植物研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (3): 455-465.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2022.03.015
刘建新, 刘瑞瑞, 刘秀丽, 贾海燕, 卜婷, 李娜
收稿日期:2021-02-15
出版日期:2022-05-20
发布日期:2022-05-20
作者简介:刘建新(1964—),男,教授,主要从事植物逆境生理生态研究。
基金资助:Jianxin LIU, Ruirui LIU, Xiuli LIU, Haiyan JIA, Ting BU, Na LI
Received:2021-02-15
Online:2022-05-20
Published:2022-05-20
About author:LIU Jianxin(1964—),male,professor,mainly engaged in the study of physiological and ecological of plant stress.
Supported by:摘要:
为了解气体信号硫化氢(H2S)对盐碱胁迫下裸燕麦(Avena nuda)活性氧(ROS)代谢的调节效应,筛选和确定H2S最佳的施用时期和适宜浓度。采用盆栽土培试验,研究了在裸燕麦不同时期(幼苗期、拔节期、抽穗期、开花期和灌浆期)喷施0、25、50、100、200、400 μmol·L-1 H2S供体硫氢化钠(NaHS)对3.0 g·kg-1盐碱混合 (NaCl∶Na2SO4∶NaHCO3∶Na2CO3摩尔比为12∶8∶9∶1)胁迫下裸燕麦叶片H2S含量、H2S生成关键酶L-半胱氨酸脱巯基酶(LCD)活性和ROS代谢相关物质含量和酶活性的影响。结果表明:喷施时期和NaHS浓度及其交互作用对盐碱胁迫下裸燕麦叶片中H2S、超氧阴离子(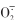 )、过氧化氢(H2O2)、丙二醛(MDA)、抗坏血酸(AsA)和谷胱甘肽(GSH)含量及LCD、超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化氢酶(CAT)、过氧化物酶(POD)、抗坏血酸过氧化物酶(APX)和谷胱甘肽还原酶(GR)活性存在显著影响。与喷施0 μmol?L-1 NaHS相比,喷施一定浓度NaHS能够提高H2S、AsA、GSH含量和LCD、SOD、CAT、POD、APX和GR活性,减少
)、过氧化氢(H2O2)、丙二醛(MDA)、抗坏血酸(AsA)和谷胱甘肽(GSH)含量及LCD、超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化氢酶(CAT)、过氧化物酶(POD)、抗坏血酸过氧化物酶(APX)和谷胱甘肽还原酶(GR)活性存在显著影响。与喷施0 μmol?L-1 NaHS相比,喷施一定浓度NaHS能够提高H2S、AsA、GSH含量和LCD、SOD、CAT、POD、APX和GR活性,减少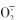 、H2O2和MDA积累,但以上各指标最佳的喷施时期和NaHS浓度存在差异。隶属函数综合分析显示,在幼苗期和拔节期喷施25~200 μmol?L-1 NaHS的综合评价值(D)最高,表明在幼苗—拔节期喷施25~200 μmol?L-1 NaHS能更好提高ROS清除能力,从而缓解盐碱胁迫诱导ROS对裸燕麦的氧化伤害。
、H2O2和MDA积累,但以上各指标最佳的喷施时期和NaHS浓度存在差异。隶属函数综合分析显示,在幼苗期和拔节期喷施25~200 μmol?L-1 NaHS的综合评价值(D)最高,表明在幼苗—拔节期喷施25~200 μmol?L-1 NaHS能更好提高ROS清除能力,从而缓解盐碱胁迫诱导ROS对裸燕麦的氧化伤害。
中图分类号:
刘建新, 刘瑞瑞, 刘秀丽, 贾海燕, 卜婷, 李娜. 不同时期喷施NaHS对盐碱胁迫下裸燕麦H2S产生和活性氧代谢的影响[J]. 植物研究, 2022, 42(3): 455-465.
Jianxin LIU, Ruirui LIU, Xiuli LIU, Haiyan JIA, Ting BU, Na LI. Effects of Spraying NaHS at Different Growth Stages on H2S Production and Reactive Oxygen Species Metabolism of Naked Oat Leaves under Saline-Alkali Stress[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(3): 455-465.
