Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (5): 720-728.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2023.05.009
• Physiology and Ecology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jiaxing CHEN, Shu WANG( ), Linli CHEN, Xiali HOU, Qingzhu YANG, Renya YIN
), Linli CHEN, Xiali HOU, Qingzhu YANG, Renya YIN
Received:2023-06-12
Online:2023-09-20
Published:2023-09-05
Contact:
Shu WANG
E-mail:lnbx625@163.com
About author:CHEN Jiaxing(1997—),male,major in plant ecology.
Supported by:CLC Number:
Jiaxing CHEN, Shu WANG, Linli CHEN, Xiali HOU, Qingzhu YANG, Renya YIN. Effects of Drought Conditions on Interspecific Interactions and Growth of Bidens pilosa and Buddleja lindleyana[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(5): 720-728.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://bbr.nefu.edu.cn/EN/10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2023.05.009
Table 1
Interspecific interaction between Bidens pilosa and Buddleja lindleyana under different water conditions
处理时间 Treatment duration/d | 植物特征 Plant traits | 水分条件 Water condition | 鬼针草Bidens pilosa | 醉鱼草Buddleja lindleyana | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
相对邻株效应指数 Relative neighbor effect | 种间相互作用 Interspecific interaction | 相对邻株效应指数 Relative neighbor effect | 种间相互作用 Interspecific interaction | |||
| 40 | 总生物量Total biomass | 对照Moist | 0.211 | - | 0.076 | - |
| 茎生物量Stem biomass | 对照Moist | 0.161 | - | -0.078 | + | |
| 叶生物量Leaf biomass | 对照Moist | 0.202 | - | 0.114 | - | |
| 根生物量Root biomass | 对照Moist | 0.256 | - | 0.112 | - | |
| 90 | 总生物量Total biomass | 对照Moist | -0.057 | + | -0.331 | + |
| 干旱Drought | -0.291 | + | 0.067 | - | ||
| 茎生物量Stem biomass | 对照Moist | -0.009 | + | -0.258 | + | |
| 干旱Drought | -0.278 | + | -0.584 | + | ||
| 叶生物量Leaf biomass | 对照Moist | -0.092 | + | 0.099 | - | |
| 干旱Drought | -0.173 | + | -0.395 | + | ||
| 根生物量Root biomass | 对照Moist | -0.089 | + | -0.424 | + | |
| 干旱Drought | -0.408 | + | 0.195 | - | ||
Table 2
Analysis of three-factor ANOVAs on species( S ), water treatment( W ), interspecific interaction( I ) and interaction on the relative growth rate of plant characteristics.
变异来源 Source of variance | 自由度 df | 相对生长率Relative growth rate | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
总生物量 Total biomass | 茎生物量 Stem biomass | 叶生物量 Leaf biomass | 根生物量 Root biomass | 根冠比 Root shoot ratio | 叶面积 Leaf area | 比叶面积 Specific leaf area | ||
| 物种(S) | 1 | 35.369** | 141.219** | 134.701** | 5.615* | 349.062** | 67.806** | 41.441** |
| 水分处理(W) | 1 | 15.323** | 2.966 | 26.557** | 10.079* | 0.053 | 65.391** | 5.970* |
| 种间作用(I) | 1 | 16.353** | 5.932* | 11.972* | 12.945* | 0.735 | 17.244** | 72.765** |
| S×W | 1 | 1.817 | 1.856 | 15.130 | 0.027 | 1.210 | 13.731** | 1.510 |
| S×I | 1 | 3.725 | 3.046 | 5.342* | 0.915 | 2.359 | 0.224 | 12.976* |
| W×I | 1 | 0.555 | 0.538 | 0.001 | 2.635 | 19.429** | 2.091 | 1.102 |
| S×W×I | 1 | 1.631 | 0.231 | 1.011 | 4.097* | 23.789** | 8.993* | 6.911* |
