Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (1): 88-97.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2025.01.010
• Original Paper • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xiaopeng MU( ), Xiaoyan MOU, Xinliang QI, Jing WANG, Yu YANG, Jiancheng ZHANG, Pengfei WANG
), Xiaoyan MOU, Xinliang QI, Jing WANG, Yu YANG, Jiancheng ZHANG, Pengfei WANG
Received:2024-08-22
Online:2025-01-20
Published:2025-01-23
Contact:
Xiaopeng MU
E-mail:15110671026@163.com
CLC Number:
Xiaopeng MU, Xiaoyan MOU, Xinliang QI, Jing WANG, Yu YANG, Jiancheng ZHANG, Pengfei WANG. Effects of Different Growth Retardant Treatments on Rooting of Prunus humilis Rhizome Cuttings[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(1): 88-97.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://bbr.nefu.edu.cn/EN/10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2025.01.010
Table 2
Primer design information
基因名称 Gene name | 上游引物(5′→3′) Forward primer sequence(5′→3′) | 下游引物(5′→3′) Reverse primer sequence(5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| ChActin | GCAGCGACTGAAGACATACAAG | GGTGGCATTAGCAAGTTCCTC |
| ChTAA1 | TTGTAGTAGCAGGCTGGCAT | TCTTCCTTGAGTCACCGCAT |
| ChTAA2 | ATGCGGTGACTCAAGGAAGA | TGGAAGAGAGTGCGTGAAGT |
| ChYUC1 | CCGAAATGGGAGTGTTGTCC | CACGGTTGTCATCCACAGTC |
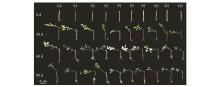
Fig.1
Rooting process of P. humilis rhizome cuttings treated with different growth retardantsCK represented the control;S1,S2 and S3 represented 25 mg?L-1,50 mg?L-1and 100 mg?L-1 S3307;P1,P2 and P3 represented 100 mg?L-1,200 mg?L-1 and 300 mg?L-1 PP333;D1,D2 and D3 represented 100 mg?L-1,200 mg?L-1and 300 mg?L-1 DPC.
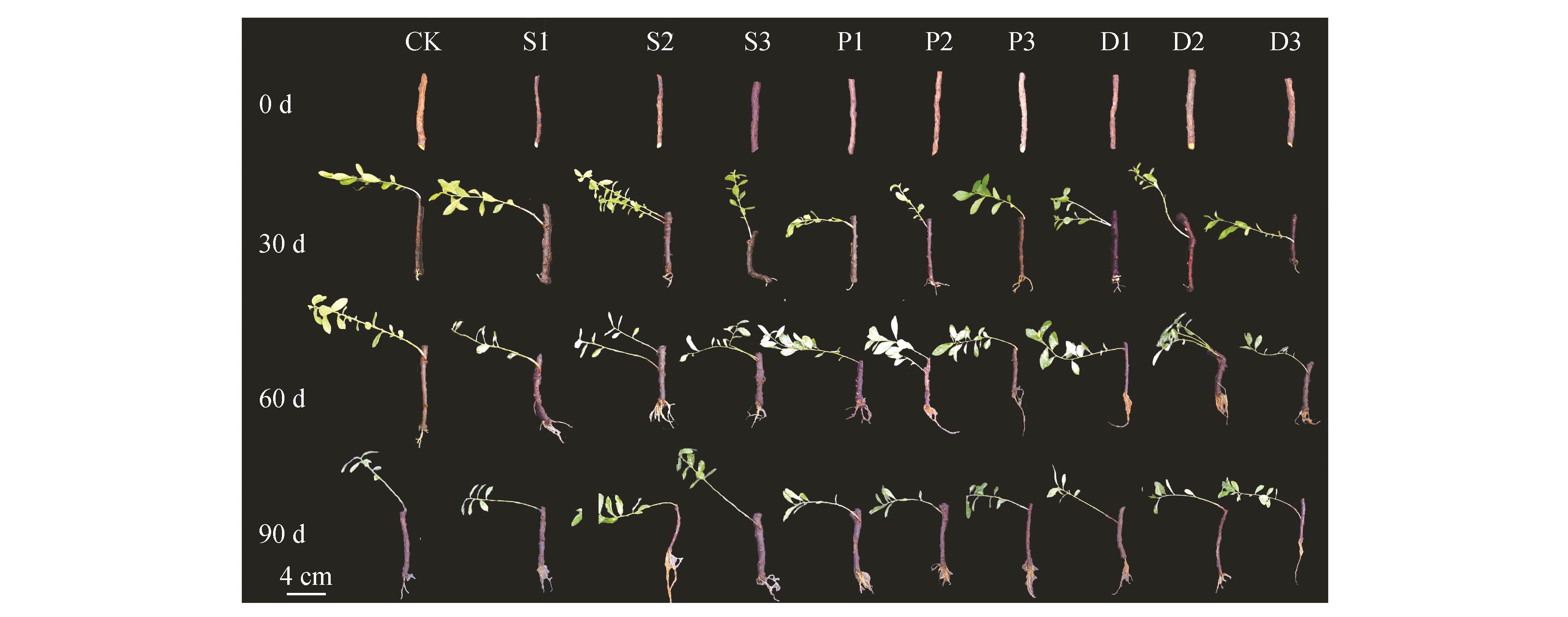

Table 3
Effects of different growth retardant treatments on bud germination and rooting indices of P. humilis rhizomes cutting
处理 Treatment | 发芽率 Bud germination rate/% | 生根率 Rooting rate/% | 总根长 Total root length/cm | 平均根直径 Average root diameter/mm | 根表面积 Root surface area/cm2 | 根系体积 Root volume /cm3 | 平均根数 Mean root number | 平均根长 Average root length/cm | 最大根长 The longest root length/cm | 根系效果指数 Root index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 44.12±0.05e | 22.16±0.03e | 34.18±1.40h | 1.55±0.01b | 16.85±1.16h | 0.73±0.06cd | 8.14±0.91d | 3.46±0.32bc | 6.87±0.35bc | 0.70±0.06e |
| S1 | 58.33±0.06bc | 43.33±0.04c | 36.60±1.02h | 1.21±0.02d | 8.88±0.66i | 0.30±0.12e | 15.00±1.17ab | 3.97±0.33b | 15.07±1.12a | 1.49±0.23cd |