表1
不同时期喷施NaHS对盐碱胁迫下裸燕麦叶片H2S含量的影响
NaHS浓度 NaHS concentrations /(µmol∙L-1) | H2S含量 H2S content /(µmol∙g-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
幼苗期 Seedling | 拔节期 Jointing | 抽穗期 Heading | 开花期 Flowering | 灌浆期 Grouting | |
| 0 | 26.95±3.45cC | 34.47±3.48bB | 31.98±3.65bB | 46.35±3.14aA | 31.47±3.10bC |
| 25 | 24.45±1.49dC | 36.19±2.51bcB | 33.28±2.43cB | 39.67±2.70bB | 45.56±3.79aB |
| 50 | 44.58±1.74aA | 34.83±4.97bB | 42.02±4.99aA | 36.68±4.55bBC | 42.31±4.51aB |
| 100 | 38.86±3.81cB | 45.61±3.79bA | 43.36±3.48bcA | 40.04±2.66cB | 61.49±4.50aA |
| 200 | 41.46±3.53aAB | 43.54±2.83aA | 35.55±2.10bB | 44.07±3.41aA | 45.67±2.76aB |
| 400 | 26.33±3.10cC | 41.53±3.43aA | 41.49±3.07aA | 34.63±3.12bC | 45.73±2.50aB |
表2
不同时期喷施NaHS对盐碱胁迫下裸燕麦叶片LCD活性的影响
NaHS浓度 NaHS concentrations /(µmol∙L-1) | LCD活性 LCD activity /(μg∙g-1∙min-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
幼苗期 Seedling | 拔节期 Jointing | 抽穗期 Heading | 开花期 Flowering | 灌浆期 Grouting | |
| 0 | 458.1±58.7cC | 585.9±59.1bB | 543.7±62.1bB | 788.0±53.4aA | 555.1±34.9bD |
| 25 | 415.7±25.3dC | 615.3±42.7bcB | 565.9±41.3cB | 674.4±45.9bBC | 813.3±40.2aB |
| 50 | 757.9±29.6aA | 592.2±84.5cB | 714.4±84.7abA | 663.6±34.3bCD | 731.1±58.2abC |
| 100 | 660.6±64.8cB | 775.4±64.4bA | 737.1±59.3bcA | 700.8±28.0bcBC | 1 035.1±58.7aA |
| 200 | 704.8±60.0aAB | 740.2±48.2aA | 604.4±35.7bB | 749.1±57.9aAB | 776.3±46.9aBC |
| 400 | 447.7±52.7cC | 706.0±58.4aA | 705.2±52.2aA | 588.7±53.0bD | 777.4±42.5aBC |
表3
不同时期喷施NaHS对盐碱胁迫下裸燕麦叶片含量的影响
NaHS浓度 NaHS concentrations /(µmol∙L-1) | 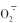 含量 含量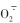 content /(μg∙g-1) content /(μg∙g-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
幼苗期 Seedling | 拔节期 Jointing | 抽穗期 Heading | 开花期 Flowering | 灌浆期 Grouting | |
| 0 | 4.79±0.57cdB | 3.41±0.93dAB | 5.94±0.71bcC | 6.58±1.23bA | 8.67±1.22aBC |
| 25 | 4.86±0.67cAB | 3.07±0.81dAB | 6.62±0.42bBC | 5.58±0.88bcAB | 10.13±1.48aA |
| 50 | 6.35±0.81aA | 2.64±0.51bB | 6.31±0.76aBC | 4.05±0.69bB | 6.95±0.72aD |
| 100 | 4.42±1.20bB | 3.71±0.86bAB | 7.82±1.17aB | 4.20±0.88bB | 7.53±1.44aC |
| 200 | 4.16±0.74cB | 4.21±0.83cA | 5.87±2.42bC | 4.63±0.67bcB | 9.57±0.75aAB |
| 400 | 5.57±1.03cAB | 4.26±0.70cA | 11.05±1.34aA | 5.10±1.02cAB | 9.01±1.85bAB |
表4
不同时期喷施NaHS对盐碱胁迫下裸燕麦叶片H2O2 含量的影响
NaHS浓度 NaHS concentrations /(µmol∙L-1) | H2O2含量 H2O2 content /(μmol∙g-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
幼苗期 Seedling | 拔节期 Jointing | 抽穗期 Heading | 开花期 Flowering | 灌浆期 Grouting | |
| 0 | 110.8±21.4bBC | 104.5±14.0bA | 178.7±29.4aA | 81.1±11.3cA | 45.2±7.5dA |
| 25 | 92.2±9.1bC | 95.9±19.8bAB | 128.7±20.8aCD | 69.4±13.4cA | 63.9±21.6cA |
| 50 | 129.6±12.1aAB | 78.8±13.9bBC | 146.7±13.4aBC | 60.0±11.7bcA | 53.8±14.2cA |
| 100 | 116.7±19.3aAB | 58.0±4.6bC | 126.5±13.9aCD | 65.5±10.2bA | 45.2±3.3bA |
