Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (4): 631-640.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2023.04.016
• Phytochemistry • Previous Articles
Hanlin ZHU1,2, Heng ZHAO1,2, Bowen ZHAI1,2, Maoyu ZHANG1,2, Yujie FU3( )
)
Received:2023-04-10
Online:2023-07-20
Published:2023-07-03
Contact:
Yujie FU
E-mail:yujie_fu@163.com
About author:ZHU Hanlin(1999—),male,master,mainly engaged in natural active biological macromolecule.
Supported by:CLC Number:
Hanlin ZHU, Heng ZHAO, Bowen ZHAI, Maoyu ZHANG, Yujie FU. Ultrasonic-Assisted Enzymatic Extraction of Polysaccharides from Schisandra chinensis and the Effects on Anti-Oxidative Stress in Cells[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(4): 631-640.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://bbr.nefu.edu.cn/EN/10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2023.04.016
Table 2
BBD experiment design and results
序号 No. | 因素A Factor A /(U·g-1) | 因素B Factor B /W | 因素C Factor C /min | 因素D Factor D | 多糖得率 Yield of SCPs /% | 序号 No. | 因素A Factor A /(U·g-1) | 因素B Factor B /W | 因素C Factor C /min | 因素D Factor D | 多糖得率 Yield of SCPs /% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 200 | 455 | 60 | 1 g∶40 mL | 18.77 | 16 | 1 200 | 455 | 60 | 1 g∶20 mL | 20.43 |
| 2 | 1 200 | 390 | 40 | 1 g∶40 mL | 13.97 | 17 | 1 200 | 390 | 60 | 1 g∶30 mL | 14.23 |
| 3 | 1 200 | 455 | 40 | 1 g∶30 mL | 20.57 | 18 | 1 800 | 455 | 40 | 1 g∶40 mL | 18.67 |
| 4 | 600 | 520 | 40 | 1 g∶30 mL | 13.87 | 19 | 1 200 | 455 | 40 | 1 g∶30 mL | 20.95 |
| 5 | 1 800 | 455 | 40 | 1 g∶20 mL | 17.21 | 20 | 1 200 | 455 | 20 | 1 g∶20 mL | 13.25 |
| 6 | 600 | 455 | 60 | 1 g∶30 mL | 13.47 | 21 | 1 200 | 455 | 20 | 1 g∶40 mL | 13.67 |
| 7 | 1 200 | 520 | 60 | 1 g∶30 mL | 19.71 | 22 | 600 | 455 | 40 | 1 g∶20 mL | 13.76 |
| 8 | 1 200 | 455 | 40 | 1 g∶30 mL | 21.73 | 23 | 1 800 | 455 | 20 | 1 g∶30 mL | 15.37 |
| 9 | 1 800 | 520 | 40 | 1 g∶30 mL | 19.64 | 24 | 1 800 | 455 | 60 | 1 g∶30 mL | 19.55 |
| 10 | 600 | 390 | 40 | 1 g∶30 mL | 9.53 | 25 | 1 800 | 390 | 40 | 1 g∶30 mL | 15.42 |
| 11 | 1 200 | 390 | 40 | 1 g∶20 mL | 15.43 | 26 | 1 200 | 520 | 20 | 1 g∶30 mL | 14.69 |
| 12 | 1 200 | 520 | 40 | 1 g∶20 mL | 19.59 | 27 | 1 200 | 455 | 40 | 1 g∶30 mL | 21.09 |
| 13 | 600 | 455 | 40 | 1 g∶40 mL | 14.39 | 28 | 600 | 455 | 20 | 1 g∶30 mL | 9.26 |
| 14 | 1 200 | 520 | 40 | 1 g∶40 mL | 19.24 | 29 | 1 200 | 390 | 20 | 1 g∶30 mL | 10.57 |
| 15 | 1 200 | 455 | 40 | 1 g∶30 mL | 22.09 |
Table 3
Analysis of variance and significance test
来源 Source | 平方和 Sum of Squares | 自由度 df | 均方 Mean square | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 模型Model | 379.850 0 | 14 | 27.130 0 | 39.420 0 | <0.000 1** |
| A | 83.110 0 | 1 | 83.110 0 | 120.740 0 | <0.000 1** |
| B | 63.430 0 | 1 | 63.430 0 | 92.150 0 | <0.000 1** |
| C | 71.790 0 | 1 | 71.790 0 | 104.290 0 | <0.000 1** |
| D | 0.076 8 | 1 | 0.076 8 | 0.111 6 | 0.743 3 |
| A×B | 0.003 6 | 1 | 0.003 6 | 0.005 2 | 0.943 4 |
| A×C | 0.000 2 | 1 | 0.000 2 | 0.000 3 | 0.985 8 |
| A×D | 0.172 2 | 1 | 0.172 2 | 0.250 2 | 0.624 7 |
| B×C | 0.462 4 | 1 | 0.462 4 | 0.671 8 | 0.426 2 |
| B×D | 0.308 0 | 1 | 0.308 0 | 0.447 5 | 0.514 4 |
| C×D | 1.080 0 | 1 | 1.080 0 | 1.570 0 | 0.230 5 |
| A2 | 88.600 0 | 1 | 88.600 0 | 128.720 0 | <0.000 1** |
| B2 | 57.490 0 | 1 | 57.490 0 | 83.520 0 | <0.000 1** |
| C2 | 72.450 0 | 1 | 72.450 0 | 105.260 0 | <0.000 1** |