| S2 | 80.02±0.02a | 78.02±0.02a | 129.11±1.49c | 1.17±0.02d | 47.93±2.00b | 1.51±0.08a | 16.26±0.34ab | 5.33±0.70a | 4.78±0.17d | 2.17±0.33ab |
| S3 | 79.17±0.01a | 63.33±0.01b | 38.66±1.26h | 1.74±0.06a | 22.74±2.82f | 1.04±0.07bc | 14.55±2.01b | 2.83±0.38c | 6.75±0.31bc | 1.04±0.26de |
| P1 | 67.00±0.03b | 57.10±0.01b | 158.23±1.84b | 0.79±0.02f | 38.65±2.53cd | 1.03±0.07bc | 16.22±0.86ab | 5.71±0.54a | 5.94±0.17c | 2.23±0.53ab |
| P2 | 58.33±0.03bc | 35.83±0.03d | 87.34±1.81d | 1.06±0.05e | 29.73±1.19e | 0.61±0.45d | 11.37±3.44c | 3.94±0.22b | 6.32±0.51bc | 1.11±0.27de |
| P3 | 55.12±0.06cd | 22.50±0.02e | 76.45±1.82e | 1.37±0.05c | 35.08±4.69d | 0.80±0.16bcd | 15.47±2.36ab | 4.28±0.42b | 6.94±0.22b | 1.73±0.16bc |
| D1 | 64.00±0.03bc | 56.70±0.03b | 169.62±3.37a | 1.07±0.04e | 59.63±3.48a | 1.51±0.23a | 18.10±0.95a | 5.66±0.51a | 6.97±0.16b | 2.43±0.22a |
| D2 | 56.67±0.03cd | 28.33±0.02e | 80.13±1.64e | 1.42±0.04c | 40.29±4.18c | 1.07±0.04b | 17.22±1.42ab | 2.80±0.36c | 4.26±0.54d | 1.26±0.13cd |
| D3 | 48.33±0.03de | 22.50±0.02e | 57.13±2.19f | 0.6±0.08h | 11.83±1.02i | 0.18±0.02f | 10.36±1.06cd | 2.73±0.48c | 3.83±0.21d | 0.71±0.13e |
Table 4
Effects of different growth retardant treatments on morphological indices of P. humilis rhizome cutting seedlings
处理 | 株高 Plant height/cm | 新生枝茎粗 New branch stem diameter/mm | 叶形指数 Leaf shape index | 叶面积 Leaf area/cm2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 20.45±0.65a | 1.75±0.09b | 2.82±0.14a | 4.37±0.15a |
| S1 | 16.47±0.63bc | 1.53±0.21d | 2.46±0.11bcd | 4.20±0.06ab |
| S2 | 16.83±0.55b | 1.52±0.05d | 2.26±0.16bcd | 4.12±0.61ab |
| S3 | 11.76±0.41f | 1.38±0.06e | 2.23±0.05cd | 3.34±0.27cd |
| P1 | 12.15±0.37e | 1.71±0.10c | 2.55±0.21ab | 3.79±0.35bc |
| P2 | 12.05±0.52e | 1.38±0.02e | 2.41±0.22bcd | 3.23±0.39d |
| P3 | 14.66±0.51d | 1.34±0.05f | 2.30±0.07bcd | 2.38±0.11e |
| D1 | 16.82±0.82b | 1.87±0.05a | 2.50±0.23bc | 3.01±0.27d |
| D2 | 15.92±0.65bcd | 1.77±0.06b | 2.41±0.15bcd | 2.99±0.26d |
| D3 | 11.00±0.59f | 1.73±0.03bc | 2.17±0.13d | 2.97±0.12d |
| 1 | 何建龙,王占军,蒋齐,等.不同生根剂对欧李嫩枝扦插生根的影响[J].宁夏农林科技,2021,62(8):14-17. |
| HE J L, WANG Z J, JIANG Q,et al.Effect of different rooting reagent treatment on softwood cutting of Cerasus humilis [J].Journal of Ningxia Agriculture and Forestry Science and Technology,2021,62(8):14-17. | |
| 2 | 吴春燕,韩潇怡,吴俊英,等.欧李营养价值及开发利用研究进展[J].中国果树,2024(2):1-5,25. |
| WU C Y, HAN X Y, WU J Y,et al.Research progress on nutritional value and development and utilization of Cerasus humilis(Bge.) Sok.[J].China Fruits,2024(2):1-5,25. | |