| 200 | 119.4±21.3aAB | 60.0±8.3bC | 122.5±21.9aD | 73.3±7.6bA | 51.8±10.9bA |
| 400 | 136.5±14.8bA | 69.9±10.3cdC | 162.3±13.4aAB | 78.1±20.9cA | 53.4±16.5dA |
表5
不同时期喷施NaHS对盐碱胁迫下裸燕麦叶片MDA含量的影响
NaHS浓度 NaHS concentrations /(µmol∙L-1) | MDA含量 MDA content /(nmol∙g-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
幼苗期 Seedling | 拔节期 Jointing | 抽穗期 Heading | 开花期 Flowering | 灌浆期 Grouting | |
| 0 | 11.21±3.69dA | 17.00±2.69cA | 26.78±3.41bA | 36.30±3.59aA | 36.54±3.01aA |
| 25 | 9.07±1.74dA | 18.41±2.05cA | 24.33±3.82bAB | 38.32±4.51aA | 24.55±4.33bD |
| 50 | 10.69±3.18cA | 16.97±2.19bA | 20.90±5.71bB | 28.36±7.06aB | 33.05±5.07aAB |
| 100 | 9.81±0.48dA | 16.30±3.62cA | 28.91±3.31bA | 40.90±2.62aA | 27.30±2.99bCD |
| 200 | 8.67±1.54dA | 13.47±2.21dA | 26.90±5.61cA | 42.19±3.80bA | 32.89±5.24aABC |
| 400 | 11.78±1.54eA | 17.56±4.45dA | 23.10± 4.95cAB | 36.90±3.95aA | 29.39±8.53bBCD |
表6
不同时期喷施NaHS对盐碱胁迫下裸燕麦叶片SOD活性的影响
NaHS浓度 NaHS concentrations /(µmol∙L-1) | SOD活性 SOD activity /(U∙g-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
幼苗期 Seedling | 拔节期 Jointing | 抽穗期 Heading | 开花期 Flowering | 灌浆期 Grouting | |
| 0 | 395.0±9.0ABa | 329.2±23.4Bc | 403.9±9.4Aa | 364.6±20.4ABb | 399.3±5.8Aa |
| 25 | 393.7±9.5ABa | 295.9±32.8Cc | 387.5±6.5Aa | 339.9±26.5Cb | 351.4±5.5Cb |
| 50 | 364.2±4.9Ca | 323.4±16.7Bb | 323.7±28.5Bb | 352.5±15.9BCb | 367.4±5.6BCa |
| 100 | 392.1±11.3Ba | 317.2±28.8Bb | 380.2±8.4Aa | 383.0±9.9Aa | 379.0±11.0ABa |
| 200 | 400.9±12.8ABa | 365.4±9.7Abc | 385.6±11.2Aab | 360.3±11.9ABCc | 367.1±4.6BCbc |
| 400 | 416.1±6.7Aa | 338.4±23.9Bc | 393.2±9.9Aab | 384.0±18.6Ab | 378.0±21.8ABb |
表7
不同时期喷施NaHS对盐碱胁迫下裸燕麦叶片CAT活性的影响
NaHS浓度 NaHS concentrations /(µmol∙L-1) | CAT活性 CAT activity /(U∙g-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
幼苗期 Seedling | 拔节期 Jointing | 抽穗期 Heading | 开花期 Flowering | 灌浆期 Grouting | |
| 0 | 2787.8±398.2Ba | 1561.6±378.6Ab | 1167.0±128.6Bc | 409.6±72.1Ad | 387.2±185.4Ad |
| 25 | 3408.0±409.6Aa | 1564.8±414.4Ab | 1310.7±274.9Bb | 368.0±33.9Ac | 326.4±90.9Ac |
| 50 | 2432.0±202.7Ca | 1340.8±412.5Ab | 1724.2±339.7Ab | 422.4±128.3Ac | 499.2±96.3Ac |
| 100 | 2880.0±512.5Ba | 1718.4±601.3Ab | 1009.0±134.8BCc | 489.6±78.9Ad | 355.2±59.2Ad |
| 200 | 1337.6±363.4Da | 1450.6±299.9Aa | 713.6±214.2Cb | 563.2±130.7Ab | 361.6±31.2Ab |
| 400 | 933.8±141.0Eb | 1360.0±257.7Aa | 1292.8±136.4Bab | 489.6±120.6Ac | 540.8±30.8Ac |
表8
不同时期喷施NaHS对盐碱胁迫下裸燕麦叶片POD活性的影响
NaHS浓度 NaHS concentrations /(µmol∙L-1) | POD活性 POD activity /(U∙g-1∙min-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
幼苗期 Seedling | 拔节期 Jointing | 抽穗期 Heading | 开花期 Flowering | 灌浆期 Grouting | |
| 0 | 1572.2±198.3Ba | 1162.6±264.8Bb | 642.6±35.7Ac | 60.2±9.4Ad | 54.4±10.3Ad |
| 25 | 1844.5±439.2Aa | 1160.6±271.2Bb | 657.3±90.5Ac | 57.6±9.1Ad | 58.6±4.8Ad |
| 50 | 1573.1±371.4Ba | 1205.1±103.9Bb | 470.1±82.6Ac | 45.8±12.0Ad | 55.4±2.4Ad |
