Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (3): 470-480.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2024.03.016
• Plant synecology • Previous Articles
Lijuan LUO1, Qingxiao YIN2, Wei SUN2, Xi ZAN2, Qingmao SHI2, Jing ZHANG3, Yamei CHEN1( ), Xiao XU1
), Xiao XU1
Received:2023-10-31
Online:2024-05-20
Published:2024-05-14
Contact:
Yamei CHEN
E-mail:YameiChen316@163.com
CLC Number:
Lijuan LUO, Qingxiao YIN, Wei SUN, Xi ZAN, Qingmao SHI, Jing ZHANG, Yamei CHEN, Xiao XU. Soil Enzyme Activities and Stoichiometric Characteristics of Different Plant Communities under Natural Fagus Forest in Micang Mountain Nature Reserve, Sichuan[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(3): 470-480.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://bbr.nefu.edu.cn/EN/10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2024.03.016
Table 1
Two-way ANOVA analysis of soil physicochemical properties at different plant communities and soil depth in the understory of Fagus forest
变异来源 Source of variation | 自由度 df | pH | 土壤含水量 SMC | 全碳 TC | 全氮 TN | 全磷 TP | 土壤碱解氮 SAN | 土壤速效磷 SAP | 碳氮比 C∶N | 碳磷比 C∶P | 氮磷比 N∶P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PT | 2 | 47.992*** | 55.019*** | 29.178*** | 32.595*** | 9.807** | 4.483* | 10.778*** | 87.561*** | 20.356*** | 9.838** |
| SD | 1 | 0.021 | 1540.491*** | 4125.637*** | 1 617.784*** | 39.437*** | 109.315*** | 44.663*** | 6.752* | 16.895*** | 13.174** |
| PT×SD | 2 | 4.585* | 93.914*** | 18.824*** | 4.919* | 0.674 | 1.467 | 2.114 | 6.672** | 0.010 | 0.138 |
Table 2
Soil physicochemical properties of different plant communities in the understory of Fagus forest
土壤性质 Soil property | 土壤深度 Soil depth/cm | 林下植物群落类型 Types of understory plant communities | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
无植物群落 No plant community | 野扇花 Sarcococca ruscifolia | 箭竹 Fargesia spathacea | ||
| pH | 0<h≤10 cm | 5.05±0.28Ab | 5.56±0.11Aa | 5.72±0.06Aa |
| 10 cm<h≤20 cm | 5.23±0.03Ac | 5.40±0.06Ab | 5.67±0.02Aa | |
土壤含水量 SMC/% | 0<h≤10 cm | 40.79±0.28Ab | 44.85±0.39Aa | 44.83±0.19Aa |
| 10 cm<h≤20 cm | 37.38±0.23Ba | 37.54±0.93Ba | 36.01±0.23Bb | |
全碳 TC/(g·kg-1) | 0<h≤10 cm | 32.80±0.58Aa | 33.22±0.51Aa | 32.82±0.78Aa |
| 10 cm<h≤20 cm | 21.14±0.22Bb | 22.22±0.56Ba | 19.10±0.20Bc | |
全氮 TN/(g·kg-1) | 0<h≤10 cm | 3.40±0.07Aa | 3.12±0.08Ac | 3.28±0.08Ab |
| 10 cm<h≤20 cm | 2.30±0.07Ba | 2.04±0.05Bb | 2.00±0.10Bb | |
全磷 TP/(g·kg-1) | 0<h≤10 cm | 0.78±0.13Aab | 0.65±0.06Ab | 0.86±0.10Aa |
| 10 cm<h≤20 cm | 0.59±0.05Aab | 0.50±0.05Bb | 0.62±0.09Ba | |