| 3 | DONG S, ZHOU Y, WANG J C,et al.Four new compounds from the fruits of Chinese dwarf cherry (Prunus humilis Bunge)[J].Natural Product Research,2022,38(7):1207-1215. |
| 4 | FU H B, MU X P, WANG P F,et al.Fruit quality and antioxidant potential of Prunus humilis Bunge accessions[J].PLoS One,2020,15(12):e0244445. |
| 5 | 杜俊杰,中国特有林果:欧李[M].北京:中国农业科学技术出版社,2023. |
| DU J J. Prunus humilis:a unique fruity shrub in China[M].Beijing:China Agricultural Science and Technology Press,2023. | |
| 6 | 付鸿博,王鹏飞,徐豆,等.农大4号与DS-1欧李正、反交F1代果实品质的遗传变异分析[J].核农学报,2021,35(10):2223-2233. |
| FU H B, WANG P F, XU D,et al.Heredity and variation analysis of fruit quality in the F1 generation from reciprocal crosses between Nongda 4 and DS-1 Chinese dwarf cherry (Cerasus humilis)[J].Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences,2021,35(10):2223-2233. | |
| 7 | 王鹏飞,贾璐婷,杜俊杰,等.黄土丘陵沟壑区欧李栽植对土壤质量改良作用的评价[J].草业学报,2017, 26(3):65-74. |
| WANG P F, JIA L T, DU J J,et al.Improvement of soil quality by Chinese dwarf cherry cultivation in the Loess Plateau steep hill region [J].Acta Prataculturae Sinica,2017,26(3):65-75. | |
| 8 | JI Y H, CHEN G X, ZHENG X Y,et al.Comprehensive transcriptome reveals an opposite regulatory effect of plant growth retardants in controlling seedling overgrowth between roots and shoots[J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2019,20(13):3307. |
| 9 | 贾犇.欧李盒插繁殖关键影响因子的研究[D].太谷:山西农业大学,2021. |
| JIA B.Study on the key factors affecting of Cerasus humilis cuttings in closed box environment[D].Taigu:Shanxi Agricultural University,2021 | |
| 10 | 吴金群,韦建杏,田乐宇,等.植物生长调节剂对红果黄檀扦插生根的影响[J].热带农业科学,2024, 44(1):56-61. |
| WU J Q, WEI J X, TIAN L Y,et al.Effect of plant growth regulators on cutting rooting of Dalbergia tsoi [J].Chinese Journal of Tropical Agriculture,2014,44(1):56-61. | |
| 11 | 李合生.植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2000:164-182. |
| LI H S.Principles and techniques of plant physiology and biochemical experiments[M].Beijing:Higher Education Press,2000:164-182. | |
| 12 | WANG Q, QIN G C, CAO M. et al.A phosphorylation-based switch controls TAA1-mediated auxin biosynthesis in plants[J].Nature Communications,2020,11(1):679. |
| 13 | 许丽娟.生长抑制剂对大叶黄杨枝叶生长的生理调控机制[D].北京:北京林业大学,2020. |
| XU L J.Physiological mechanisims of growth inhibitors on controlling shoot and leaf growth of Euonymus japonicus Thunb[D].Beijing:Beijing Forestry University,2020. | |