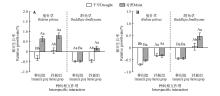
Fig.1
Effects of water treatment and interspecific interaction on the relative growth rate of leaf area(A),specific leaf area(B)Different lowercase letters indicated different water treatments of the same species(P<0.05);and different big letters indicated different interspecific treatments of the same water(P<0.05);Mean±SE;The same as below
Table 3
Effects of water treatment and interspecific interaction on root growth
物种 Species | 种间作用 Species interaction | 处理 Treatment | 相对生长率 Relative growth rate/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
根长 Root length | 根平均直径 Root average diameter | 根表面积 Root surface area | 根尖数量 Root tip number | |||
鬼针草 Bidens pilosa | 种间组 Interspecific group | 干旱Drought | 2.51±1.01Aa | 0.39±0.18Aa | 6.94±4.45Aa | 3.66±1.36Aa |
| 对照Moist | 3.38±1.32Aa | 0.40±0.15Aa | 8.75±4.17Aa | 4.71±1.66Aa | ||
挡板组 Barrier group | 干旱Drought | 0.56±0.52Ba | 0.21±0.21Aa | 1.62±1.52Bb | 0.75±0.52Ba | |
| 对照Moist | 0.87±0.47Ba | 0.34±0.11Aa | 3.14±1.28Ba | 1.40±0.88Ba | ||
醉鱼草 Buddleja lindleyana | 种间组 Interspecific group | 干旱Drought | 3.56±2.02Aa | 0.28±0.13Aa | 7.39±4.45Aa | 4.76±2.86Aa |
| 对照Moist | 3.71±1.44Aa | 0.28±0.18Aa | 7.18±3.83Aa | 5.73±2.85Aa | ||
挡板组 Barrier group | 干旱Drought | 1.57±1.00Ba | -0.10±0.10Ba | 3.45±2.24Ba | 2.22±1.34Ba | |
| 对照Moist | 1.14±0.84Ba | -0.13±0.10Ba | 1.90±1.77Ba | 3.28±1.77Ba | ||
| 1 | ASCHEHOUG E T, BROOKER R, ATWATER D Z,et al. The mechanisms and consequences of interspecific competition among plants[J].Annual Review of Ecology,Evolution,and Systematics,2016,47(1):263-281. |
| 2 | 王平,王天慧,周道玮,等.植物地上竞争与地下竞争研究进展[J].生态学报,2007,27(8):3489-3499. |
| WANG P, WANG T H, ZHOU D W,et al.A literature review on the above and below ground competition[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2007,27(8):3489-3499. | |
| 3 | CALLAWAY R M, PENNINGS S C, RICHARDS C L.Phenotypic plasticity and interactions among plants[J].Ecology,2003,84(5):1115-1128. |
| 4 | MAESTRE F T, CORTINA J.Do positive interactions increase with abiotic stress?A test from a semi-arid steppe[J].Proceedings of the Royal Society B:Biological Sciences,2004,271():S331-S333. |
| 5 | BROOKER R W, MAESTRE F T, CALLAWAY R M,et al.Facilitation in plant communities:the past,the present,and the future[J].Journal of Ecology,2008,96(1):18-34. |
| 6 | ASCHEHOUG E.Indirect interactions and plant community structure[D].Missoula:University of Montana,2011:35-37. |
| 7 | FOXX A J, FORT F.Root and shoot competition lead to contrasting competitive outcomes under water stress:A systematic review and meta-analysis[J].PLoS One,2019,14(12):e0220674. |
| 8 | 吕渡,杨亚辉,赵文慧,等.黄土高原沟壑区不同植被对土壤水分分布特征影响[J].水土保持研究,2018,25(4):60-64. |
| LÜ D, YANG Y H, ZHAO W H,et al.Impacts of vegetation types on soil water distributions in Loess Hilly Region[J].Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2018,25(4):60-64. | |
| 9 | 靳小莲,赵巍,李梦迪,等.黄土高原退耕还草土壤水分对植物地上部化学计量特征的影响[J].水土保持研究,2022,29(2):57-63. |
