Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (3): 379-387.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2023.03.007
• Physiology and Ecology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jingzhe WANG1, Chaokui NIU1, Xinyuan LIANG1, Chenjing SHEN1, Jing YIN1,2( )
)
Received:2022-11-01
Online:2023-05-20
Published:2023-05-11
Contact:
Jing YIN
E-mail:yinjing20135@163.com
About author:WANG Jingzhe(2001—),female,undergraduate,mainly engaged in the research of plant salinity tolerance and secondary production regulation.
Supported by:CLC Number:
Jingzhe WANG, Chaokui NIU, Xinyuan LIANG, Chenjing SHEN, Jing YIN. Regulation of Salicylic Acid on Tolerance to Saline Alkali Stress at Seedling Stages of Betula platyphylla[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(3): 379-387.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://bbr.nefu.edu.cn/EN/10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2023.03.007
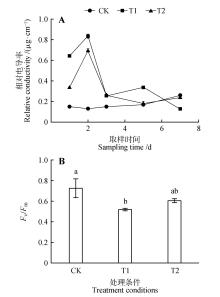
Fig.1
Relative electrical conductivity and Chlorophyll fluorescence parameters Fv/Fm of leaves of birch seedlings indifferent treatment groupsT1.Represented for 200 mmol·L-1 NaHCO3;T2.Represented for 200 mmol·L-1 NaHCO3+360 μmol·L-1 SA;Different letters indicated that the difference reached a significant level(P<0.05);The same as below
| 1 | RAHMAN M M, MOSTOFA M G, KEYA S S,et al.Adaptive mechanisms of halophytes and their potential in improving salinity tolerance in plants[J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2021,22(19):10733. |
| 2 | HANIN M, EBEL C, NGOM M,et al.New insights on plant salt tolerance mechanisms and their potential use for breeding[J].Frontiers in Plant Science,2016,7:1787. |
| 3 | 李金霞,储博彦,尹新彦,等.白桦研究现状综述[J].湖北农业科学,2019,58(2):5-9,32. |
| LI J X, CHU B Y, YIN X Y,et al.Research progress on Betula platyphylla [J].Hubei Agricultural Sciences,2019,58(2):5-9,32. | |
| 4 | 丁福安.白桦人工用材林营造技术与措施[J].牡丹江师范学院学报(自然科学版),2014,89(4):38-39. |
| DING F A.Technology and measures of Betula platyphylla plantation construction[J].Journal of Mudanjiang Normal University(Natural Sciences Edition),2014,89(4):38-39. | |
| 5 | 李影,徐林琳,张一彤,等.白桦酯酸及其衍生物的生物活性及作用机制研究进展[J].中草药,2020,51(24):6377-6390. |
| LI Y, XU L L, ZHANG Y T,et al.Research progress on biological activities and mechanism of betulinic acid and their derivatives[J].Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2020,51(24):6377-6390. | |
| 6 | PINZARU I, SARAU C, CORICOVAC D,et al.Silver nanocolloids loaded with betulinic acid with enhanced antitumor potential:physicochemical characterization and in vitro evaluation[J].Nanomaterials,2021,11(1):152. |
| 7 | HOENKE S, HEISE N V, KAHNT M,et al.Betulinic acid derived amides are highly cytotoxic,apoptotic and selective[J].European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry,2020,207:112815. |
| 8 | 李春晓,尹静,詹亚光,等.水分、氮肥及MeJA处理对白桦三萜积累特性的影响[J].西北植物学报,2012,32(1):155-161. |
| LI C X, YIN J, ZHAN Y G,et al.Effects of water,nitrogen and methyl jasmonate treatment on triterpenes accumulation in birch(Betula platyphylla Suk.)[J].Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica,2012,32(1):155-161. | |
| 9 | 李可鑫,赵微,徐林琳,等.温度胁迫对白桦丛生苗次生产物合成及抗逆酶积累的影响[J].北京林业大学学报,2021,43(7):31-39. |
| LI K X, ZHAO W, XU L L,et al.Effects of temperature stress on the accumulation of secondary metabolites and defensive enzymes in multiple shoots of Betula platyphylla [J].Journal of Beijing Forestry University,2021,43(7):31-39. | |
| 10 | YIN J, LIANG T, WANG S Y,et al.Effect of drought and nitrogen on betulin and oleanolic acid accumulation and OSC gene expression in white birch saplings[J].Plant Molecular Biology Reporter,2015,33(3):705-715. |
