Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (6): 986-996.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2022.06.008
• Molecular biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Liran YUE1, Yingjie LIU1, Chenxu LIU2, Yunwei ZHOU3( )
)
Received:2021-10-20
Online:2022-11-20
Published:2022-11-22
Contact:
Yunwei ZHOU
E-mail:dlzhyw@126.com
About author:YUE Liran(1978—),female,Ph.D,associate professor,engaged in Garden plant resources and Application.
Supported by:CLC Number:
Liran YUE, Yingjie LIU, Chenxu LIU, Yunwei ZHOU. Cloning and Functional Analysis of miR398a from Chrysanthemum× grandiflora in Response to Salt Stress[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(6): 986-996.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://bbr.nefu.edu.cn/EN/10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2022.06.008
Table 1
List of PCR primer sequences
引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 Primer sequence(5′→3′) |
|---|---|
| cgr-MIR398a-F | TACACTTCTCAACAAGGGCA |
| cgr-MIR398a-R | TAAGATAAATGTGAAGTGATTTGTAGAC |
| U6-F | GGAACGATACAGAGAAGATTAGC |
| U6-R | TGGAACGCTTCACGAATTTGCG |
| cgr-mir398a-F | GGAGTGACACTCAGAACACATG |
| cgr-MIR398aM-F | GGTACCTACACTTCTCAACAA |
| cgr-MIR398aM-R | GTCGACCGGTGTACCAATCAATTT |
| TRINITY_DN123102_c0_g2-F | GGCCTAATGTTGTGGTCGGA |
| TRINITY_DN123102_c0_g2-R | CACCACACCACAAGCAAGTC |
| TRINITY_DN96068_c0_g2-F | TGAAGCCTTGGAGCAGACAG |
| TRINITY_DN96068_c0_g2-R | GAACAATGACGATTGGCGCA |
| TRINITY_DN94774_c3_g5-F | GGACCCAAGAGATGCTCCAC |
| TRINITY_DN94774_c3_g5-R | CTTGGCAATGGCATCACGAC |
| CmEF1a-F | TTTTGGTATCTGGTCCTGGAG |
| CmEF1a-R | CCATTCAAGCGACAGACTCA |
| PBI121-GFP-F | TCATTTCATTTGGAGAGAACAC |
| PBI121-GFP-R | TTGCCAAATGTTTGAACGATC |
| At2g28190-F | ATGACACACGGAGCTCCAGAA |
| At2g28190-R | ATTGTTGTTTCTGCCACGCCA |
| At1g12520-F | GAGCCATGCCTCAGCTTCTTAC |
| At1g12520-R | TCACAGCATTAACACAACCCTCAC |

Fig.3
The pre-miR398a sequences and the conserved nucleotide sequence of pre-miR395a in Chrysanthemum× grandifloraA.Mature miR395a sequence is showed with the red square;B.Different colors represent the conservative degrees,and the red is the most conservative,the blue is the lest conservative
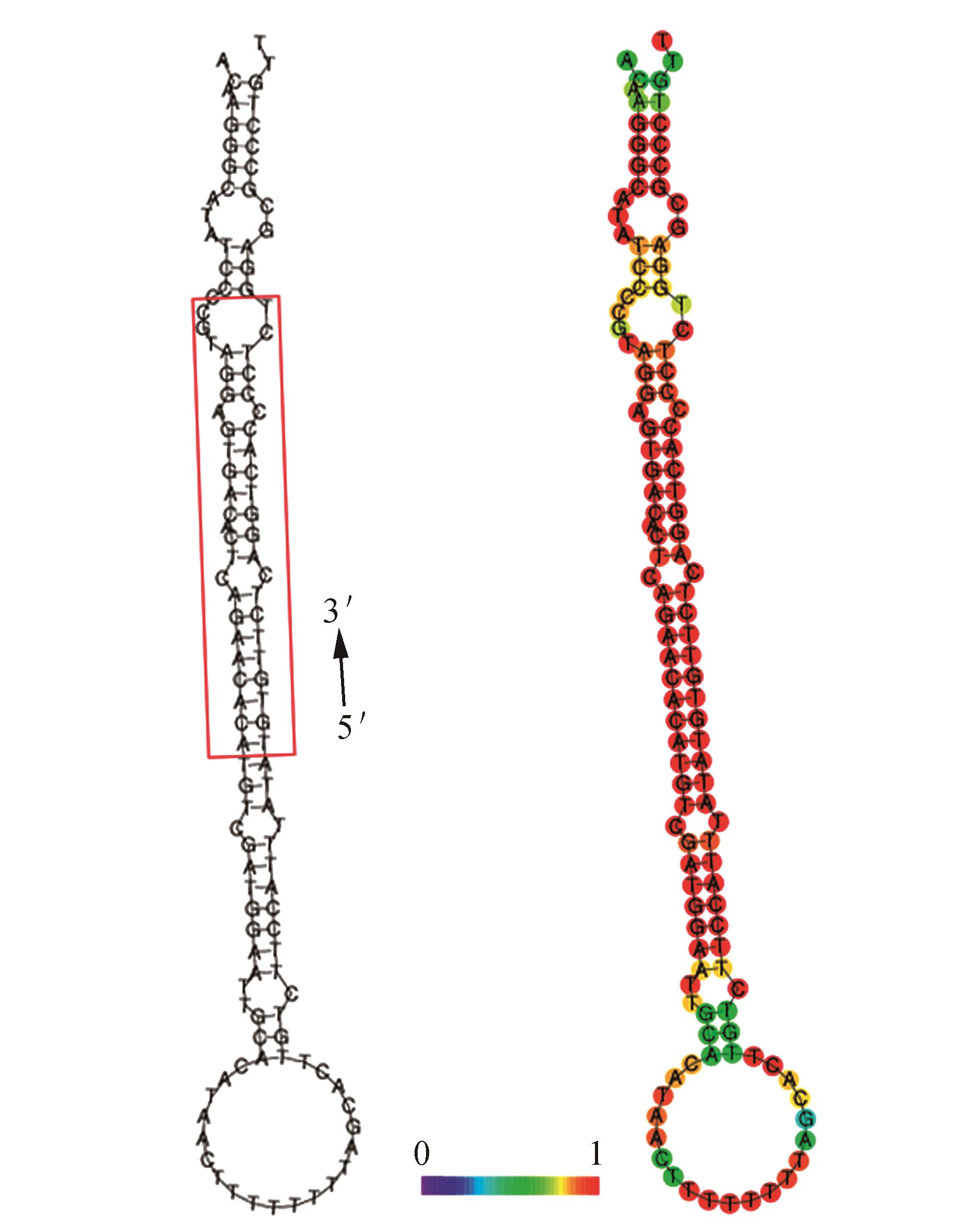
Table 2
Target genes of cgr-miR398a ofChrysanthemum×grandiflora
植物组织 Plant tissue | 靶基因 Target gene | 功能注释 Annotation |
|---|---|---|
叶和根 Leaf and root | TRINITY_DN118743_c0_g1 | 硫醇酶 Thiolase(PED1) |
| TRINITY_DN121349_c0_g1 | 含CCT结构域的蛋白质 CCT domain-containing protein(APRR7) | |
| TRINITY_DN123102_c0_g2 | 叶绿体中铜-锌超氧化物歧化酶 Superoxide dismutase[Cu-Zn],chloroplastic(CSD2) | |
| TRINITY_DN96068_c0_g2 | 铜伴侣蛋白 Copper chaperone for SOD1(CCS) | |
| TRINITY_DN97624_c8_g1 | ||
叶 Leaf | TRINITY_DN93471_c1_g2 | 未表征的蛋白质 Uncharacterized protein LOC107643668 |
| TRINITY_DN116098_c5_g1 | 叶绿体酶2 Chlorophyllase 2 (CLH2) | |