| 14 | MU H Z, JIN X H, MA X Y,et al.Ortet age effect,anatomy and physiology of adventitious rooting in Tilia mandshurica softwoodcuttings[J].Forests,2022,13(9):1427. |
| 15 | LI X L, YE L, ZHANG X P,et al.Root‐tip cutting and uniconazole treatment improve the colonization rate of Tuber indicum on Pinus armandii seedlings in the greenhouse[J].Microbial Biotechnology, 2020,13(2):535-547. |
| 16 | 何倩倩.植物生长调节剂影响欧李嫩枝扦插生根的机理研究[D].太谷:山西农业大学,2022. |
| HE Q Q.Study on the mechanism of plant growth regulators affecting the rooting of Cerasus humilis softwood cutting[D].Taigu:Shanxi Agricultural University,2022. | |
| 17 | 杨贞,张永春,李心,等.不同浓度生长调节剂对矾根扦插生根的影响[J].上海农业学报,2023,39(1):66-71. |
| YANG Z, ZHANG Y C, LI X,et al.Effects of different growth regulator on cutting rooting of Heuchera spp[J].Acta Agriculturae Shanghai,2023,39(1):66-71. | |
| 18 | 柳政戎,马明呈,吕才忠,等.不同处理对陕甘花楸扦插生根的影响[J].青海农林科技,2024(1):63-69. |
| LIU Z R, MA M C, LÜ C Z,et al.Effects of different treatments on cuttings rooting of Sorbus koehneana schneid[J].Science and Technology of Qinghai Agriculture and Forestry,2024(1):63-69. | |
| 19 | 姜英,彭彦,李志辉,等.多效唑、烯效唑和矮壮素对金钱树的矮化效应[J].园艺学报,2010,37(5):823-828. |
| JIANG Y, PENG Y, LI Z H,et al.Effects of paclobutrazol,uniconazole and chlorcholinchlorid on dwarfing of Zamioculcasz amiifolia [J].Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2010,37(5):823-828. | |
| 20 | 董志君,张建军,范永明,等.3种植物生长延缓剂对盆栽芍药的矮化效应[J].东北林业大学学报,2020, 48(9):62-66. |
| DONG Z J, ZHANG J J, FAN Y M,et al.Dwarfing effects of paclobutrazol,unicnazle and chlormequat on potted Paeonia lactiflora [J].Journal of Northeast Forestry University,2020,48(9):62-66. | |
| 21 | 黄晓霜,芦斌,郑永强,等.喷施植物生长延缓剂对北美冬青春梢生长的影响[J].北方园艺,2024(5):68-74. |
| HUANG X S, LU B, ZHENG Y Q,et al.Effects of spraying plant growth retarders on growth of spring tips Ilex verticillata [J].Northern Horticulture,2024(5):68-74. | |
| 22 | SUN D, ZHAO X L, AI J,et al.Study on the rooting physiological mechanism of Schisandra chinensis(Turcz.) Baill. green-branched cuttings[J].Forests,2023,14(7):1365. |
| 23 | 何倩倩,张婕,穆霄鹏,等.叶面喷施植物生长调节剂对欧李嫩枝扦插生根与生理变化的影响[J].植物生理学报,2024,60(1):108-116. |
| HE Q Q, ZHANG J, MU X P,et al.Effects of foliar spraying plant growth regulator on rooting and physiological changes of Cerasus humilis softwood cuttings[J].Plant Physiology Journal,2024,60(1):108-116. | |
| 24 | LI Z Y, SHI Y F, ZHAO M Q,et al.Plant growth regulators improve the growth and physiology of transplanted Thalassia Hemprichii fragments[J].Frontiers in Marine Science,2024,11:1334937. |
