Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2021, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (3): 429-435.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2021.03.013
• Research report • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xu ZHANG1,2, Xiu-Jiao ZHANG1, Yong-Peng MA3, Zheng-Hong LI1, You-Ming WAN1, Hong MA1( )
)
Received:2020-03-17
Online:2021-05-20
Published:2021-03-24
Contact:
Hong MA
E-mail:hortscience@163.com
About author:ZHANG Xu(1994—),male,past graduate,major in conservation biology of Rhododendron plants.
Supported by:CLC Number:
Xu ZHANG, Xiu-Jiao ZHANG, Yong-Peng MA, Zheng-Hong LI, You-Ming WAN, Hong MA. Genetic Diversity Assessment of Rhododendron sinofalconeri with Genotyping by Sequencing(GBS)[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(3): 429-435.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://bbr.nefu.edu.cn/EN/10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2021.03.013

Fig.1
Statistics on the distribution of base and qualitiesA.Base distribution(Different colors represent different base types,and N represent bases that cannot be identified in sequencing.On the left side of the dotted line is the base distribution of double-terminal sequencing R1-terminal Reads,and on the right side is the base distribution of R2-terminal Reads);B.Quality distribution(The left side of the dotted line is the base quality value distribution of the double-end sequencing R1-terminal Reads,and the right side is the base quality value distribution of the R2-terminal Reads. A darker color indicates that the quality value of bases has a higher percentage in the data)
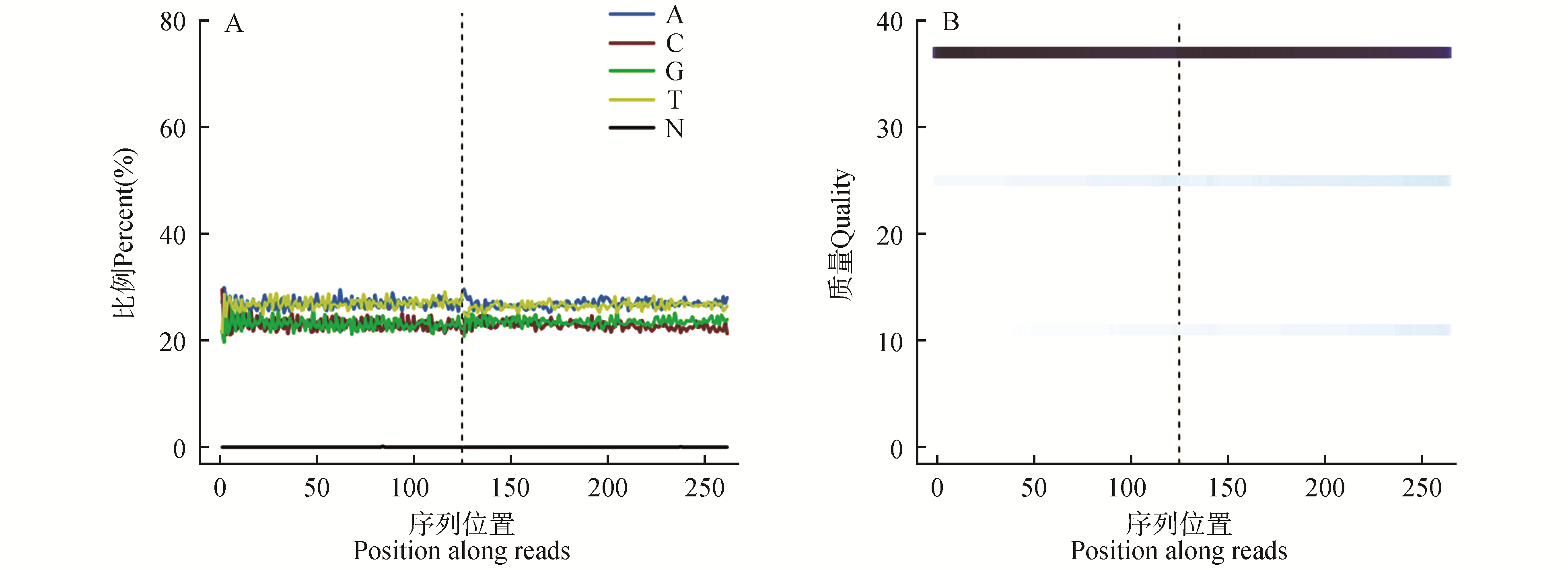
Table 1
Genetic diversity indexes of R.sinofalconeri of different groups
来源 Origins | 等位基因数 Na | 有效等位基因数 Ne | 观测杂合度 Ho | 期望杂合度 He | 多态信息含量 PIC | 核苷酸多样性 Pi |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1.539 0 | 1.310 5 | 0.189 4 | 0.185 2 | 0.149 4 | 0.206 5 |
| B | 1.548 6 | 1.311 2 | 0.188 5 | 0.186 4 | 0.150 7 | 0.207 9 |
| C | 1.454 3 | 1.291 0 | 0.194 8 | 0.170 9 | 0.136 8 | 0.205 1 |
| A1 | 1.682 5 | 1.319 8 | 0.185 2 | 0.196 1 | 0.160 4 | 0.205 7 |
| B1 | 1.583 9 | 1.309 6 | 0.187 1 | 0.187 7 | 0.152 6 | 0.205 2 |
| C1 | 1.581 1 | 1.309 6 | 0.182 1 | 0.187 6 | 0.152 4 | 0.205 1 |
| 平均Average | 1.564 9 | 1.308 6 | 0.187 8 | 0.185 6 | 0.150 4 | 0.205 9 |
Table 2
Genetic differentiation coefficient(Fst:above diagonal) and genetic distance(DR:below diagonal) between populations
| 种群Population | A | B | C | A1 | B1 | C1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | — | 0.001 700 | 0.012 700 | 0.194 800 | 0.194 100 | 0.192 000 |
| B | 0.001 650 | — | -0.000 200 | 0.189 600 | 0.189 300 | 0.187 500 |
| C | 0.012 650 | -0.000 230 | — | 0.199 900 | 0.201 100 | 0.199 100 |
| A1 | 0.177 000 | 0.172 700 | 0.181 200 | — | -0.002 000 | 0.004 900 |
| B1 | 0.176 400 | 0.172 500 | 0.182 200 | -0.002 000 | — | 0.001 900 |
| C1 | 0.174 700 | 0.171 000 | 0.180 500 | 0.004 882 | 0.001 932 | — |
| 1 | Gibbs D,Chamberlain D,Argent G.The red list of rhododendrons[M].Richmond: Botanic Gardens Conservation International,2011. |
| 2 | Species Survival Commission.Red list categories and criteria:version 3.1[M].Cambridge:IUCN Species Survival Commission,2001. |
| 3 | 韩聪,杨秀梅,彭绿春,等.宽杯杜鹃贮藏花粉特性及其与马缨杜鹃杂交的应用评价[J].江西农业学报,2018,30(6):6-11. |