土壤碱解氮 SAN/(mg·kg-1) | 0<h≤10 cm | 265.67±24.53Aa | 293.57±38.68Aa | 293.22±15.86Aa |
| 10 cm<h≤20 cm | 195.65±0.32Bb | 223.38±15.45Ba | 195.56±0.25Bb | |
土壤速效磷 SAP/(mg·kg-1) | 0<h≤10 cm | 10.04±0.78Aa | 5.93±1.00Ab | 8.81±1.32Aa |
| 10 cm<h≤20 cm | 6.10±3.25Ba | 3.29±0.91Ba | 3.09±1.48Ba | |
碳氮比 C∶N | 0<h≤10 cm | 9.65±0.12Ac | 10.65±0.36Aa | 9.99±0.13Ab |
| 10 cm<h≤20 cm | 9.21±0.19Bc | 10.87±0.18Aa | 9.55±0.31Bb | |
碳磷比 C∶P | 0<h≤10 cm | 42.80±5.77Ab | 51.17±5.05Aa | 38.38±4.43Ab |
| 10 cm<h≤20 cm | 35.97±3.75Ab | 44.41±4.18Aa | 31.09±4.36Bb | |
氮磷比 N∶P | 0<h≤10 cm | 4.44±0.62Aab | 4.81±0.54Aa | 3.83±0.41Ab |
| 10 cm<h≤20 cm | 3.91±0.37Aa | 4.07±0.32Ba | 3.25±0.46Ab | |
Fig.1
Soil enzyme activities of different plant communities in the understory of Fagus forestNS.No plant community;SR.Sarcococca ruscifolia;FS.Fargesia spathacea;Different lowercase letters indicated significant differences in soil enzyme activity among different understory plant communities. X indicated significant differences in soil enzyme activity at different depths of the same understory plant community;PT.Types of understory plant communities;SD.Soil depth;*P<0.05;**P<0.01;***P<0.001;The same as below.
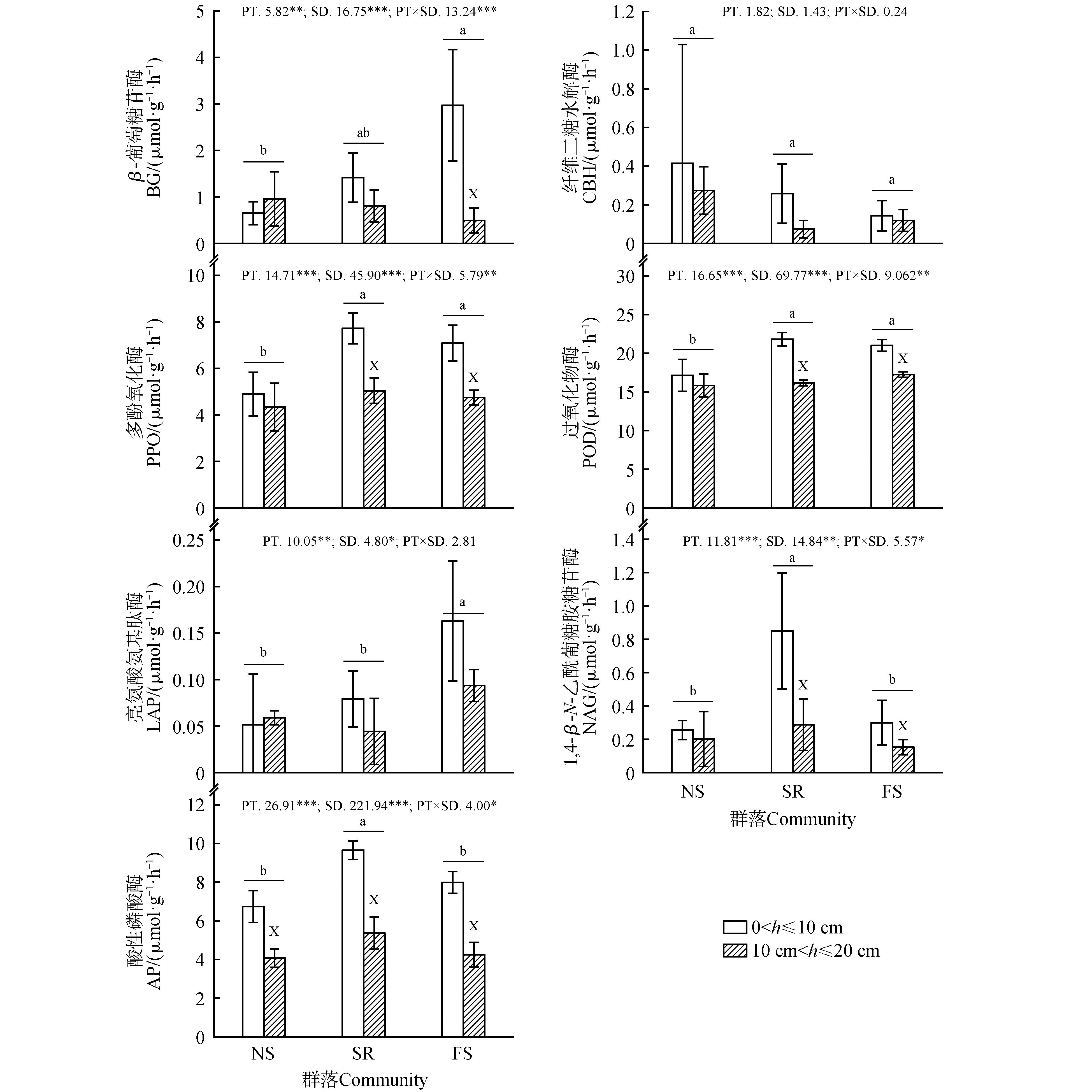
Table 3
Correlation coefficient between soil physicochemical properties and soil enzyme activities and enzyme stoichiometric characteristics
因子 Factor | pH | SMC | TC | TN | TP | SAN | SAP | C∶N | C∶P | N∶P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BG | 0.386* | 0.626** | 0.472** | 0.456* | 0.493** | 0.556** | 0.339 | 0.087 | 0.080 | 0.057 |
| CBH | -0.307 | 0.118 | 0.200 | 0.226 | 0.036 | 0.122 | 0.264 | -0.098 | 0.162 | 0.236 |
| POD | 0.583** | 0.822** | 0.681** | 0.590** | 0.526** | 0.648** | 0.203 | 0.339 | 0.281 | 0.186 |
| PPO | 0.450* | 0.807** | 0.641** | 0.534** | 0.370* | 0.642** | 0.149 | 0.430* | 0.381* | 0.281 |
| LAP | 0.447* | 0.417* | 0.245 | 0.250 | 0.308 | 0.249 | 0.259 | -0.056 | -0.051 | -0.053 |
| NAG | 0.177 | 0.570** | 0.485** | 0.360 | 0.000 | 0.544** | 0.084 | 0.446* | 0.618** | 0.535** |
| AP | 0.201 | 0.916** | 0.857** | 0.751** | 0.410* | 0.833** | 0.327 | 0.479** | 0.605** | 0.532** |
| EC∶EN | 0.052 | 0.000 | -0.056 | -0.002 | 0.136 | -0.038 | 0.048 | -0.199 | -0.194 | -0.141 |
| EC∶EP | 0.270 | 0.400* | 0.236 | 0.235 | 0.292 | 0.328 | 0.259 | -0.002 | 0.006 | 0.006 |
| EN∶EP | 0.194 | 0.418* | 0.315 | 0.233 | 0.055 | 0.378* | 0.181 | 0.286 | 0.332 | 0.265 |
| CQI | -0.146 | -0.506** | -0.391* | -0.377* | -0.320 | -0.472** | -0.330 | -0.079 | -0.166 | -0.169 |