| D2 | 13.000 0 | 1 | 13.000 0 | 18.890 0 | 0.000 7** |
| 残差Residual | 9.640 0 | 14 | 0.688 3 | — | — |
| 失拟项Lack of Fit | 8.130 0 | 10 | 0.812 9 | 2.160 0 | 0.238 7 |
| 纯误差Pure Error | 1.510 0 | 4 | 0.376 9 | — | — |
| 总误差Cor Total | 389.490 0 | 28 | — | — | — |
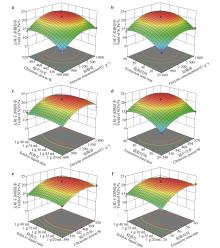
Fig.2
The response surfaces of ultrasonic-assisted enzymatic hydrolysis extraction of SCPsa.Ultrasonic power and enzyme concentration;b.Extraction time and enzyme concentration;c.Solid to liquid ratio and enzyme concentration;d.Extraction time and ultrasonic power;e.Solid to liquid ratio and ultrasonic power;f.Solid to liquid ratio and extraction time

| 1 | 孙金花,张天杰.药用植物五味子繁育栽培及盆栽造景[J].现代园艺,2020,43(1): 73-74. |
| SUN J H, ZHANG T J.Propagation and cultivation of medicinal plant Schisandra chinensis and pot landscape[J].Modern Horticulture,2020,43(1):73-74. | |
| 2 | 周鑫.五味子的组织培养[J].中国林副特产,2001(4):6-7. |
| ZHOU X.Tissue culture of Schisandra chinensis [J].Forest By-Product and Speciality in China,2001(4):6-7. | |
| 3 | 刘博,傅俊范,周如军,等.五味子叶枯病病原菌鉴定[J].植物病理学报,2008,38(4):425-428. |
| LIU B, FU J F, ZHOU R J,et al.Identification of pathogen of leaf blight of Schisandra chinensis [J].Acta Phytopathologica Sinica,2008,38(4):425-428. | |
| 4 | 薛彩云,严雪瑞,林天行,等.五味子茎基腐病发生初报[J].植物保护,2007,33(4):96-99. |
| XUE C Y, YAN X R, LIN T X,et al.A preliminary report on occurrence of Schisandra berry stalk rot[J].Plant Protection,2007,33(4):96-99. | |
| 5 | 白文宇,王厚恩,王冰瑶,等.五味子化学成分及其药理作用研究进展[J].中成药,2019,41(9):2177-2183. |
| BAI W Y, WANG H E, WANG B Y,et al.Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological action of Schisandra chinensis [J].Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine,2019,41(9):2177-2183. | |
| 6 | AHN T S, KIM D G, HONG N R,et al.Effects of Schisandra chinensis extract on gastrointestinal motility in mice[J].Journal of ethnopharmacology,2015,169:163-169. |
| 7 | YAN T X, XU M J, WAN S T,et al. Schisandra chinensis produces the antidepressant-like effects in repeated corticosterone-induced mice via the BDNF/TrkB/CREB signaling pathway[J].Psychiatry Research,2016,243:135-142. |
| 8 | SU L L, MAO C Q, WANG X C,et al.The anti-colitis effect of Schisandra chinensis polysaccharide is associated with the regulation of the composition and metabolism of gut microbiota[J].Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology,2020,10:519479. |
| 9 | XU M J, YAN T X, FAN K Y,et al.Polysaccharide of Schisandra chinensis Fructus ameliorates cognitive decline in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease[J].Journal of ethnopharmacology,2019,237:354-365. |
| 10 | ZHAO T, MAO G H, MAO R W,et al.Antitumor and immunomodulatory activity of a water-soluble low molecular weight polysaccharide from Schisandra chinensis(Turcz.) Baill[J].Food and Chemical Toxicology,2013,55:609-616. |
| 11 | LIU Y, HUANG G L.Extraction and derivatisation of active polysaccharides[J].Journal of Enzyme Inhibition and Medicinal Chemistry,2019,34(1):1690-1696. |
| 12 | CHEN R H, CHANG J R, SHYUR J S.Effects of ultrasonic conditions and storage in acidic solutions on changes in molecular weight and polydispersity of treated chitosan[J].Carbohydrate Research,1997,299(4):287-294. |
| 13 | LI Z J, HE X, LIU F,et al.A review of polysaccharides from Schisandra chinensis and Schisandra sphenanthera:properties,functions and applications[J].Carbohydrate Polymers,2018,184:178-190. |