| 11 | KHAN M S S, ISLAM F, CHEN H,et al.Transcriptional coactivators:driving force of plant immunity[J].Frontiers in Plant Science,2022,13:823937. |
| 12 | 夏方山,毛培胜,闫慧芳,等.水杨酸对植物种子及幼苗抗逆性的影响[J].草业科学,2014,31(7):1367-1373. |
| XIA F S, MAO P S, YAN H F,et al.Effects of salicylic acid on stress resistance of seeds and seedling[J].Pratacultural Science,2014,31(7):1367-1373. | |
| 13 | 李润枝,靳晴,李召虎,等.水杨酸提高甘草种子萌发和幼苗生长对盐胁迫耐性的效应[J].作物学报,2020,46(11):1810-1816. |
| LI R Z, JIN Q, LI Z H,et al.Salicylic acid improved salinity tolerance of Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch during seed germination and seedling growth stages[J].Acta Agronomica Sinica,2020,46(11):1810-1816. | |
| 14 | 王艳,尹静,马泓思,等.钙离子在介导SA诱导白桦悬浮细胞三萜合成途径中的作用[J].北京林业大学学报,2014,36(2):51-58. |
| WANG Y, YIN J, MA H S,et al.Role of calcium ion in mediating the triterpenoid synthesis induced by SA in suspension cells of Betula platyphylla [J].Journal of Beijing Forestry University,2014,36(2):51-58. | |
| 15 | 包颖,魏琳燕,陈超.水杨酸和茉莉酸甲酯对盐胁迫下月季品种月月粉生理特性的影响[J].云南农业大学学报(自然科学版),2020,35(6):1040-1045. |
| BAO Y, WEI L Y, CHEN C.Effects of exogenous salicylic acid and methyl jasmonate on the physiological characteristics of Rosa chinensis ‘Old Blush’ under salt stress[J].Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University(Natural Science),2020,35(6):1040-1045. | |
| 16 | DEHNAVI A R, ZAHEDI M, LUDWICZAK A,et al.Foliar application of salicylic acid improves salt tolerance of sorghum(Sorghum bicolor(L.) Moench)[J].Plants,2022,11(3):368. |
| 17 | 王立红,张巨松,李星星,等.外源水杨酸对盐胁迫下棉花幼苗光合作用的影响[J].核农学报,2016,30(9):1864-1871. |
| WANG L H, ZHANG J S, LI X X,et al.Effects of exogenous salicylic acid on photosynthesis of cotton seedlings under salt stress[J].Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences,2016,30(9):1864-1871. | |
| 18 | 高明远,甘红豪,李清河,等.外源水杨酸对盐胁迫下白榆生理特性的影响[J].林业科学研究,2018,31(6):138-143. |
| GAO M Y, GAN H H, LI Q H,et al.The effect of exogenous salicylic acid on the physiological characteristics of Ulmus pumila plantlet under NaCl stress[J].Forest Research,2018,31(6):138-143. | |
| 19 | 沙汉景,刘化龙,王敬国,等.水杨酸调控作物耐盐性生理机制[J].东北农业大学学报,2017,48(3):80-88. |
| SHA H J, LIU H L, WANG J G,et al.Physiological mechanism of salicylic acid regulating salt tolerance of crops[J].Journal of Northeast Agricultural University,2017,48(3):80-88. | |
| 20 | YIN J, SUN L, LI Y,et al.Functional identification of BpMYB21 and BpMYB61 transcription factors responding to MeJA and SA in birch triterpenoid synthesis[J].BMC Plant Biology,2020,20(1):374. |
| 21 | YIN J, LI C X, ZHAN Y G,et al.The response of physiological characteristics,expression of OSC genes,and accumulation of triterpenoids in Betula platyphylla Sukto MeJA and SA treatment[J].Plant Molecular Biology Reporter,2016,34(2):427-439. |
| 22 | YIN J, LI X, ZHAN Y G,et al.Cloning and expression of BpMYC4 and BpbHLH9 genes and the role of BpbHLH9 in triterpenoid synthesis in birch[J].BMC Plant Biology,2017,17(1):214. |
| 23 | 美合日古丽·米吉提,王玉成.东北白桦(Betula platyphylla Suk.)LEA基因的克隆及盐胁迫响应基因的鉴定[J].分子植物育种,2017,15(7):2570-2578. |
| MIJITI M, WANG Y C.Cloning and identification of the LEA genes from Betula platyphylla Suk.in response to salt stress[J].Molecular Plant Breeding,2017,15(7):2570-2578. | |
| 24 | 叶查龙,颜斌,申婷婷,等.转BpmiR156基因白桦株系的耐盐性分析[J].南京林业大学学报(自然科学版),2020,44(6):147-151. |
| YE Z L, YAN B, SHEN T T,et al.Analysis of salt tolerance in BpmiR156 overexpression Betula platyphylla [J].Journal of Nanjing Forestry University(Natural Sciences Edition),2020,44(6):147-151. | |
| 25 | 张群,及晓宇,贺子航,等.白桦BpGRAS1基因的克隆及耐盐功能分析[J].南京林业大学学报(自然科学版),2021,45(5):38-46. |
| ZHANG Q, JI X Y, HE Z H,et al.Cloning and salt tolerance analysis of BpGRAS1 gene in Betula platyphylla [J].Journal of Nanjing Forestry University(Natural Sciences Edition),2021,45(5):38-46. | |