| VL | 0.120 | 0.105 | 0.014 | 0.057 | 0.181 | 0.055 | 0.104 | -0.161 | -0.152 | -0.110 |
| VA | -0.202 | -0.405* | -0.303 | -0.223 | -0.067 | -0.370* | -0.170 | -0.278 | -0.303 | -0.233 |
| 1 | NILSSON M C, WARDLE D A.Understory vegetation as a forest ecosystem driver:evidence from the northern Swedish boreal forest[J].Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment,2005,3(8):421-428. |
| 2 | YANG Y, ZHANG X Y, WANG H M,et al.How understory vegetation affects the catalytic properties of soil extracellular hydrolases in a Chinese fir(Cunninghamia lanceolata) forest[J].European Journal of Soil Biology,2019,90:15-21. |
| 3 | 张坤,包维楷,杨兵,等.林下植被对土壤微生物群落组成与结构的影响[J].应用与环境生物学报,2017,23(6):1178-1184. |
| ZHANG K, BAO W K, YANG B. et al.The effects of understory vegetation on soil microbial community composition and structure[J].Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology,2017,23(6):1178-1184. | |
| 4 | 朱小林,梁辰飞,蔡锡安,等.尾叶桉林下5种木本植物土壤微生物群落特征[J].生态环境学报,2015,24(4):617-623. |
| ZHU X L, LIANG C F, CAI X A,et al.Soil Microbial Community characteristics of 5 tree species in Eucalyptus urophylla plantation[J].Ecology and Environment,2015,24(4):617-623. | |
| 5 | 杨洋,王继富,张心昱,等.凋落物和林下植被对杉木林土壤碳氮水解酶活性的影响机制[J].生态学报,2016,36(24):8102-8110. |
| YANG Y, WANG J F, ZHANG X Y,et al.Mechanism of litter and understory vegetation effects on soil carbon and nitrogen hydrolase activities in Chinese fir forests[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2016,36(24):8102-8110. | |
| 6 | ZHAO F Z, WANG J Y, ZHANG L,et al.Understory plants regulate soil respiration through changes in soil enzyme activity and microbial C,N and P stoichiometry following afforestation[J].Forests,2018,9(7):436. |
| 7 | SINSABAUGH R L, FOLLSTAD SHAH J J.Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry and ecological theory[J].Annual Review of Ecology,Evolution,and Systematics,2012,43(1):313-343. |
| 8 | 许伟佳,陈林,李敬王,等.秸秆还田配施不同激发剂对潮土有机碳和微生物群落的影响[J].江苏农业学报,2023,39(2):383-392. |
| XU W J, CHEN L, LI J W,et al.Effects of straw returning combined with different activators on organic carbon and microbial community in fluvo-aquic soil[J].Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences,2023,39(2):383-392. | |
| 9 | SINSABAUGH R L, LAUBER C L, WEINTRAUB M N,et al.Stoichiometry of soil enzyme activity at global scale[J].Ecology Letters,2008,11(11):1252-1264. |
| 10 | 何艺玲,傅懋毅.人工林林下植被的研究现状[J].林业科学研究,2002,15(6):727-733. |
| HE Y L, FU M Y.Review of studies on understorey of plantations[J].Forest Research,2002,15(6):727-733. | |
| 11 | 张贾宇,佘婷,鄂晓伟,等.杨树人工林幼林阶段林下植被管理对土壤微生物生物量碳、氮酶活性的影响[J].生态学报,2021,41(24):9898-9909. |