| 14 | ANDREAUS J, AZEVEDO H, CAVACO-PAULO A.Effects of temperature on the cellulose binding ability of cellulase enzymes[J].Journal of Molecular Catalysis B:Enzymatic,1999,7(1/2/3/4):233-239. |
| 15 | 朱亚伟,王立涛,安娟艳,等.响应面优化酶解—微波辅助提取桑叶多糖的工艺研究[J].植物研究,2020,40(4):635-640. |
| ZHU Y W, WANG L T, AN J Y,et al.Response surface optimized enzymatic hydrolysis-microwave assisted extraction process of mulberry leaf polysaccharide[J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2020,40(4):635-640. | |
| 16 | 孙彤彤,王忠娟,张秀娟,等.响应面法优化提取虎耳草总酚及其抑制五步蛇毒PLA2酶活性的相关性[J].植物研究,2022,42(2):259-267. |
| SUN T T, WANG Z J, ZHANG X J,et al.Optimization on extraction of total phenols by response surface from Saxifraga stolonifera and its correlation in inhibiting the activity of PLA2 in Deinagkistrodon acutus Venom[J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2022,42(2):259-267. | |
| 17 | 姜守刚,谭笑,吴磊,等.向日葵茎芯多糖的提取工艺优化及其体外抗肿瘤活性研究[J].植物研究,2018,38(5):795-800. |
| JIANG S G, TAN X, WU L,et al.Study of the extraction technology and antitumor activity in vitro of water-soluble polysaccharides from the wick of Helianthus annuus L.[J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2018,38(5):795-800. | |
| 18 | 张耿崚,陈细妹,韩业钜,等.表面活性剂辅助离子液体预处理稻秆的酶解动力学与结构变化分析[J].环境科学学报,2017,37(2):686-693. |
| ZHANG G L, CHEN X M, HAN Y J,et al.Enzymatic kinetics and structure change analysis of rice straw by surfactant-assisted ionic liquid pretreatment[J].Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2017,37(2):686-693. | |
| 19 | OLAWUYI I F, KIM S R, HAHN D,et al.Influences of combined enzyme-ultrasonic extraction on the physicochemical characteristics and properties of okra polysaccharides[J].Food Hydrocolloids,2020,100:105396. |
| 20 | 张琪琳.香菇多糖的结构鉴定及抗肿瘤作用机制研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2015. |
| ZHANG Q L.Structural elucidation and antitumor mechanisms of polysaccharides isolated from Lentinus edodes [D].Wuhan:Huazhong University of Science and Technology,2015. | |
| 21 | 张莹,王洪源,周宇航,等.超声波辅助提取和热水浸提五味子多糖的比较研究[J].特产研究,2015,37(3):52-57. |
| ZHANG Y, WANG H Y, ZHOU Y H,et al.Study on the extraction of Schisandra chinensis Baill Polysaccharides by ultrasonic wave and hot water method[J].Special Wild Economic Animal and Plant Research,2015,37(3):52-57. | |
| 22 | 宋海燕,程振玉,马朝红.响应面优化酶法提取五味子多糖的工艺及抗氧化活性研究[J].食品工业,2016,37(3):159-163. |
| SONG H Y, CHENG Z Y, MA C H.Enzyme-assisted extraction technology of polysaccharides from Schisandra chinensis Baill by RSM and its antioxidation activity[J].The Food Industry,2016,37(3):159-163. | |
| 23 | 吴金松,耿广威,任聪,等.超声辅助酶法提取山药皮水溶性多糖的工艺优化[J].食品研究与开发,2022,43(8):90-97. |
| WU J S,GENG G W,REN C,et al,Optimization of Enzymolysis-Ultrasonic assisted extraction of water-soluble polysaccharides from peel of Rhizoma dioscoreae [J].Food Research and Development,2022,43(8):90-97. |
| [1] | Yu LI, Xiao YANG, Xiao YE, Jie-Qiong DENG, Wei-Nian HUANG, Sha DAI. Optimization on the Main Active Components Extraction Using Ultrasonic-assisted Method from Safflower [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(5): 824-835. |
| [2] | Yuan GAO, Wen-Xin XING, Hui-Mei WANG. Macroporous Resin Purifying Polyphenols from Empetrum nigrum Aerial Parts [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(4): 626-632. |