| 25 | UDDIN S, MUNIR M Z, LARRIBA E,et al.Temporal profiling of physiological,histological,and transcriptomic dissection during auxin-induced adventitious root formation in tetraploid Robinia pseudoacacia micro-cuttings[J].Planta,2024,259:66. |
| 26 | ZHAO Y Q, CHEN Y J, JIANG C,et al.Exogenous hormones supplementation improve adventitious root formation in woody plants[J].Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology,2022,10:1009531. |
| 27 | 李世民,郑鑫华,段华超,等.ABT-1处理对树头菜扦插生根及生理生化特性的影响[J].江西农业大学学报,2021,43(1):116-125. |
| LI S M, ZHENG X H, DUAN H C,et al.Effects of ABT-1 treatment on rooting capacity and physiological and biochemical characteristic of Crateva unilocalaris cuttings[J].Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis,2021,43(1):116-125. | |
| 28 | POULET A, KRIECHBAUMER V.Bioinformatics analysis of phylogeny and transcription of TAA/YUC auxin biosynthetic genes[J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2017,18(8):1791. |
| 29 | 杨庆春,李国雷.不同植物生长调节剂对栓皮栎嫩枝扦插的影响[J].东北林业大学学报,2017,45(6):12-16. |
| YANG Q C, LI G L.Effects of plant growth regulators on the rooting of softwood cutting of Quercus variabilis [J].Journal of Northeast Forestry University,2017,45(6):12-16. | |
| 30 | HU D, HE X R, MA Y Z,et al.Effects of ABT on the morphogenesis and inclusions of Taxus chinensis(pilger) Rehd f. baokangsis cutting rooting[J].Notulae Botanicae Horti Agrobotanici Cluj-Napoca,2021,49(2):12200. |
| [1] | Galip NARGIZA, Yuxin XIAO, Boyi SONG, Weiwei ZHUANG. Effects of “Fertilizer Island” Effect of Desert Plants on Spatial Distribution of Soil Nutrients [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(6): 868-880. |
| [2] | Liben PAN, Xue YAN, Jia LIU, Kexin WU, Yang LIU, Shaochong LIU. Physiological Characteristics of Early Spring Flowering Plants under Northeast Forest [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(4): 657-666. |
| [3] | Guobin Liu, Ting Liao, Ye Wang, Liqin Guo, Jinzhe Zhao, Yanwu Yao, Jun Cao. Regulation Mechanism of Endogenous Hormones in Adventitious Roots Formation of Platycladus orientalis ‘Beverleyensis’ [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(2): 278-288. |
| [4] | Yang-Jing ZHAO, Nan TANG, Dao-Cheng TANG, Jing ZHANG. An Optimized HPLC Procedure for Analyzing Three Endogenous Hormones in Tulip Bulbs [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(1): 130-137. |