| 100 | 1148.8±325.3Cb | 1489.6±158.9Aa | 510.4±85.9Ac | 42.6±9.2Ad | 65.2±10.6Ad |
| 200 | 1115.8±239.3Ca | 1160.0±216.8Ba | 510.1±99.9Ab | 61.8±11.9Ac | 57.6±7.8Ac |
| 400 | 994.9±217.0Ca | 1073.6±181.9Ba | 139.0±15.1Ab | 56.3±11.6Ab | 55.0±6.2Ab |
表9
不同时期喷施NaHS对盐碱胁迫下裸燕麦叶片APX活性的影响
NaHS浓度 NaHS concentrations /(µmol∙L-1) | APX活性 APX activity /(μmol∙g-1∙min-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
幼苗期 Seedling | 拔节期 Jointing | 抽穗期 Heading | 开花期 Flowering | 灌浆期 Grouting | |
| 0 | 1.51±0.31Bb | 3.67±0.22Aa | 2.09±0.60Ab | 1.83±0.22Bb | 1.95±0.48Cb |
| 25 | 1.78±0.51ABb | 3.72±0.65Aab | 2.21±0.47Ab | 3.43±0.44Aa | 2.21±0.65BCb |
| 50 | 1.75±0.54ABc | 2.08±0.55Bc | 2.04±0.25Ac | 2.91±0.80Ab | 4.06±0.29Aa |
| 100 | 1.83±0.34ABb | 1.97±0.12Bb | 1.89±0.41Ab | 3.09±0.57Aa | 2.79±0.64Ba |
| 200 | 1.54±0.30Bc | 2.26±0.29Bbc | 1.85±0.83Abc | 3.02±0.56Aa | 2.52±0.87BCab |
| 400 | 2.42±0.55Aab | 1.66±0.45Bb | 1.86±0.19Ab | 2.71±0.71Aa | 1.80±0.35Cb |
表10
不同时期喷施NaHS对盐碱胁迫下裸燕麦叶片AsA含量的影响
NaHS浓度 NaHS concentrations /(µmol∙L-1) | AsA含量 AsA content /(μmol∙g-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
幼苗期 Seedling | 拔节期 Jointing | 抽穗期 Heading | 开花期 Flowering | 灌浆期 Grouting | |
| 0 | 3.10±0.38ABa | 1.78±0.08Bb | 1.77±0.13Cb | 1.51±0.27ABCc | 1.60±0.15Ac |
| 25 | 3.42±0.56Aa | 1.76±0.07Bc | 2.32±0.06Bb | 1.09±0.15Dd | 1.35±0.20Ad |
| 50 | 2.20±0.40Dab | 2.41±0.04Aa | 2.01±0.47BCb | 1.63±0.06ABc | 1.40±0.23Ac |
| 100 | 2.46±0.10CDa | 1.70±0.06Bb | 2.75±0.04Aa | 1.70±0.10Ab | 1.56±0.25Ab |
| 200 | 2.82±0.43BCa | 2.36±0.05ABb | 2.77±0.19Aa | 1.29±0.17BCDc | 1.47±0.19Ac |
| 400 | 3.10±0.64ABa | 2.02±.040Bb | 3.11±0.24Aa | 1.18±0.30CDc | 1.25±0.14Ac |
表11
不同时期喷施NaHS对盐碱胁迫下裸燕麦叶片GSH含量的影响
NaHS浓度 NaHS concentrations /(µmol∙L-1) | GSH含量 GSH content /(μmol∙g-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
幼苗期 Seedling | 拔节期 Jointing | 抽穗期 Heading | 开花期 Flowering | 灌浆期 Grouting | |
| 0 | 22.8±3.8Bc | 22.5±4.8Ac | 39.3±4.1Ba | 26.6±4.7Cbc | 30.0±4.1ABb |
| 25 | 22.7±2.4Bbc | 19.8±1.9Ac | 30.6±3.5Ca | 25.0±2.2Cbc | 26.7±3.9Bab |
| 50 | 26.1±2.1ABb | 19.4±3.3 Ac | 37.1±1.6Ba | 38.7±4.5Aa | 25.6±3.9Bb |
| 100 | 28.2±5.1Ab | 21.8±1.5Ac | 36.5±2.8Ba | 32.1±3.3Bab | 14.9±2.9Cd |
| 200 | 26.6±1.5ABb | 22.1±3.6Ab | 34.7±4.5Ba | 33.4±1.6Ba | 32.7±2.5Aa |
| 400 | 24.3±1.5ABc | 20.0±2.0Acd | 44.3±3.1Aa | 30.1±4.5BCb | 17.5±2.6Cd |
表12
不同时期喷施NaHS对盐碱胁迫下裸燕麦叶片GR活性的影响
NaHS浓度 NaHS concentrations /(µmol∙L-1) | GR活性 GR activity /(U∙g-1∙min-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
幼苗期 Seedling | 拔节期 Jointing | 抽穗期 Heading | 开花期 Flowering | 灌浆期 Grouting | |
| 0 | 159.5±18.4bD | 243.7±36.5aABC | 226.1±43.9aA | 157.9±48.3bB | 144.5±47.6bB |
| 25 | 225.6±53.4aBC | 185.6±24.9aC | 214.9±48.9aA | 180.8±36.8aB | 193.6±31.8aAB |
| 50 | 220.8±41.8abBCD | 187.7±38.9bC | 273.6±60.8aA | 283.7±48.5aA | 182.9±29.3bB |