| JIN X L, ZHAO W, LI M D,et al.Effects of soil moisture on the stoichiometric characteristics of aboveground plants following conversion of farmland to grassland on the Loess plateau[J].Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2022,29(2):57-63. | |
| 10 | 陈禹含,罗亦夫,孙鑫晟,等.根部水淹和土壤养分提升对三峡库区消落带水蓼生长和繁殖特性的影响[J].植物生态学报,2020,44(11):1184-1194. |
| CHEN Y H, LUO Y F, SUN X S,et al.Effects of waterlogging and increased soil nutrients on growth and reproduction of Polygonum hydropiper in the hydro-fluctuation belt of the Three gorges Reservoir Region[J].Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology,2020,44(11):1184-1194. | |
| 11 | WANG S, CALLAWAY R M.Plasticity in response to plant-plant interactions and water availability[J].Ecology,2021,102(6):e03361. |
| 12 | KIÆR L P, WEISBACH A N, WEINER J.Root and shoot competition:a meta‐analysis[J].Journal of Ecology,2013,101(5):1298-1312. |
| 13 | 李博,陈家宽.生物入侵生态学:成就与挑战[J].世界科技研究与发展,2002,24(2):26-36. |
| LI B, CHEN J K.Ecology of biological invasions:achievements and challenges[J].World Sci-Tech R&D,2002,24(2):26-36. | |
| 14 | 王瑞龙,韩萌,梁笑婷,等.三叶鬼针草生物量分配与化感作用对大气温度升高的响应[J].生态环境学报,2011,20(6):1026-1030. |
| WANG R L, HAN M, LIANG X T,et al.Responses of biomass allocation patterns and allelopathic potential of Bidens pilosa L. to elevated temperature[J].Ecology and Environmental Sciences,2011,20(6):1026-1030. | |
| 15 | 洪岚,沈浩,杨期和,等.外来入侵植物三叶鬼针草种子萌发与贮藏特性研究[J].武汉植物学研究,2004,22(5):433-437. |
| HONG L, SHEN H, YANG Q H,et al.Studies on seed germination and storage of the invasive alien species Bidens pilosa L.[J].Journal of Wuhan Botanical Research,2004,22(5):433-437. | |
| 16 | 杜凤移,张苗苗,马丹炜,等.三叶鬼针草化感作用的初步研究[J].中国植保导刊,2007,27(9):8-11. |
| DU F Y, ZHANG M M, MA D W,et al.Preliminary study on the allelopathic effects of Bidens pilosa [J].China Plant Protection,2007,27(9):8-11. | |
| 17 | REJMANEK M, RICHARDSON D M.What attributes make some plant species more invasive?[J].Ecology,1996,77(6):1655-1661. |
| 18 | 王俊峰,冯玉龙.光强对两种入侵植物生物量分配、叶片形态和相对生长速率的影响[J].植物生态学报,2004,28(6):781-786. |
| WANG J F, FENG Y L.The effect of light intensity on biomass allocation,leaf morphology and relative growth rate of two invasive plants[J].Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology,2004,28(6):781-786. | |
| 19 | 陈金艺,张静,李素慧,等.模拟喀斯特异质性小生境下三叶鬼针草地上地下协同生长对策[J].植物科学学报,2020,38(6):762-772. |
| CHEN J Y, ZHANG J, LI S H,et al.Synergistic aboveground-belowground growth of Bidens pilosa L.in heterogeneous karst habitats[J].Plant Science Journal,2020,38(6):762-772. | |
| 20 | 柳牧青,杨小凤,石钰铭,等.模拟酸雨对入侵植物豚草与伴生种鬼针草竞争关系的影响[J].植物生态学报,2022,46(8):932-940. |
| LIU M Q, YANG X F, SHI Y M,et al.Effects of simulated acid rain on the competitive relationship between invasive Ambrosia artemisiifolia and its co-occurring indigenous forb Bidens bipinnata [J].Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology,2022,46(8):932-940. | |
| 21 | 沈伟,岑湘涛,吴晓倩,等.入侵植物白花鬼针草与2种牧草混播时的竞争效应[J].江苏农业学报,2020,36(3):795-797. |
