regulates the related gene expression in salt-stressed wheat seedlings[J].Gene,2013,529(2):321-325. |
| 20 | BAILLO E H, KIMOTHO R N, ZHANG Z B,et al.Transcription factors associated with abiotic and biotic stress tolerance and their potential for crops improvement[J].Genes,2019,10(10):771. |
| 21 | DAI W S, WANG M, GONG X Q,et al.The transcription factor FcWRKY40 of Fortunella crassifolia functions positively in salt tolerance through modulation of ion homeostasis and proline biosynthesis by directly regulating SOS2 and P5CS1 homologs[J].New Phytologist,2018,219(3):972-989. |
| 22 | HAN D G, DU M, ZHOU Z Y,et al.Overexpression of a Malus baccata NAC transcription factor gene MbNAC25 increases cold and salinity tolerance in Arabidopsis [J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2020,21(4):1198. |
| 23 | WANG N, QU C Z, WANG Y C,et al.MdMYB4 enhances apple callus salt tolerance by increasing MdNHX1 expression levels[J].Plant Cell,Tissue and Organ Culture,2017,131:283-293. |
| 24 | SONG Y S, YANG W J, FAN H,et al. TaMYB86B encodes a R2R3-type MYB transcription factor and enhances salt tolerance in wheat[J].Plant Science,2020,300:110624. |
| 25 | DONG N Q, LIN H X.Contribution of phenylpropanoid metabolism to plant development and plant-environment interactions[J].Journal of Integrative Plant Biology,2021,63(1):180-209. |
| 26 | CHUN H J, BAEK D, CHO H M,et al.Lignin biosynthesis genes play critical roles in the adaptation of Arabidopsis plants to high-salt stress[J].Plant Signaling and Behavior,2019,14(8):1625697. |
| 27 | DUAN A Q, TAO J P, JIA L L,et al.AgNAC1,a celery transcription factor,related to regulation on lignin biosynthesis and salt tolerance[J].Genomics,2020,112(6):5254-5264. |
| 28 | BABA S A, VISHWAKARMA R A, ASHRAF N.Functional characterization of CsBGlu12,a β-Glucosidase from Crocus sativus,provides insights into its role in abiotic stress through accumulation of antioxidant flavonols[J].Journal of Biological Chemistry,2017,292(11):4700-4713. |
| [1] | Jingzhe WANG, Chaokui NIU, Xinyuan LIANG, Chenjing SHEN, Jing YIN. Regulation of Salicylic Acid on Tolerance to Saline Alkali Stress at Seedling Stages of Betula platyphylla [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(3): 379-387. |
| [2] | Chenjing SHEN, Wenbo WU, Luran GENG, Fulong WANG, Pengzhou ZHAO, Jinhui SONG, Yaguang ZHAN, Jing YIN. Regulatory Effects of Salicylic Acid,Nano-zinc Oxide and Growth-promoting Fungi YZ13-1 on the Resistance to Drought Stress of Fraxinus mandshurica [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(3): 388-395. |
| [3] | Li LI, Xin WANG, Yuejing ZHANG, Lingyun JIA, Hailong PANG, Hanqing FENG. Effects of Abiotic Stresses on the Intracellular and Extracellular ATP Levels of Tobacco Suspension Cells [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(2): 179-185. |
| [4] | Shixian LIAO, Yuting WANG, Liben DONG, Yongmei GU, Fenglin JIA, Tingbo JIANG, Boru ZHOU. Function Analysis of the Transcription Factor PsnbZIP1 of Populus simonii×P. nigra in Response to Salt Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(2): 288-299. |
| [5] | Senyao LIU, Fenglin JIA, Qing GUO, Gaofeng FAN, Boru ZHOU, Tingbo JIANG. Response Analysis of Transcription Factor PsnbHLH162 Gene in Populus simonii × P. nigra under Salt Stress and Low Temperature Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(2): 300-310. |
| [6] | Hong YANG, Lifeng WANG, Longjun DAI, Bingbing GUO. Effects of Tapping Panel Dryness on Mitochondrial Ultrastructure and ROS Metabolism in Barks of Rubber Tree (Hevea brasiliensis) [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(1): 69-75. |
| [7] | Mengshuo LI, Yingze LIU, Huan LU, Sheng QIANG. Photosynthetic Capacity Differentiation and Gene Transcription in Different Geographical Populations of Arabidopsis thaliana under Common Garden conditions [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(1): 90-99. |
| [8] | Liran YUE, Yingjie LIU, Chenxu LIU, Yunwei ZHOU. Cloning and Functional Analysis of miR398a from Chrysanthemum× grandiflora in Response to Salt Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(6): 986-996. |
| [9] | Bi QIN, Mingyang LIU, Meng WANG, Lifeng WANG, Fei HUANG. Cloning and Expression Analysis of DELLA gene HbRGL1 from Hevea brasiliensis Müll. Arg [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(6): 997-1004. |
| [10] | Longjun DAI, Mingyang LIU, Jianghua YANG, Kai ZHOU, Bingbing GUO, Hong YANG, Lifeng WANG. Structural and Gene Expression Analysis of a DUF1262 Domain Protein in Latex from Hevea brasiliensis [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(5): 802-810. |
| [11] | Denggao LI, Rui LIN, Qinghui MU, Na ZHOU, Yanru ZHANG, Wei BAI. Cloning and Functional Analysis of StNPR4 gene in Solanum tuberosum [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(5): 821-829. |
| [12] | Huan WANG, Yunfei XU, Yibo LIU, Qinsong LIU, Wenjuan XU, Yun LONG, Xiao XU. Allelopathic Effects on Seed Germination and Seedling Growth of Brassica pekinensi, Caused by Water Extracts of Branches and Leaves from Davidia involucrata and Bothrocaryum controversum [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(5): 866-875. |
| [13] | Jiaorao CHEN, Xu XU, Zhangli HU, Shuang YANG. Recent Advances on Salt Stress Sensitivity and Related Calcium Signals in Plants [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(4): 713-720. |
| [14] | Sisi CHEN, Muhong XIE, Maokai CUI, Wenkai LI, Zhenggang XU, Caixia JIA, Guiyan YANG. Identification of Broussonetia papyrifera Transcription Factor BpbZIP1 and Analysis of Its Response to Cadmium Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(3): 394-402. |
| [15] | He CHENG, Shuanghui TIAN, Yang ZHANG, Cong LIU, De’an XIA, Zhigang WEI. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analysis of nsLTP Gene Family in Populus trichocarpa [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(3): 412-423. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||