| 100 | 187.2±55.3bcCD | 212.2±32.8abcBC | 261.3±62.9aA | 171.7±17.7cB | 250.1±29.4abA |
| 200 | 380.3±60.2aA | 289.6±51.9bA | 210.1±34.2cA | 187.7±32.7cB | 196.3±20.5cAB |
| 400 | 267.2±55.2aB | 268.8±55.9aAB | 266.7±27.5aA | 208.5±48.6abB | 151.5±16.6bB |
表13
NaHS喷施浓度和喷施时期对裸燕麦H2S产生和活性氧代谢的双因素方差分析结果
因子 Factor | F | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2S | LCD | 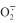 | H2O2 | MDA | SOD | CAT | POD | APX | ASA | GSH | GR | |
| 喷施时期Spraying period | 45.6* | 60.3* | 109.6* | 174.5* | 211.0* | 69.1* | 252.6* | 403.4* | 21.5* | 176.3* | 90.2* | 10.8* |
| NaHS浓度Concentration | 39.4* | 44.9* | 8.1* | 7.3* | 2.7* | 20.1* | 15.6* | 9.0* | 4.8* | 2.9* | 6.2* | 7.9* |
| 交互作用Interaction | 15.9* | 17.5* | 6.2* | 4.5* | 3.6* | 5.4* | 14.4* | 5.0* | 7.9* | 11.0* | 7.9* | 6.4* |
| 1 | 张新军,杨才,曾昭海,等.叶面喷施硒肥对裸燕麦产量和品质的影响[J].麦类作物学报,2015,35(3):408-412. |
| ZHANG X J, YANG C, ZENG Z H,et al.Effect of Se foliar fertilizer rate on yield and quality of naked oat(Avena nuda)[J].Journal of Triticeae Crops,2015,35(3):408-412. | |
| 2 | MICEK P, KULIG B, WOŹNICA P,et al.The nutritive value for ruminants of faba bean(Vicia faba) seeds and naked oat(Avena nuda) grain cultivated in an organic farming system[J].Journal of Animal and Feed Sciences,2012,21(4):773-786. |
| 3 | 郑殿升,张宗文.大粒裸燕麦(莜麦)(Avena nuda L.)起源及分类问题的探讨[J].植物遗传资源学报,2011,12(5):667-670. |
| ZHENG D S, ZHANG Z W.Discussion on the origin and taxonomy of naked oat(Avena nuda L.)[J].Journal of Plant Genetic Resources,2011,12(5):667-670. | |
| 4 | 林伟静,吴广枫,李春红,等.品种与环境对我国裸燕麦营养品质的影响[J].作物学报,2011,37(6):1087-1092. |
| LIN W J, WU G F, LI C H,et al.Effects of cultivar and environment on nutritional quality of Chinese naked oats[J].Acta Agronomica Sinica,2011,37(6):1087-1092. | |
| 5 | 林叶春,曾昭海,任长忠,等.局部根区灌溉对裸燕麦光合特征曲线及叶绿素荧光特性的影响[J].作物学报,2012,38(6):1062-1070. |
| LIN Y C, ZENG Z H, REN C Z,et al.Effects of partial root zone irrigation on leaf photosynthetic curves and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters in naked oat[J].Acta Agronomica Sinica,2012,38(6):1062-1070. | |
| 6 | 孙仁国,赵桂琴,胡凯军,等.盐胁迫对燕麦地上干物质积累及灌浆期光合特性的影响[J].中国草地学报,2010,32(5):15-20. |
| SUN R G, ZHAO G Q, HU K J,et al.Effect of salinity stress on aboveground dry matter accumulation of oat and photosynthesis at grain filling stage[J].Chinese Journal of Grassland,2010,32(5):15-20. | |
| 7 | 刘建新,王金成,王瑞娟,等.混合盐碱胁迫对燕麦幼苗矿质离子吸收和光合特性的影响[J].干旱地区农业研究,2017,35(1):178-184,239. |
| LIU J X, WANG J C, WANG R J,et al.Effect of complex saline-alkali stress on the mineral ions absorption and photosynthetic characteristics of oat seedlings[J].Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas,2017,35(1):178-184,239. | |
| 8 | 闫永庆,王文杰,朱虹,等.混合盐碱胁迫对青山杨渗透调节物质及活性氧代谢的影响[J].应用生态学报,2009,20(9):2085-2091. |