| [5] | WANG Ning, DONG Ying-Ying, YUAN Mei-Li, WANG Ya-Nan, ZENG Sheng-Yun. Effect of Warm Water Soaking on Protective Enzyme Activity and Endogenous Hormones Content of Eucommia ulmoides Seed During Different Stages of Germination [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(4): 523-529. |
| [6] | ZHENG Ya-Qiong, ZHAI Jun-Tuan, CHEN Jia-Li, HAN Zhan-Jiang, JIAO Pei-Pei, LI Zhi-Jun. Seasonal Variations of Clonal Propagation Characteristics of Populus pruinosa Schrenk,Organ Nutrient and Soil Fertility, and Their Coupling Associations in the Forest and Forest Edges [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2019, 39(3): 347-357. |
| [7] | CHEN Guo-Ping, ZU Li-Hong, GAO Zhang-Ying, ZHOU Mei-Li, QIAO Yan-Yun, ZHAO Tie-Jian, FENG Xiao-Mei, SHI Fu-Chen. The Characteristics of Forest Floor Nutrients and Soil Fertility Assessment for Deciduous Broad-Leaved Forest with Different Site Conditions [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2016, 36(6): 878-885. |
| [8] | YANG Liu, WANG Le, XIE Zhong-Kui, GUO Zhi-Hong, ZHANG Yu-Bao. Influence of Endogenous IAA and GA3 on in vitro Lily Seedling Growth [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2016, 36(5): 760-767. |
| [9] | LI Hui, WANG Bai-Tian, CAO Yuan-Bo, LIU Qing-Qing, LI De-Ning. Difference Feature of Planted Vegetation Biomass and Litter Biomass for Three Plantations and Their Relationship with Soil Nutrients in Lvliang Mountainous Region [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2016, 36(4): 573-580. |
| [10] | LIU Jian-Cai;CHEN Jin-Ling;JIN Guang-Ze*. Response of Soil Organic Carbon and Nutrients to Simulated Nitrogen Deposition in Typical Mixed Broadleaved-Korean Pine Forest [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2014, 34(1): 121-130. |
| [11] | DENG Shao-Li;JIANG Guo-Bin*;REN Xian;JIN Hua;MA Jin-Long;ZOU Ji-Xiang. Responses of Endogenous Hormones to Drought Stress in the Apoplast of Populus [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2013, 33(6): 690-696. |
| [12] | SUN Hong-Mei;LI Tian-Lai*;LI Yun-Fei. Changes of endogenous hormones in Lilium davidii var. unicolor bulbs during bulb development and storage at low temperature for dormancy release [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2006, 26(5): 570-576. |
| [13] | ZHAO Wen, DONG Shuang-lin, SHENTU Qing-chun, ZHANG Zhao-qi, DAI Yun-di. STUDIES OF AQUATIC MACROPHYTES IN SALINE-ALKALINE PONDS [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2001, 21(1): 140-146. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||