| Han C,Yang X M,Peng L C,et al.Characteristics of stored pollen of Rhododendron sinofalconeri and evaluation of its hybridization with Rhododendron delavayi[J].Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi,2018,30(6):6-11. | |
| 4 | Fu Y B,Cheng B F,Peterson G W.Genetic diversity analysis of yellow mustard(Sinapis alba L.) germplasm based on genotyping by sequencing[J].Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution,2014,61(3):579-594. |
| 5 | Gürcan K,Teber S,Ercisli S,et al.Genotyping by sequencing(GBS) in apricots and genetic diversity assessment with GBS-derived single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)[J].Biochemical Genetics,2016,54(6):854-885. |
| 6 | Pootakham W,Ruang-Areerate P,Jomchai N,et al.Construction of a high-density integrated genetic linkage map of rubber tree(Hevea brasiliensis) using genotyping-by-sequencing(GBS)[J].Frontiers in Plant Science,2015,6:367. |
| 7 | Qi P,Gimode D,Saha D,et al.UGbS-Flex,a novel bioinformatics pipeline for imputation-free SNP discovery in polyploids without a reference genome:finger millet as a case study[J].BMC Plant Biology,2018,18(1):117. |
| 8 | Andrews S.FastQC:a quality control tool for high throughput sequence data[Z].Babraham Bioinformatics,Babraham Institute,Cambridge,United Kingdom,2010. |
| 9 | Catchen J,Hohenlohe P A,Bassham S,et al.Stacks:an analysis tool set for population genomics[J].Molecular Ecology,2013,22(11):3124-3140. |
| 10 | Gordon A,Hannon G J.FASTX-toolkit[EB/OL].. |
| 11 | Langdon W B.Performance of genetic programming optimised Bowtie2 on genome comparison and analytic testing(GCAT) benchmarks[J].BioData Mining,2015,8(1):1. |
| 12 | Danecek P,Auton A,Abecasis G,et al.The variant call format and VCFtools[J].Bioinformatics,2011,27(15):2156-2158. |
| 13 | Ruan J,Li H,Chen Z Z,et al.TreeFam:2008 update[J].Nucleic Acids Research,2008,36(S1):D735-D740. |
| 14 | Purcell S,Neale B,Todd-Brown K,et al.PLINK:a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses[J].The American Journal of Human Genetics,2007,81(3):559-575. |
| 15 | Li M W,Chen S F,Shi S,et al.High genetic diversity and weak population structure of Rhododendron jinggangshanicum,a threatened endemic species in Mount Jinggangshan of China[J].Biochemical Systematics and Ecology,2015,58:178-186. |
| 16 | Wang X L,Zhao W,Li L,et al.Clonal plasticity and diversity facilitates the adaptation of Rhododendron aureum Georgi to alpine environment[J].PLoS One,2018,13(5):e0197089. |
| 17 | Wang S Z,Jin Z Q,Luo Y Y,et al.Genetic diversity and population structure of Rhododendron simsii(Ericaceae) as revealed by microsatellite markers[J].Nordic Journal of Botany,2019,37(4),doi:10.1111/njb.02251. |
| 18 | Wu F Q,Shen S K,Zhang X J,et al.Genetic diversity and population structure of an extremely endangered species:the world's largest Rhododendron[J].AoB Plants,2015,7:plu082. |
| 19 | Xu J J,Zhang L Y,Zhao B,et al.Assessment of genetic diversity among six populations of Rhododendron triflorum in Tibet using ISSR and AFLP markers[J].South African Journal of Botany,2017,108:175-183. |
| 20 | 李太强.极小种群野生植物长梗杜鹃的保护生物学研究[D].北京:中国林业科学研究院,2018. |
| Li T Q.Conservation biology of the plant species with extremely small population Rhododendron longipedicellatum[D].Beijing:Chinese Academy of Forestry,2018. | |
| 21 | Wu F Q,Shen S K,Zhang X,et al.Inferences of genetic structure and demographic history of Rhododendron protistum var.giganteum——The world’s largest Rhododendron using microsatellite markers[J].Flora,2017,233:1-6. |