| SHEN W, CEN X T, WU X Q,et al.Competition effect of invasive plant Bidens pilosa var.radiata and two forages under different mixed sowing patterns[J].Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences,2020,36(3):795-797. | |
| 22 | 欧阳晟,秦思思,陈王赋,等.基于Maxent和ARCGIS的醉鱼草属植物适生区预测[J].生态科学,2021,40(3):165-173. |
| OUYANG S, QIN S S, CHEN W F,et al.Prediction of potential distribution of Buddleja based on the Maxent and ARCGIS[J].Ecological Science,2021,40(3):165-173. | |
| 23 | 徐鑫洋.喀斯特土壤异质性和AM真菌对鬼针草生长及养分利用的影响[D].贵阳:贵州大学,2020:9-10. |
| XU X Y.Effects of karst soil heterogeneity and AM fungi ongrowth and nutrients utilization of Bidens pilosa [D].Guiyang:Guizhou University,2020:9-10. | |
| 24 | 田学军,沈云玫,陶宏征,等.入侵植物肿柄菊对三叶鬼针草的化感作用[J].生态环境学报,2015,24(7):1128-1131. |
| TIAN X J, SHEN Y M, TAO H Z,et al.Allelopathy of invasive Tithonia diversifolia on Bidens pilosa [J].Ecology and Environmental Sciences,2015,24(7):1128-1131. | |
| 25 | 程晶.单性木兰响应于多种环境因子交互作用的表型可塑性[D].贵阳:贵州大学,2021:16-18. |
| CHEN J.Phenotypic plasticity of Kmeria septentrionalis Dandy in response to the interaction of various environmental factors[D].Guiyang:Guizhou University,2021:16-18. | |
| 26 | 夏超.醉马草—内生真菌共生体对干旱胁迫的响应[D].兰州:兰州大学,2018:35-36. |
| XIA C,Responses of Epichloë gansuensis-Achnatherum inebrians symbiont to drought stress[D].Lanzhou:Lanzhou University,2018:35-36. | |
| 27 | 宋会兴,彭远英,钟章成.干旱生境中接种丛枝菌根真菌对三叶鬼针草(Bidens pilosa L.)光合特征的影响[J].生态学报,2008,28(8):3744-3751. |
| SONG H X.PENG Y Y,ZHON Z C.Photosynthetic responses of AMF-infected and AMF-free Bidens pilosa L.to drought stress conditions[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2008,28(8):3744-3751. | |
| 28 | 王青宁,衣学慧,王晗生,等.干旱胁迫下6种固沙灌木叶片水分状况研究[J].河南农业科学,2014,43(2):63-67. |
| WANG Q N, YI X H, WANG H S,et al.Study on leaf water status of six sand-fixing shrubs under drought stress[J].Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences,2014,43(2):63-67. | |
| 29 | WANG S, CALLAWAY R M, ZHOU D W,et al.Experience of inundation or drought alters the responses of plants to subsequent water conditions[J].Journal of Ecology,2017,105(1):176-187. |
| 30 | MARKHAM J, CHANWAY C P.Measuring plant neighbor effects[J].Functional Ecology,1996,10(4):548-549. |
| 31 | ARMAS C, ORDIALES R, PUGNAIRE F I.Measuring plant interactions:a new comparative index[J].Ecology,2004,85(10):2682-2686. |
| 32 | CALLAWAY R M, BROOKER R W, CHOLER P,et al.Positive interactions among alpine plants increase with stress[J].Nature,2002,417(6891):844-848. |
| 33 | WRIGHT A, SCHNITZER S A, REICH P B.Daily environmental conditions determine the competition-facilitation balance for plant water status[J].Journal of Ecology,2015,103(3):648-656. |
| 34 | BRISSON J, REYNOLDS J F.The effect of neighbors on root distribution in a creosotebush (Larrea tridentata) population[J].Ecology,1994,75(6):1693-1702. |
| 35 | VALLADARES F, GIANOLI E, GÓMEZ J M.Ecological limits to plant phenotypic plasticity[J].New Phytologist,2007,176(4):749-763. |