| [3] | Yong-Mei MIAO, Yuan Tong, Da Fang, Yu-Hao Wang. Effects of Rare Earth Element Lanthanum on Adventitious Buds Induction, Plantlets Growth and Synthesis of Secondary Metabolites of Dendrobium officinale [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(6): 839-845. |
| [4] | ZHANG Xiao-Nan, ZHU Hong-Wei, ZHAO Shan-Bo, BAI Chen, SHI Ya-Nan, XU Hao-Peng, YIN Lian, HU Shu-Min, YIN Hua. Optimization of Ultrasound-assisted Extraction of Dihydromyricetin from Seeds of Hovenia dulcis Thunb. Using Response Surface Methodology [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(5): 775-781. |
| [5] | ZHU Ya-Wei, WANG Li-Tao, AN Juan-Yan, Lü Mu-Jie, SUN Jian-Hang, GUO Na, FU Yu-Jie. Response Surface Optimized Enzymatic Hydrolysis-microwave Assisted Extraction Process of Mulberry Leaf Polysaccharide [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(4): 635-640. |
| [6] | JIANG Shou-Gang, TAN Xiao, WU Lei, WU Bi, YUAN Ying-Jie, ZU Yuan-Gang. Study of the Extraction Technology and Antitumor Activity in vitro of Water-Soluble Polysaccharides from the Wick of Helianthus annuus L. [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2018, 38(5): 795-800. |
| [7] | LI Zhan-Jun, LIU Yun-Wei, ZHANG Zhong-Lin, ZHANG Zhi-Huan, MA Ke, YANG Feng-Jian. Decolorization Process of Polysaccharide from Tara Seed [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2018, 38(3): 475-480. |
| [8] | YUAN De-Cheng, ZHAO Han-Mei, YANG Feng-Jian. Study on Orthogonal Optimization and Antioxidation of Polysaccharide from Tara Seeds [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2018, 38(1): 155-160. |
| [9] | ZHAO Han-Mei, YUAN De-Cheng, YANG Feng-Jian. Optimization of Ultrasonic Extraction of Polysaccharides from Tara Seed and Its Antioxidant Activity [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2017, 37(4): 635-640. |
| [10] | LIU Yan, CHEN Xiao-Yin, YANG Li-Li, XIE Rui, HE Nan, ZHANG Ji. Extraction Process Optimization of Inulin from Helianthus tuberosus L. by Response Surface Methodology [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2016, 36(4): 627-633. |
| [11] | CHEN Qing1;JIANG Lei-Yu1;WANG Yan1;ZHU Fang-Li1;TANG Hao-Ru1*;WANG Xiao-Rong1,2. Optimization of Prokaryotic Expression Factors for Blackberry UGT78H2 Using Responsive Surface Methodology and Protein Purification [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2015, 35(5): 724-729. |
| [12] | WANG Yi-Feng;HOU Hong-Hong;JIN Jie;ZHAO Bo;CAO Jia-Hao;LI Xiao-Jiao. Microwave-assisted Polysaccharide Extraction of Aralia chinensis L. Root and Composition Determination of Monosaccharide [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2015, 35(5): 779-785. |
| [13] | WANG Hong-Zheng1,2;LI Yuan-Yuan1,2;LIU Wei1,2;WANG Hua1,2,3;ZU Yuan-Gang1,2*;ZHAO Xiu-Hua1,2. Optimizing Polysaccharide Extraction from Peony Tree Pod Using Response Surface Method and Assessing Its Antioxidative Activity [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2015, 35(1): 127-132. |
| [14] | LU Qi;GAO Yue;XIANG Feng-Ying;ZU Yuan-Gang*;ZHANG Ying. Polysaccharide Extraction from Peony Seed Pods by Water Bath [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2015, 35(1): 154-157. |
| [15] | GAO Yin-Xiang1,2;ZU Yuan-Gang1;YANG Feng-Jian1;YU Xue-Ying1;YAO Li-Ping1*. Distribution and Accumulating Regularity of Secondary Metabolites in Helianthus annuus L. [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2014, 34(6): 782-786. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||