| ZHANG J Y, SHE T, E X W,et al.Effects of understory vegetation management on soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen and extracellular enzyme activities in the early stages of poplar plantation[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2021,41(24):9898-9909. | |
| 12 | YANG Y, ZHANG X Y, ZHANG C,et al.Understory vegetation plays the key role in sustaining soil microbial biomass and extracellular enzyme activities[J].Biogeosciences,2018,15(14):4481-4494. |
| 13 | 刘仁,袁小兰,刘俏,等.林下植被去除对杉木人工林土壤酶活性及其化学计量比的影响[J].林业科学研究,2020,33(5):121-128. |
| LIU R, YUAN X L, LIU Q,et al.Effects of understory vegetation removal on soil hydrolytic enzyme activity and stoichiometric ratio of Chinese fir plantation[J].Forest Research,2020,33(5):121-128. | |
| 14 | LIU Q, WANG F C, LIU R,et al.Aboveground litter input alters the effects of understory vegetation removal on soil microbial communities and enzyme activities along a 60-cm profile in a subtropical plantation forest[J].Applied Soil Ecology,2022,176:104489. |
| 15 | 郑琳琳,赵琼,曾德慧.林下植被去除对樟子松人工林土壤酶活性的影响[J].生态学杂志,2017,36(11):3056-3063. |
| ZHENG L L, ZHAO Q, ZENG D H.Effects of understory removal on soil enzyme activities in a Pinus sylvestris var.mongolica plantation in Horqin Sandy Land[J].Chinese Journal of Ecology,2017,36(11):3056-3063. | |
| 16 | 高雨秋,戴晓琴,王建雷,等.亚热带人工林下植被根际土壤酶化学计量特征[J].植物生态学报,2019,43(3):258-272. |
| GAO Y Q,DAI X Q,WANG J L,et al,Characteristics of soil enzymes stoichiometry in rhizosphere of understory vegetation in subtropical forest plantations[J].Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology,2019,43(3):258-272. | |
| 17 | 陈坚.米仓山自然保护区水青冈属(Fagus)资源调查报告[J].中国野生植物资源,2014,33(2):47-52. |
| CHEN J.Report of investigation on Fagus of micangshan nature reserve[J].Chinese Wild Plant Resources,2014,33(2):47-52. | |
| 18 | 王霞.水青冈群落更新研究进展[J].温带林业研究,2023,6(1):50-54. |
| WAGN X.Research progress on regeneration of Fagus community[J].Journal of Temperate Forestry Research,2023,6(1):50-54. | |
| 19 | 蒙振思,向卫,黄尤优,等.四川米仓山自然保护区台湾水青冈种群与土壤化学特征的关系研究[J].西北植物学报,2016,36(8):1671-1677. |
| MENG Z S, XIANG W, HUANG Y Y,et al.Soil chemical properties as a predictor of population properties of Fagus hayatae in Micangshan Nature Reserve,Sichuan[J].Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica,2016,36(8):1671-1677. | |
| 20 | 何毓蓉.米仓山林区土壤的肥力特征及保护研究[J].水土保持学报,1991(4):73-79. |
| HE Y R.Study on protective fertility and properties of soil fertility in forest region of the Micang Mountain[J].Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,1991(4):73-79. | |