| 36 | FUNK J L.Differences in plasticity between invasive and native plants from a low resource environment[J].Journal of Ecology,2008,96(6):1162-1173. |
| 37 | WANG Y B, MENG B, ZHONG S Z,et al.Aboveground biomass and root/shoot ratio regulated drought susceptibility of ecosystem carbon exchange in a meadow steppe[J].Plant and Soil,2018,432(1):259-272. |
| 38 | 杜浩,只佳增,资家文,等.白花鬼针草入侵对菠萝蜜园杂草群落演替的影响[J].亚热带农业研究,2022,18(1):59-63. |
| DU H, ZHI J Z, ZI J W,et al.Effect of Bidens pilosa invasion on weed community succession in Artocarpus heterophyllus plantation[J].Subtropical Agriculture Research,2022,18(1):59-63. | |
| 39 | 于良瑞,朱政财,潘晓云.喜旱莲子草对同基因型邻体根系的表型可塑性:入侵地和原产地的比较[J].生物多样性,2020,28(6):651-657. |
| YU L R, ZHU Z Z, PAN X Y.Phenotypic plasticity of Alternanthera philoxeroides in response to root neighbors of kin:introduced vs.native genotypes[J].Biodiversity Science,2020,28(6):651-657. | |
| 40 | DAEHLER C C.Performance comparisons of co-occurring native and alien invasive plants:Implications for conservation and restoration[J].Annual Review of Ecology,Evolution,and Systematics,2003,34(1):183-211. |
| 41 | 刘君.不同入侵程度的加拿大一枝黄花对本地植物群落物种多样性和功能多样性的影响[D].镇江:江苏大学,2017:11-13. |
| LIU J.Effects of Solidago canadensis L.with different invasive degrees on species diversity and functional diversity of native plant communities[D].Zhenjiang:Jiangsu university,2017:11-13. | |
| 42 | 陈彤,刘文莉,张崇邦,等.加拿大一枝黄花入侵对本土植物群落动态的影响及其机制[J].植物生态学报,2012,36(3):253-261. |
| CHEN T, LIU W L, ZHANG C B,et al.Effects of Solidago canadensis invasion on dynamics of native plant communities and their mechanisms[J].Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology,2012,36(3):253-261. | |
| 43 | 严文斌,全国明,章家恩,等.环境因子对三叶鬼针草与鬼针草种子萌发的影响[J].生态环境学报,2013,22(7):1129-1135. |
| YAN W B, QUAN G M, ZHANG J E,et al.Effects of environmental factors on seed germination of Bidens pilosa and Bidens bipinnata [J].Ecology and Environmental Sciences,2013,22(7):1129-1135. | |
| 44 | 熊韫琦,赵彩云.表型可塑性与外来植物的成功入侵[J].生态学杂志,2020,39(11):3853-3864. |
| XIONG Y Q, ZHAO C Y.Phenotypic plasticity and the successful invasion of alien plants[J].Chinese Journal of Ecology,2020,39(11):3853-3864. |
| [1] | Chenjing SHEN, Wenbo WU, Luran GENG, Fulong WANG, Pengzhou ZHAO, Jinhui SONG, Yaguang ZHAN, Jing YIN. Regulatory Effects of Salicylic Acid,Nano-zinc Oxide and Growth-promoting Fungi YZ13-1 on the Resistance to Drought Stress of Fraxinus mandshurica [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(3): 388-395. |
| [2] | Anying HUANG, Dean XIA, Yang ZHANG, Dongchen NA, Qing YAN, Zhigang WEI. Cloning and Drought Tolerance Expression Analysis of PtrWRKY51 Gene in Populus trichocarpa [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(6): 1005-1013. |
| [3] | Bin WEI, Yi LI, Shiping SU. The Effect of Exogenous Proline on the Stomata of Nitraria tangutorum Leaves under Natural Drought [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(3): 492-501. |