| YAN Y Q, WANG W J, ZHU H,et al.Effects of salt-alkali stress on osmoregulation substance and active oxygen metabolism of Qingshan poplar(Populus pseudo-cathayana×P.deltoides)[J].Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2009,20(9):2085-2091. | |
| 9 | 赵婷,杨建宁,吴玉霞,等.外源H2S处理对盐碱胁迫下垂丝海棠幼苗生理特性的影响[J].果树学报,2020,37(8):1156-1167. |
| ZHAO T, YANG J N, WU Y X,et al.Effects of exogenous H2S treatment on physiological characteristics of salt-alkali stressed seedling of Malus halliana [J].Journal of Fruit Science,2020,37(8):1156-1167. | |
| 10 | 王佺珍,刘倩,高娅妮,等.植物对盐碱胁迫的响应机制研究进展[J].生态学报,2017,37(16):5565-5577. |
| WANG Q Z, LIU Q, GAO Y N,et al.Review on the mechanisms of the response to salinity-alkalinity stress in plants[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2017,37(16):5565-5577. | |
| 11 | 田雲,蒋景龙,李丽,等.信号分子硫化氢调控植物抗逆性研究进展[J].核农学报,2017,31(11):2279-2287. |
| TIAN Y, JIANG J L, LI L,et al.Research advances in plant stress resistance regulated by signal molecule hydrogen sulfide[J].Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences,2017,31(11):2279-2287. | |
| 12 | CHEN J, SHANG Y T, WANG W H,et al.Hydrogen sulfide-mediated polyamines and sugar changes are involved in hydrogen sulfide-induced drought tolerance in Spinacia oleracea seedlings[J].Frontiers in Plant Science,2016,7:1173. |
| 13 | CHEN X D, CHEN Q, ZHANG X M,et al.Hydrogen sulfide mediates nicotine biosynthesis in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) under high temperature conditions[J].Plant Physiology and Biochemistry,2016,104:174-179. |
| 14 | 周超凡,吴春涛,李丹丹,等.外源H2S通过减轻低温光抑制增强黄瓜幼苗耐冷性[J].植物生理学报,2018,54(3):411-420. |
| ZHOU C F, WU C T, LI D D,et al.Hydrogen sulfide promotes chilling tolerance of cucumber seedlings by alleviating low-temperature photoinhibition[J].Plant Physiology Journal,2018,54(3):411-420. | |
| 15 | CHEN Z, CHEN M S, JIANG M.Hydrogen sulfide alleviates mercury toxicity by sequestering it in roots or regulating reactive oxygen species productions in rice seedlings[J].Plant Physiology and Biochemistry,2017,111:179-192. |
| 16 | CHEN J, WANG W H, WU F H,et al.Hydrogen sulfide enhances salt tolerance through nitric oxide-mediated maintenance of ion homeostasis in barley seedling roots[J].Scientific Reports,2015,5(1):12516. |
| 17 | DENG Y Q, BAO J, YUAN F,et al.Exogenous hydrogen sulfide alleviates salt stress in wheat seedlings by decreasing Na+ content[J].Journal of Plant Growth Regulation,2016,79(3):391-399. |
| 18 | SHAN C, LIU H, ZHAO L,et al.Effects of exogenous hydrogen sulfide on the redox states of ascorbate and glutathione in maize leaves under salt stress[J].Biologia Plantarum,2014,58(1):169-173. |
| 19 | 黄菡,郭莎莎,陈良超,等.外源硫化氢对盐胁迫下茶树抗氧化特性的影响[J].植物生理学报,2017,53(3):497-504. |
| HUANG H, GUO S S, CHEN L C,et al.Effects of exogenous hydrogen sulfide on the antioxidant characteristics of tea plant(Camellia sinensis) under salt stress[J].Plant Physiology Journal,2017,53(3):497-504. | |