| 21 | 鲁如坤.土壤农业化学分析方法[M].北京:中国农业科技出版社,2000. |
| LU R K.Soil agrochemical analysis methods[M].Beijing:China Agricultural Science and Technology Press,2000. | |
| 22 | SINSABAUGH R L, ANTIBUS R K, LINKINS A E,et al.Wood decomposition over a first-order watershed:mass loss as a function of lignocellulase activity[J].Soil Biology and Biochemistry,1992,24(8):743-749. |
| 23 | SINSABAUGH R L, ANTIBUS R K, LINKINS A E,et al.Wood decomposition:nitrogen and phosphorus dynamics in relation to extracellular enzyme activity[J].Ecology,1993,74(5):1586-1593. |
| 24 | HILL B H, ELONEN C M, HERLIHY A T,et al.Microbial ecoenzyme stoichiometry,nutrient limitation,and organic matter decomposition in wetlands of the conterminous United States[J].Wetlands Ecology and Management,2018,26:425-439. |
| 25 | SINSABAUGH R L, FOLLSTAD SHAH J J.Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry of recalcitrant organic matter decomposition:the growth rate hypothesis in reverse[J].Biogeochemistry,2011,102:31-43. |
| 26 | MOORHEAD D L, RINKES Z L, SINSABAUGH R L,et al.Dynamic relationships between microbial biomass,respiration,inorganic nutrients and enzyme activities:informing enzyme-based decomposition models[J].Frontiers in Microbiology,2013,4:223. |
| 27 | 罗美,周运超,唐凤华.不同植被下碳酸盐岩石发育形成土壤属性研究[J].中国岩溶,2023,42(2):277-289. |
| LUO M, ZHOU Y C, TANG F H.Soil properties of carbonate rocks under different vegetation types[J].Carsologica Sinica,2023,42(2):277-289. | |
| 28 | 杨媛媛,陈奇伯,黎建强,等.滇中地区常绿阔叶林土壤酶活性与理化因子通径分析[J].中南林业科技大学学报,2017,37(3):86-91. |
| YANG Y Y, CHEN Q B, LI J Q,et al.Path analysis of soil enzyme activity and soil chemical-physical factors of evergreen broad-leaved forest in middle Yunnan region,China[J].Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology,2017,37(3):86-91. | |
| 29 | 庞学勇,刘世全,刘庆,等.川西亚高山针叶林植物群落演替对土壤性质的影响[J].水土保持学报,2003,17(4):42-45. |
| PAGN X Y, LIU S Q, LIU Q,et al.Influence of plant community succession on soil physical properties during subalpine coniferous plantation rehabilitation in western[J].Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2003,17(4):42-45. | |
| 30 | LV J L, YAN M J, SONG B L,et al.Ecological stoichiometry characteristics of soil carbon,nitrogen,and phosphorus in an oak forest and a black locust plantation in the Loess hilly region[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2017,37(10):3385-3393. |
| 31 | YU Y H, CHI Y.Ecological stoichiometric characteristics of soil at different depths in a karst plateau mountain area of China[J].Polish Journal of Environmental Studies,2019,29:969-978. |