| 22 | 陈珍慧.珍稀特有植物华顶杜鹃的种群特征和保护遗传学研究[D].杭州:杭州师范大学,2016. |
| Chen Z H.Studies on population characteristics and protective genetics of Rhododendron huadingense,a rare species endemic to China[D].Hangzhou:Hangzhou Normal University,2016. | |
| 23 | Bruni I,De Mattia F,Labra M,et al.Genetic variability of relict Rhododendron ferrugineum L.populations in the Northern Apennines with some inferences for a conservation strategy[J].Plant Biosystems-An International Journal Dealing with all Aspects of Plant Biology,2012,146(1):24-32. |
| 24 | Ma Y P,Wu Z K,Dong K,et al.Pollination biology of Rhododendron cyanocarpum(Ericaceae):an alpine species endemic to NW Yunnan,China[J].Journal of Systematics and Evolution,2015,53(1):63-71. |
| 25 | Brown A H D,Clegg M T,Kahler A L,et al.Plant population genetics,breeding,and genetic resources[M].Sunderland:Sinauer Associates,1990:43-63. |
| 26 | Hamrick J L,Godt M J W,Sherman Broyles S L.Gene flow among plant populations:evidence from genetic markers[M]//Hoch P C,Stephenson A G.Experimental and molecular approaches to plant biosystematics.St.Louis:Missouri Botanical Garden Press,1995:215-232. |
| 27 | Ng S C,Corlett R T.Genetic variation and structure in six Rhododendron species(Ericaceae) with contrasting local distribution patterns in Hong Kong,China[J].Molecular Ecology,2000,9(7):959-969. |
| 28 | Angeloni F,Ouborg N J,Leimu R.Meta-analysis on the association of population size and life history with inbreeding depression in plants[J].Biological Conservation,2011,144(1):35-43. |
| 29 | Shen S K,Wang Y H,Wang B Y,et al.Distribution,stand characteristics and habitat of a critically endangered plant Euryodendron excelsum H.T.Chang(Theaceae):implications for conservation[J].Plant Species Biology,2009,24(2):133-138. |
| 30 | Findlay C S T,Bourdages J.Response time of wetland biodiversity to road construction on adjacent lands[J].Conservation Biology,2000,14(1):86-94. |
| 31 | Essl F,Dullinger S,Rabitsch W,et al.Delayed biodiversity change:no time to waste[J].Trends in Ecology & Evolution,2015,30(7):375-378. |
| 32 | Zhang Y H,Ni J,Tang F P,et al.The effects of different human disturbance regimes on root fungal diversity of Rhododendron ovatum in subtropical forests of China[J].Canadian Journal of Forest Research,2017,47(5):659-666. |
| 33 | 王书珍,张霖,杨雯,等.大别山不同龄级映山红种群遗传多样性的SSR分析[J].林业科学研究,2018,31(5):125-130. |
| Wang S Z,Zhang L,Yang W,et al.Genetic diversity of Rhododendron simsii populations on Dabieshan at different life stages based on SSR markers[J].Forest Research,2018,31(5):125-130. | |
| 34 | Setoguchi H,Mitsui Y,Ikeda H,et al.Genetic structure of the critically endangered plant Tricyrtis ishiiana(Convallariaceae) in relict populations of Japan[J].Conservation Genetics,2011,12(2):491-501. |
| [1] | Siru TANG, Tiejuan WANG, Fang XIU, Mengyao LIU, Hui ZHANG. Genetic Structure and Phylogeography Analysis of Artemisia intramongolica Based on Single Copy Nuclear Genes [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(6): 956-963. |
| [2] | Ermei CHANG, Jianfeng LIU, Yuening HUANG, Hongli LI, Bingyan SHAN, Zeping JIANG, Xiulian ZHAO. Comparison of Genetic Diversity Between Wild and ex-situ Conservation Populations of Cupressus chengiana [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(5): 772-779. |
| [3] | Yang ZHANG, Zilan MA, Shanshan XU, Xu SU, Meiying LI. Phylogeography of Xanthopappus subacaulis(Asteraceae), an Endemic Species from the Northeastern of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(4): 565-573. |