| 20 | 郑州元,林海荣,崔辉梅.外源硫化氢对盐胁迫下加工番茄幼苗光合参数及叶绿素荧光特性的影响[J].核农学报,2017,31(7):1426-1435. |
| ZHENG Z Y, LIN H R, CUI H M.Effect of exogenous hydrogen sulfide on photosynthesis parameters and chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics of processing tomato(Lycopersicon esculentum Mill ssp.subspontaneum Brezh) seedlings under NaCl stress[J].Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences,2017,31(7):1426-1435. | |
| 21 | DING H N, MA D Y, HUANG X,et al.Exogenous hydrogen sulfide alleviates salt stress by improving antioxidant defenses and the salt overly sensitive pathway in wheat seedlings[J].Acta Physiologiae Plantarum,2019,41(7):123. |
| 22 | 高晓兰,吴雪莲,张淑辉,等.外源H2S对桃根系构型及叶片光合特性的影响[J].植物生理学报,2019,55(1):91-98. |
| GAO X L, WU X L, ZHANG S H,et al.Effect of exogenous H2S on root architecture and leaf photosynthetic characteristics of peach seedlings[J].Plant Physiology Journal,2019,55(1):91-98. | |
| 23 | CHEN J, WU F H, WANG W H,et al.Hydrogen sulphide enhances photosynthesis through promoting chloroplast biogenesis,photosynthetic enzyme expression,and thiol redox modification in Spinacia oleracea seedlings[J].Journal of Experimental Botany,2011,62(13):4481-4493. |
| 24 | 高俊凤.植物生理学实验指导[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2006:210-223. |
| GAO J F.Experimental guidance for plant physiology[M].Beijing:Higher Education Press,2006:210-223. | |
| 25 | SERGIEV I, ALEXIEVA V, KARANOV E.Effect of spermine,atrazine and combination between them on some endogenous protective systems and stress markers in plants[J].Comptes Rendus de I’ Academie Bulgare des Sciences,1997,51(2):121-124. |
| 26 | 陈建勋,王晓峰.植物生理学实验指导[M].广州:华南理工大学出版社,2002:68-77. |
| CHEN J X, WANG X F.Plant physiology experiment guidance[M].Guangzhou:South China University of Technology Press,2002:68-77. | |
| 27 | FOSTER J G, HESS J L.Responses of superoxide dismutase and glutathione reductase activities in cotton leaf tissue exposed to an atmosphere enriched in oxygen[J].Plant Physiology,1980,66(3):482-487. |
| 28 | WANG Y Q, LI L, CUI W T,et al.Hydrogen sulfide enhances alfalfa(Medicago sativa) tolerance against salinity during seed germination by nitric oxide pathway[J].Plant and Soil,2012,351(1-2):107-119. |
| 29 | 刘建新,欧晓彬,刘秀丽,等.过氧化氢缓解裸燕麦幼苗低温胁迫的主成分和隶属函数分析[J].植物研究,2018,38(5):748-756. |
| LIU J X, OU X B, LIU X L,et al.Principal component and subordinate function of the alleviating effects of hydrogen peroxide(H2O2) on low-temperature stress in naked oat(Avena nuda) seedlings[J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2018,38(5):748-756. | |
| 30 | 冯岚,严岩,闫兴成,等.乙草胺胁迫下水位对湿地芦苇生长及土壤酶活性的影响[J].森林工程,2021,37(2):24-29. |
| FENG L, YAN Y, YAN X C,et al.Effects of water levels on wetland reed growth and soil enzyme activities under acetochlor stress[J].Forest Engineering,2021,37(2):24-29. | |