| TRINITY_DN97061_c0_g1 | DNAJ热激家族蛋白 DNAJ heat shock family protein (DJA6) | |
| TRINITY_DN97655_c1_g2 | 过氧体(S)-2-羟基酸氧化酶球状体 Peroxisomal (S)-2-hydroxy-acid oxidase GLO1-like (GLO1) | |
| TRINITY_DN94774_c3_g5 | 类A20/AN1-l锌指家族蛋白 A20/AN1-like zinc finger family protein (SAP8) | |
| TRINITY_DN99012_c1_g2 | 假定蛋白Ccrd_005494 Hypothetical protein Ccrd_005494 (KAI2) | |
根 Root | TRINITY_DN105234_c5_g1 | 蛋白激酶样域 Protein kinase-like domain |
| TRINITY_DN110642_c2_g2 | 糖苷水解酶,含催化域蛋白 Glycoside hydrolase, catalytic domain-containing protein (TAF15B) | |
| TRINITY_DN118599_c0_g1 | Aux/IAA-ARF-二聚反应 Aux/IAA-ARF-dimerization(ARF9) | |
| TRINITY_DN122683_c2_g2 | 双功能多黏菌素抗性蛋白 Bifunctional polymyxin resistance protein | |
| TRINITY_DN124647_c1_g1 | 核苷酸结合相关 Nucleotide-binding, alpha-beta plait | |
| TRINITY_DN102787_c0_g1 | 假定蛋白CTI12_AA198490 Hypothetical protein CTI12_AA198490 | |
| TRINITY_DN117385_c1_g3 | 含有PH、RCC1和FYVE结构域的蛋白质1样异构体X3 PH,RCC1 and FYVE domains-containing protein 1-like isoform X3 (UVR8) |
| 1 | SU C, YANG X Z, GAO S Q,et al.Identification and characterization of a subset of microRNAs in wheat(Triticum aestivum L.)[J].Genomics,2014,103(4):298-307. |
| 2 | SINGH D,JHA B.The isolation and identification of salt-responsive novel microRNAs from Salicornia brachiata,an extreme halophyte[J].Plant Biotechnology Reports,2014,8(4):325-336. |
| 3 | RAMAN S, GREB T, PEAUCELLE A,et al.Interplay of mir164,cup-shaped Cotyledon genes and lateral suppressor controls axillary meristem formation in Arabidopsis thaliana [J].The Plant Journal,2008,55(1):65-76. |
| 4 | GAO P, BAI X, YANG L,et al. Osa-MIR393:a salinity- and alkaline stress-related microRNA gene[J].Molecular Biology Reports,2011,38(1):237-242. |
| 5 | MA H S, LIANG D, SHUAI P,et al.The salt- and drought-inducible poplar GRAS protein SCL7 confers salt and drought tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana [J].Journal of Experimental Botany,2010,61(14):4011-4019. |
| 6 | ZHOU M, LI D Y, LI Z G,et al.Constitutive expression of a miR319 gene alters plant development and enhances salt and drought tolerance in transgenic creeping bentgrass[J].Plant Physiology,2013,161(3):1375-1391. |
| 7 | REYES J L, CHUA N H.ABA induction of miR159 controls transcript levels of two MYB factors during Arabidopsis seed germination[J].The Plant Journal,2007,49(4):592-606. |
| 8 | JONES-RHOADES M W, BARTEL D P.Computational identification of plant microRNAs and their targets,including a stress-induced miRNA[J].Molecular Cell,2004,14(6):787-799. |
| 9 | YAMASAKI H, HAYASHI M, FUKAZAWA M,et al. SQUAMOSA promoter binding protein-like7 is a central regulator for copper homeostasis in Arabidopsis [J].The Plant Cell,2009,21(1):347-361. |