| [4] | Hongbin ZHANG, Dong LÜ, Ming ZHAO, Hu ZHAO, Xingpeng ZHAO, Wei LI. Genetic Structure Analysis of Picea crassifolia Based on Genome-wide SNP Molecular Markers [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(3): 373-382. |
| [5] | Yibo Yin, Jixiang Li, Yingjie Guo, Ziting Lu, Ying Xiao, Hualing Liu, Yaguang Zhan, Fansuo Zeng. Variation of Lignin Content and Association Analysis of FmPAL Nucleotide Polymorphism in Progenies of Interspecific Hybrids of Fraxinus [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(2): 191-199. |
| [6] | Jingya Yu, Mingze Xia, Hao Xu, Faqi Zhang. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of Three Artemisia Species in Qinghai Tibet Plateau [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(2): 200-210. |
| [7] | Yi-Liang LI, Fen-Cheng ZHAO, Yang LIU, Sui-Ying ZHONG, Chang-Ming LIN, Zhi-Qiang TAN, Fu-Ming LI, Fang-Yan LIAO, Hui-Shan WU, Wen-Bin GUO, Zhe WANG. Relationship Between Parental Genetic Distance and Heterosis of Growth Traitsin Pinus elliottii × P.caribaea var. Hondurensis Based on SNP marker [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(5): 738-743. |
| [8] | ZHANG Zhong-Hua, SONG Xiao-Qian, TANG Zhong-Hua, LIANG Zheng-Wei. An Assessment of Phylogenetic Diversity and Dissimilarity of Halophytes Across Different Provincial Region,China [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(3): 330-338. |
| [9] | ZHANG Shan-Shan, KANG Hong-Mei, YANG Wen-Zhong. Population Genetic Analysis of Nyssa yunnanensis by Reduced-representation Sequencing Technique [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2019, 39(6): 899-907. |
| [10] | YANG Yun, CHEN Meng-Jiao, DU Qing-Xin, ZHU Jing-Le, DU Hong-Yan, YANG Shao-Bin. SNP Sites Developed by Whole Genome Resequencing Analysis in Eucommia ulmoides ‘Hongye’ [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2019, 39(6): 947-954. |
| [11] | DUAN Yi-Zhong, WANG Jian-Wu, DU Zhong-Yu, KANG Fu-Ren. SNP Sites Developed by Specific Length Amplification Fragment Sequencing(SLAF-seq) and Genetic Analysis in Ammopitanthus mongolicus [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2018, 38(1): 141-147. |
| [12] | LI Tai-Qiang, LIU Xiong-Fang, WAN You-Ming, LI Zheng-Hong, QI Guo-Hai, LI Yu-Ying, LIU Xiu-Xian, HE Rui, MA Yan, MA Hong. Transcriptome Analysis for Rhododendron longipedicellatum (Plant Species with Extremely Small Populations) Based on High Throughput Sequencing [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2017, 37(6): 825-834. |
| [13] | HAO Jiu-Cheng, JIA Xin, MU Xiao-Hong, ZHANG Heng-Qing. Genetic Diversity between Island and Mainland Natural Populations of Polygonatum odoratum in Dalian Area by ISSR [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2017, 37(5): 709-714. |
| [14] | TIAN Zun-Zhe, GAO Qing-Bo, CHEN Shi-Long, ZHANG Fa-Qi. Characteristics of SSR and SNP in Gentiana veitchiorum in Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau,by High-throughput Sequencing [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2016, 36(5): 747-752. |
| [15] | ZHANG Tian;WANG Ma-Li;ZHAO Peng*. Sequence Analysis of Nuclear DNA JRD5680 for Determining Genetic Diversity and Genetic Structure Analysis of Common Walnut(Juglans regia L.) [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2016, 36(2): 232-241. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||