| 26 | 田增智,贺子航,王智博,等.白桦BpPAT1基因的表达模式及耐盐性分析[J].北京林业大学学报,2021,43(10):18-27. |
| TIAN Z Z, HE Z H, WANG Z B,et al.Expression patterns and salt tolerance analysis of BpPAT1 gene in Betula platyphylla [J].Journal of Beijing Forestry University,2021,43(10):18-27. | |
| 27 | 任春林,尹静,潘亚婕,等.水杨酸对白桦悬浮细胞中齐墩果酸积累及防御酶活性的影响[J].中草药,2012,43(5):972-977. |
| REN C L, YIN J, PAN Y J,et al.Effects of salicylic acid on accumulation of oleanolic acid and defense enzyme activity in suspension cells of Betula platyphylla [J].Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2012,43(5):972-977. | |
| 28 | 郝再彬,苍晶,徐仲.植物生理实验[M].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学出版社,2004:101-104. |
| HAO Z B, CANG J, XU Z.Plant physiological experiment[M].Harbin:Harbin Institute of Technology Press,2004:101-104. | |
| 29 | 萧浪涛,王三根.植物生理学实验技术[M].北京:中国农业出版社,2005:152-223. |
| XIAO L T, WANG S G.Experimental techniques in plant physiology[M].Beijing:China Agriculture Press,2005:152-223. | |
| 30 | 李琳,焦新之.应用蛋白染色剂考马斯蓝D-250测定蛋白质的方法[J].植物生理学通讯,1980(6):54-57. |
| LI L, JIAO X Z.Determination of protein using coomassie blue D-250 protein stain[J].Plant Physiology Journal,1980(6):54-57. | |
| 31 | 李合生.植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2000:164-165. |
| LI H S.Principles and techniques of plant physiological and biochemical experiments[M].Beijing:Higher Education Press,2000:164-165. | |
| 32 | 陈建勋,王晓峰.植物生理学实验指导[M].广州:华南理工大学出版社,2006:70-73. |
| CHEN J X, WANG X F.Experimental guidance in plant physiology[M].Guangzhou:South China University of Technology Press,2006:70-73. | |
| 33 | YIN J, REN C L, ZHAN Y G,et al.Distribution and expression characteristics of triterpenoids and OSC genes in white birch(Betula platyphylla Suk.)[J].Molecular Biology Reports,2012,39(3):2321-2328. |
| 34 | 马泓思,潘亚婕,王艳,等.Ca2+在介导MeJA诱导白桦悬浮培养三萜合成中的作用[J].植物研究,2015,35(1):117-126. |
| MA H S, PAN Y J, WANG Y,et al.Effect of Ca2+ on mediating the MeJA-induced synthesis of triterpenoid in suspension cells of Betula platyphylla Suk.[J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2015,35(1):117-126. | |
| 35 | 王佺珍,刘倩,高娅妮,等.植物对盐碱胁迫的响应机制研究进展[J].生态学报,2017,37(16):5565-5577. |
| WANG Q Z, LIU Q, GAO Y N,et al.Review on the mechanisms of the response to salinity-alkalinity stress in plants[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2017,37(16):5565-5577. | |
| 36 | 魏婧,徐畅,李可欣,等.超氧化物歧化酶的研究进展与植物抗逆性[J].植物生理学报,2020,56(12):2571-2584. |
| WEI J, XU C, LI K X,et al.Progress on superoxide dismutase and plant stress resistance[J].Plant Physiology Journal,2020,56(12):2571-2584. | |
| 37 | 徐国前,张振文,郭安鹊,等.植物多酚抗逆生态作用研究进展[J].西北植物学报,2011,31(2):423-430. |
| XU G Q, ZHANG Z W, GUO A Q,et al.Progress on the stress-resistant ecological function of plant polyphenols[J].Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica,2011,31(2):423-430. | |
| 38 | 李波,方志坚,邬婷婷,等.盐碱胁迫下紫花苜蓿叶片蛋白组的初步分析[J].草地学报,2019,27(3):574-580. |
| LI B, FANG Z J, WU T T,et al.Preliminary analysis of alfalfa leaf proteome under salt-alkali stress[J].Acta Agrestia Sinica,2019,27(3):574-580. | |
| 39 | 卫乐,姚爱兵,孙福华,等.盐碱胁迫对“丰花2号”花瓣多酚类物质的影响[J].北方园艺,2021(17):81-89. |
| WEI L, YAO A B, SUN F H,et al.Effects of saline-alkali stress on polyphenols,flavonoids and anthocyanins of ‘Fenghua No.2’ rose petals[J].Northern Horticulture,2021(17):81-89. | |
| 40 | 李欣,李影,曲子越,等.bHLH转录因子在茉莉酸信号诱导植物次生产物合成中的作用及分子机制[J].植物生理学报,2017,53(1):1-8. |
| LI X, LI Y, QU Z Y,et al.The molecular mechanism and the function of bHLH regulating jasmonic acid-mediated secondary metabolites synthesis[J].Plant Physiology Journal,2017,53(1):1-8. |