| 10 | JAVEDMOHAMMED,SINHAANSHIKA,LATA ISRANI SHUKLA. Evaluation of mature miR398 family,expression analysis and the post-transcriptional regulation evidence in gamma-irradiated and nitrogen-stressed Medicago sativa seedlings[J/OL].International Journal of Radiation Biology:1-36[2017-12-17].. |
| 11 | SUNKAR R, LI Y F, JAGADEESWARAN G.Functions of microRNAs in plant stress responses[J].Trends in Plant Science,2012,17(4):196-203. |
| 12 | FENG X M, QIAO Y, MAO K,et al.Ectopic overexpression of AtmiR398b gene in tobacco influences seed germination and seedling growth[J].Plant Cell,Tissue and Organ Culture,2010,102(1):53-59. |
| 13 | HE Y, ZHOU J X, HU Y F,et al.Overexpression of sly-miR398b increased salt sensitivity likely via regulating antioxidant system and photosynthesis in tomato[J].Environmental and Experimental Botany,2021,181:104273. |
| 14 | GUAN Q M, LU X Y, ZENG H T,et al.Heat stress induction of miR398 triggers a regulatory loop that is critical for thermotolerance in Arabidopsis [J].The Plant Journal,2013,74(5):840-851. |
| 15 | LI L H, YI H L, XUE M Z,et al.miR398 and miR395 are involved in response to SO2 stress in Arabidopsis thaliana [J].Ecotoxicology,2017,26(9):1181-1187. |
| 16 | ZHU C, DING Y F, LIU H L.MiR398 and plant stress responses[J].Physiologia Plantarum,2011,143(1):1-9. |
| 17 | JAGADEESWARAN G, SAINI A, SUNKAR R.Biotic and abiotic stress down-regulate miR398 expression in Arabidopsis [J].Planta,2009,229(4):1009-1014. |
| 18 | 丁艳菲,王光钺,傅亚萍,等.miR398在植物逆境胁迫应答中的作用[J].遗传,2010,32(2):129-134. |
| DING Y F, WANG G Y, FU Y P,et al.The role of miR398 in plant stress responses[J].Hereditas,2010,32(2):129-134. | |
| 19 | 刘晓东,丁冰,张敩方,等.地被菊的区域栽培试验[J].东北林业大学学报,1996,24(5):50-56. |
| LIU X D, DING B, ZHANG X F,et al.Experiment on regional cultivation of dendranthemax grandiflor tzrel[J].Journal of Northeast Forestry University,1996,24(5):50-56. | |
| 20 | ADDO-QUAYE C, MILLER W, AXTELL M J.CleaveLand:a pipeline for using degradome data to find cleaved small RNA targets[J].Bioinformatics,2008,25(1):130-131. |
| 21 | ADDO-QUAYE C, ESHOO T W, BARTEL D P,et al.Endogenous siRNA and miRNA targets identified by sequencing of the Arabidopsis degradome[J].Current Biology,2008,18(10):758-762. |
| 22 | 安聪,张一,张皖皖,等.菊花CmPAL基因的克隆及表达分析[J].南京农业大学学报,2019,42(1):73-80. |
| AN C, ZHANG Y, ZHANG W W,et al.Cloning and expression analysis of CmPAL gene in Chrysanthemum morifolium [J].Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University,2019,42(1):73-80. | |
| 23 | 王学奎.植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M].2版.北京:高等教育出版社,2006. |
| WANG X K.Principles and techniques of plant physiological biochemical experiment[M].2nd.Beijing:Higher Education Press,2006. | |
| 24 | O.Origin VOINNET,biogenesis,and activity of plant microRNAs[J].Cell,2009,136(4):669-687. |
| 25 | BOKSZCZANIN K L, KREZDORN N, FRAGKOSTEFANAKIS S,et al.Identification of novel small ncRNAs in pollen of tomato[J].BMC Genomics,2015,16(1):714. |