| 31 | 徐子棋,张瑜,杨献坤.吉林省西部菊芋品质及耐盐碱性优选研究[J].森林工程,2019,35(6):6-15. |
| XU Z Q, ZHANG Y, YANG X K.Optimization research of quality and saline-alkaline resistance of Helianthus tuberosus L. in the Western Jilin Province[J].Forest Engineering,2019,35(6):6-15. | |
| 32 | 王芳,陆志民,王君,等.低温胁迫下红松与西伯利亚红松光合与气孔特性[J].植物研究,2021,41(2):205-212. |
| WANG F, LU Z M, WANG J,et al.Photosynthetic and stomatal characteristics of Pinus koraiensis and P.sibirica under low temperature stress[J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2021,41(2):205-212. | |
| 33 | 周超凡,吴帼秀,李婷,等.外源H2S对低温下日光温室黄瓜光合作用及抗氧化系统的影响[J].园艺学报,2016,43(3):462-472. |
| ZHOU C F, WU G X, LI T,et al.Effect of exogenous hydrogen sulfide on photosynthesis and antioxidant system of cucumber leaves under low temperature in solar-greenhouse[J].Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2016,43(3):462-472. | |
| 34 | 吴延朋,李洪旺,侯丽霞,等.ABC转运体位于H2S上游参与盐胁迫诱导的拟南芥气孔关闭[J].植物生理学报,2014,50(4):401-406. |
| WU Y P, LI H W, HOU L X,et al.ATP-Binding cassettee transporter signals salt-induced stomatal closure in Arabidopsis thaliana L.by H2S pathway[J].Plant Physiology Journal,2014,50(4):401-406. | |
| 35 | JIN Z P, PEI Y X.Physiological implications of hydrogen sulfide in plants:pleasant exploration behind its unpleasant odour[J].Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity,2015,2015:1-6. |
| [1] | 庄舒尧, 许恒博, 胡骁彧, 戴上, 张彦妮. 盐碱胁迫对彩叶矾根‘银扇’幼苗生长和生理特性的影响[J]. 植物研究, 2023, 43(4): 520-530. |
| [2] | 孙宇, 张艺腾, 成慧慧. 紫穗槐WRKY42基因耐盐碱性的功能研究[J]. 植物研究, 2023, 43(4): 612-621. |
| [3] | 刘建新, 刘瑞瑞, 刘秀丽, 欧晓彬, 贾海燕, 卜婷, 李娜. 外源硫化氢对盐碱胁迫下裸燕麦叶片有机酸和激素含量的影响[J]. 植物研究, 2023, 43(1): 76-89. |
| [4] | 刘建新, 刘瑞瑞, 刘秀丽, 贾海燕, 卜婷, 李娜. 外源H2S供体NaHS浸种对盐碱胁迫下裸燕麦种子萌发特性的影响[J]. 植物研究, 2021, 41(6): 870-877. |
| [5] | 刘建新, 欧晓彬, 王金成. 胞质Ca2+参与外源H2S促进盐碱胁迫下裸燕麦种子萌发[J]. 植物研究, 2020, 40(1): 58-65. |
| [6] | 刘志强, 曹纯玉, 李亚文, 渠娟娟, 贾云乾, 裴雁曦. H2S作为植物个体间交流的气体信号分子[J]. 植物研究, 2019, 39(5): 779-787. |
| [7] | 刘建新, 欧晓彬, 王金成. 外源H2O2对盐碱混合胁迫下裸燕麦幼苗生长和抗性生理的影响[J]. 植物研究, 2019, 39(2): 181-191. |
| [8] | 赵敏, 王玥萱, 徐运飞, 赵启安, 刘博, 杨宁. 干旱胁迫下拟南芥中H2S与ABA信号关系研究[J]. 植物研究, 2019, 39(1): 104-112. |
| [9] | 赵敏, 赵启安, 刘博, 王玥萱, 张莉环, 杨宁. H2S对干旱胁迫下高山离子芥的作用研究[J]. 植物研究, 2018, 38(6): 902-912. |
| [10] | 刘建新, 欧晓彬, 刘秀丽, 王金成. 过氧化氢缓解裸燕麦幼苗低温胁迫的主成分和隶属函数分析[J]. 植物研究, 2018, 38(5): 748-756. |
| [11] | 赵敏, 杨宁, 陈璐, 安炎黄, 李文领, 赵峰峰. 拟南芥中H2S与PLDα1响应干旱胁迫的作用研究[J]. 植物研究, 2018, 38(3): 406-414. |
| [12] | 刘建新, 王金成, 刘秀丽, 王风琴. 外源H2O2对混合盐碱胁迫下燕麦幼苗叶片脯氨酸积累和代谢途径的影响[J]. 植物研究, 2016, 36(3): 427-433. |
| [13] | 刘建新1,2;王金成1,2;王瑞娟1,2;贾海燕1,2. 混合盐碱胁迫下裸燕麦的种子萌发和幼苗逆境生理特征[J]. 植物研究, 2016, 36(2): 224-231. |
| [14] | 赵玉琳1;杨桂燕1,2;于丽丽1;郭宇聪1;赵震1;高彩球1*. 甲基紫精胁迫下转TheIF1A基因烟草的活性氧代谢[J]. 植物研究, 2016, 36(1): 129-133. |
| [15] | 刘建新;王金成;王瑞娟;贾海燕. KCl对NaCl胁迫下燕麦幼苗活性氧代谢和渗透溶质积累的影响[J]. 植物研究, 2015, 35(2): 233-239. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||