| [1] | Binghua CHEN, Jie ZHANG, Guifeng LIU, Siting LI, Yuanke GAO, Huiyu LI, Tianfang LI. Selection of Excellent Families and Evaluation of Selection Method for Pulpwood Half-sibling Families of Betula platyphylla [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(5): 690-699. |
| [2] | Lei XU, Xiao XU, Qinsong LIU. Effects of Exogenous Salicylic Acid on Antioxidant System and Gene Expression of Davidia involucrata Seedlings under Salt Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(4): 572-581. |
| [3] | Chenjing SHEN, Wenbo WU, Luran GENG, Fulong WANG, Pengzhou ZHAO, Jinhui SONG, Yaguang ZHAN, Jing YIN. Regulatory Effects of Salicylic Acid,Nano-zinc Oxide and Growth-promoting Fungi YZ13-1 on the Resistance to Drought Stress of Fraxinus mandshurica [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(3): 388-395. |
| [4] | Jinxia DU, Tingting SHEN, Haoran WANG, Yiping LIN, Huiyu LI, Lianfei ZHANG. Construction of Suppression Expression Vector and Genetic Transformation of BpSPL9 gene from Betula platyphylla [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(1): 30-35. |
| [5] | Kun CHEN, Gonggui FANG, Huaizhi MU, Jing JIANG. Analysis of the Promoter Sequence and Response Characteristics of the BpPIN3 gene in Betula platyphylla [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(4): 592-601. |
| [6] | Yunli Yang, Chang Qu, Yang Wang, Guifeng Liu, Jing Jiang. Tissue-specific Expression and Analysis of Exogenous Hormone Response of BpPIN5 Gene Promoter in Betula platyphylla [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(1): 104-111. |
| [7] | Qing MA, Fang-Rui LI, Gui-Feng LIU, Hui-Yu LI. Analysis on the Growth Characters of Betula platyphylla in the Aerospace Mutation [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(4): 540-546. |
| [8] | Yi-Ping GUO, Jia-Xin LIU, Ying YU, Chao WANG, Chuan-Ping YANG. Expression Profile Analysis ofXylem Development Regulated by BpNAC012 Gene from Betula platyphylla [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(2): 251-261. |
| [9] | LIU Jia-Xin, LIU Hui-Zi, SHI Jing-Jing, YU Ying, WANG Chao. Expression of MYB Genes of Birch in Response to Hormones,Salt and Drought [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(5): 743-750. |
| [10] | WANG Wan-Qi, QI Wan-Zhu, ZHAO Qiu-Shuang, ZENG Dong, LIU Yi, FU Peng-Yue, QU Guan-Zheng, ZHAO Xi-Yang. Cloning and Expression Analysis of BpJMJ18 Gene Promoter in Betula platyphylla [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(5): 751-759. |
| [11] | LIU Jin-Yu, GAO Yue-Hao, HUANG Jin-Shuo, ZHANG Qin. Effects of Exogenous Salicylic Acid on Physiological and Electrical Impedance Parameters of Trollius chinensis Seedlings under High Temperature Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(4): 543-551. |
| [12] | JIANG Cheng, ZHANG Xi, TIAN Qing, LI Li. Isolation of the BpbHLH112 Gene and Expression Analysis of Its Promoter in Betula platyphylla [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(4): 583-592. |
| [13] | SUN Shuo, WANG Xiu-Wei, DU Meng-Tian, LI Jing-Hang, WANG Bo-Yi, LIU Gui-Feng. Root CO2 Efflux Variations of Betula platyphylla Among Sites and Root Diameter Classes in 12 Different Provenances [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(3): 476-480. |
| [14] | QIN Lin-Lin, ZHANG Xi, JIANG Cheng, LI Li. Cloning and Functional Analysis of BpZFP4 Promoter from Birch(Betula platyphylla) [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2019, 39(6): 917-926. |
| [15] | YAN Bin, WU Dan-Yang, LI Hui-Yu. Genetic Transformation and Resistance Analysis of BpBEE2 Gene from Betula platyphylla [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2019, 39(2): 287-293. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||