| 26 | YANG Z M, ZHU P P, KANG H,et al.High-throughput deep sequencing reveals the important role that microRNAs play in the salt response in sweet potato(Ipomoea batatas L.)[J].BMC Genomics,2020,21(1):164. |
| 27 | MANAVELLA P A, KOENIG D, RUBIO-SOMOZA I,et al.Tissue-specific silencing of Arabidopsis SU(VAR)3-9 HOMOLOG8 by miR171a[J].Plant Physiology,2013,161(2):805-812. |
| 28 | LU X Y, GUAN Q M, ZHU J H.Downregulation of CSD2 by a heat-inducible miR398 is required for thermotolerance in Arabidopsis [J].Plant Signaling & Behavior,2013,8(8):e24952. |
| 29 | ZHU J F, LI W F, YANG W H,et al.Identification of microRNAs in Caragana intermedia by high-throughput sequencing and expression analysis of 12 microRNAs and their targets under salt stress[J].Plant Cell Reports,2013,32(9):1339-1349. |
| 30 | GIRI J, DANSANA P K, KOTHARI K S,et al.SAPs as novel regulators of abiotic stress response in plants[J].BioEssays,2013,35(7):639-648. |
| 31 | SAAD R BEN, ZOUARI N, RAMDHAN W BEN,et al.Improved drought and salt stress tolerance in transgenic tobacco overexpressing a novel A20/AN1 zinc-finger “AlSAP” gene isolated from the halophyte grass Aeluropus littoralis [J].Plant Molecular Biology,2010,72(1/2):171-190. |
| 32 | 王康君,樊继伟,陈凤,等.植物对盐胁迫的响应及耐盐调控的研究进展[J].江西农业学报,2018,30(12):31-40. |
| WANG K J, FAN J W, CHEN F,et al.Research advances in response of plants to salt stress and regulation of salinity tolerance[J].Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi,2018,30(12):31-40. | |
| 33 | KORAMUTLA M K, KAUR A, NEGI M,et al.Elicitation of jasmonate-mediated host defense in Brassica juncea L. attenuates population growth of mustard aphid Lipaphis erysimi Kalt.[J].Planta,2014,240(1):177-194. |
| 34 | RAY P D, HUANG B W, TSUJI Y.Reactive oxygen species(ROS) homeostasis and redox regulation in cellular signaling[J].Cellular Signalling,2012,24(5):981-990. |
| [1] | Lei XU, Xiao XU, Qinsong LIU. Effects of Exogenous Salicylic Acid on Antioxidant System and Gene Expression of Davidia involucrata Seedlings under Salt Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(4): 572-581. |
| [2] | Li LI, Xin WANG, Yuejing ZHANG, Lingyun JIA, Hailong PANG, Hanqing FENG. Effects of Abiotic Stresses on the Intracellular and Extracellular ATP Levels of Tobacco Suspension Cells [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(2): 179-185. |
| [3] | Shixian LIAO, Yuting WANG, Liben DONG, Yongmei GU, Fenglin JIA, Tingbo JIANG, Boru ZHOU. Function Analysis of the Transcription Factor PsnbZIP1 of Populus simonii×P. nigra in Response to Salt Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(2): 288-299. |
| [4] | Senyao LIU, Fenglin JIA, Qing GUO, Gaofeng FAN, Boru ZHOU, Tingbo JIANG. Response Analysis of Transcription Factor PsnbHLH162 Gene in Populus simonii × P. nigra under Salt Stress and Low Temperature Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(2): 300-310. |