| 32 | ZHANG K, SU Y Z, YANG R.Variation of soil organic carbon,nitrogen,and phosphorus stoichiometry and biogeographic factors across the desert ecosystem of Hexi Corridor,northwestern China[J].Journal of Soils and Sediments,2019,19:49-57. |
| 33 | 刘兴诏,周国逸,张德强,等.南亚热带森林不同演替阶段植物与土壤中N、P的化学计量特征[J].植物生态学报,2010,34(1):64-71. |
| LIU X Z, ZHOU G Y, ZHANG D Q,et al.N and P stoichiometry of plant and soil in lower subtropical forest successional series in southern China[J].Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology,2010,34(1):64-71. | |
| 34 | 刘明辉,谢婷婷,李瑞,等.三峡库区消落带池杉-土壤碳氮磷生态化学计量特征[J].生态学报,2020,40(9):3072-3084. |
| LIU M H, XIE T T, LI R,et al.Carbon,nitrogen,and phosphorus ecological stoichiometric characteristics between Taxodium ascendens and soil in the water-level fluctuation zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir region[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica.2020,40(9):3072-3084 | |
| 35 | TIAN H Q, CHEN G S, ZHANG C,et al.Pattern and variation of C∶N∶P ratios in China’s soil:a synthesis of observational data[J].Biogeochemistry,2010,98:139-151. |
| 36 | TAYLOR J P, WILSON B, MILLS M S,et al.Comparison of microbial numbers and enzymatic activities in surface soils and subsoils using various techniques[J].Soil Biology and Biochemistry,2002,34(3):387-401. |
| 37 | 王小平,肖肖,唐天文,等.连香树人工林根系分泌物输入季节性变化及其驱动的根际微生物特性研究[J].植物研究,2018,38(1):47-55. |
| WANG X P, XIAO X, TANG T W,et al.Seasonal changes of the input of root exudates and its driving characteristics of rhizosphere microbe in a Cercidiphyllum japonicum Sieb.plantation[J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2018,38(1):47-55. | |
| 38 | 吴怡,董炜华,李晓强,等.土壤酶活性对土壤环境变化的响应研究进展[J].南方农业,2023,17(15):42-46. |
| WU Y, DONG W H, LI X Q,et al.Research progress on the response of soil enzyme activity to soil environmental changes[J].South China Agriculture,2023,17(15):42-46. | |
| 39 | 陈双林,郭子武,杨清平.毛竹林土壤酶活性变化的海拔效应[J].生态学杂志,2010,29(3):529-533. |
| CHEN S L, GUO Z W, YANG Q P.Soil enzyme activities in Moso bamboo forests along an altitude gradient[J].Chinese Journal of Ecology,2010,29(3):529-533. | |
| 40 | 徐冬梅,刘广深,许中坚,等.模拟酸雨对土壤酸性磷酸酶活性的影响及机理[J].中国环境科学,2003,23(2):176-179. |
| XU D M, LIU G S, XU Z J,et al.Effects and mechanism of simulated acid rain on the activities of soil acid phosphatase[J].China Environmental Science,2003,23(2):176-179. | |
| 41 | 王涵,王果,黄颖颖,等.pH变化对酸性土壤酶活性的影响[J].生态环境,2008,17(6):2401-2406. |
| WANG H, WANG G, HUANG Y Y,et al.The effects of pH change on the activities of enzymes in an acid soil[J].Ecology and Environment,2008,17(6):2401-2406. | |