| [4] | Mengjiao Wang, Yuxue Cao, Yongsheng Xu, Fenge Ding, Qiao Su. Overexpression of Marine Microbial Metagenomic MbCSP Enhanced Drought and Cold Tolerance of Transgenic Arabidopsisthaliana [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(2): 243-251. |
| [5] | Feng HE, Hong-Yan DU, Pan-Feng LIU, Lu WANG, Jun QING, Lan-Ying DU. Effects of Drought Stress on Leaf Structure of Eucommia ulmoides [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(6): 947-956. |
| [6] | Meng-Ke WANG, Meng-Ni TIAN, Quan-Xin BI, Xiao-Juan LIU, Hai-Yan YU, Li-Bing WANG. Evaluation of Drought Tolerance Based on Stomatal Characters and Selection of Germplasm Resources from Xanthoceras sorbifolia [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(6): 957-964. |
| [7] | Shuang-Hui TIAN, He CHENG, Yang ZHANG, Cong LIU, De-An XIA, Zhi-Gang WEI. Genome-wide Identification and Expressional Analysis of Carotenoid Cleavage Dioxygenases(CCD) Gene Family in Populus trichocarpa under Drought and Salt Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(6): 993-1005. |
| [8] | Dong ZHANG, Yan LIU, Han ZHANG, Zi-Jian ZHANG, Yang WANG, Mei-Cen LIU. Response of Photosynthesis and Leaf Morphological Characteristics to Drought Stress in Glycyrrhiza uralensis [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(3): 449-457. |
| [9] | Dong QIU, Jing ZHANG, Nan WU, Ye TAO. Effects of Micro-habitats on Water Retention and Loss of a Drought-tolerant Saxicolous Moss Grimmia pilifera [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(2): 180-190. |
| [10] | Xiao-Chi YU, Gui-Juan YANG, Ju-Lan DONG, Jun-Hui WANG, Wen-Jun MA, Peng ZHANG. Physiological Responses to Drought Stress of Five Speciesfrom Catalpa Scop [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(1): 44-52. |
| [11] | Wen-Hai HU, Xiao-Hong YAN, Xiao-Hong LI, Zao-Gui CAO. Effects of 24-Epibrassinolide on the Chlorophyll Fluorescence Transient in Leaves of Pepper under Drought Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(1): 53-59. |
| [12] | Ke-Xin MA, Mei ZHANG, Xin FANG, Li-Li TANG, Jian-Hua HAN, Li-Fang YANG, Fu-Chen SHI. Effects of Invasive Plant Datura stramonium on the Functional Traits of Native Plants and the Stoichiometric Characteristics of Soil Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(6): 867-875. |
| [13] | FANG Zi-Wen, ZHANG Xia-Yan, TAO Jun, ZHAO Da-Qiu. Ameliorative Effect of Ferulic Acid on Paeonia ostii under Drought Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(3): 353-359. |
| [14] | QIAO Bin-Jie, WANG De-Qiu, GAO Hai-Yan, LI Zhao-Min, GE Li-Li, DING Wen-Ya, ZHAO Xi-Yang. Photosynthetic and Stomatal Morphological Variation of Poplar Clones in Seedling Stage under Drought Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(2): 177-188. |
| [15] | ZHAO Min, HAO Wen-Ying, NING Xin-Zhe, HAO Long-Fei, YAN Hai-Xia, MU Ya-Nan, BAI Shu-Lan. Screening of Excellent Ectomycorrhizal Fungi-tree for Drought Resistant with Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(1): 133-140. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||