| [5] | Denggao LI, Rui LIN, Qinghui MU, Na ZHOU, Yanru ZHANG, Wei BAI. Cloning and Functional Analysis of StNPR4 gene in Solanum tuberosum [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(5): 821-829. |
| [6] | Jiaorao CHEN, Xu XU, Zhangli HU, Shuang YANG. Recent Advances on Salt Stress Sensitivity and Related Calcium Signals in Plants [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(4): 713-720. |
| [7] | He CHENG, Shuanghui TIAN, Yang ZHANG, Cong LIU, De’an XIA, Zhigang WEI. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analysis of nsLTP Gene Family in Populus trichocarpa [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(3): 412-423. |
| [8] | Bo-Chao ZHANG, Jia-Lin WANG, Yuan YIN, Yi-Da CHE, Jun-Jie DENG, Rong-Shu ZHANG. Tissue Expression Patterns of PdPapWRKY51 in Shanxin Poplar (Populus davidiana × P. alba var. pyramidlis) under Stress Conditions [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(6): 911-920. |
| [9] | Shuang-Hui TIAN, He CHENG, Yang ZHANG, Cong LIU, De-An XIA, Zhi-Gang WEI. Genome-wide Identification and Expressional Analysis of Carotenoid Cleavage Dioxygenases(CCD) Gene Family in Populus trichocarpa under Drought and Salt Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(6): 993-1005. |
| [10] | Fang CHEN, Ting-Ting SHE, Lin ZHANG, Hao-Tian GAO, Guo-Liang LI, Jian WANG. Mechanism of Sm-miR858 Negatively Regulateda R2R3-MYB Transcription Factor SmPAP1 in Salvia miltiorrhiza [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(4): 522-530. |
| [11] | Dong-Lin LÜ, Teng LI, Yi-Wen GUO, Jing JIANG, Hai-Jiao HUANG. Determination of Seed Vigor and Genetic Analysis of Foreign Genes in Different Transgenic Birch Hybrids [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(4): 564-572. |
| [12] | Meng-Xuan REN, Yang ZHANG, Shuang WANG, Rui-Qi WANG, Cong LIU, Zhi-Gang WEI. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analysis GATA Family of Populus trichocarpa [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(1): 107-118. |
| [13] | CAO Ming-Wu, LUO Rui, AN Hui, PANG Qiu-Ying. Physiological Response of Suspension Cells of Helianthus tuberosus to NaCl Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2019, 39(2): 222-228. |
| [14] | ZHAO Xiao-Ju, ZHANG Li-Xia, MAN Xiu-Ling. Effects of Exogenous NO on Seed Germination and Physiological Metabolism in Catharanthus roseus Seedling under NaCl Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2018, 38(5): 669-674. |
| [15] | ZHANG Li-Li, ZHANG Fu-Chun. Transcriptomic Analysis of the Halostachys caspica in Response to Short-term Salt Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2018, 38(1): 91-99. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||