| 42 | HERNÁNDEZ D L, HOBBIE S E.The effects of substrate composition,quantity,and diversity on microbial activity[J].Plant and Soil,2010,335:397-411. |
| 43 | 万忠梅,吴景贵.土壤酶活性影响因子研究进展[J].西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版),2005,33(6):87-92. |
| WAN Z M, WU J G.Study progress on factors affecting soil enzyme activity[J].Journal of Northwest A&F University(Natural Science Edition),2005,33(6):87-92. | |
| 44 | BANERJEE S, BORA S, THRALL P H,et al.Soil C and N as causal factors of spatial variation in extracellular enzyme activity across grassland-woodland ecotones[J].Applied Soil Ecology,2016,105:1-8. |
| 45 | BOWLES T M, ACOSTA-MARTÍNEZ V, CALDERÓN F,et al.Soil enzyme activities,microbial communities,and carbon and nitrogen availability in organic agroecosystems across an intensively-managed agricultural landscape[J].Soil Biology and Biochemistry,2014,68:252-262. |
| 46 | 刘顺,许格希,陈淼,等.坡向对川西亚高山土壤酶活性和微生物养分限制的影响[J/OL].应用生态学报,(2023-09-19) [2023-10-13].. |
| LIU S, XU G X, CHEN M,et al.Effects of slope aspect on soil enzyme activity and microbial nutrient limitation in subalpine region of wes-tern Sichuan,China[J/OL].Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,(2023-09-19) [2023-10-13].. | |
| 47 | LUCAS-BORJA M E, HEDO J, CERDÁ A,et al.Unravelling the importance of forest age stand and forest structure driving microbiological soil properties,enzymatic activities and soil nutrients content in Mediterranean Spanish black pine(Pinus nigra Ar.ssp.salzmannii) Forest[J].Science of The Total Environment,2016,562:145-154. |
| 48 | KARA Ö, BOLAT İ, ÇAKIROĞLU K,et al.Plant canopy effects on litter accumulation and soil microbial biomass in two temperate forests[J].Biology and Fertility of Soils,2008,45(2):193-198. |
| 49 | MOORHEAD D L, SINSABAUGH R L, HILL B H,et al.Vector analysis of ecoenzyme activities reveal constraints on coupled C,N and P dynamics[J].Soil Biology and Biochemistry,2016,93:1-7. |
| 50 | YANG Y, LIANG C, WANG Y Q,et al.Soil extracellular enzyme stoichiometry reflects the shift from P- to N-limitation of microorganisms with grassland restoration[J].Soil Biology and Biochemistry,2020,149:107928. |
| 51 | 殷爽,王传宽,金鹰,等.东北地区大秃顶子山土壤-微生物-胞外酶C∶N∶P化学计量特征沿海拔梯度的变化[J].植物生态学报,2019,43(11):999-1009. |
| YIN S, WANG C K, JIN Y,et al.Changes in soil-microbe-exoenzyme C∶N∶P stoichiometry along an altitudinal gradient in Mt.Datudingzi,Northeast China[J].Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology,2019,43(11):999-1009. | |
| 52 | CHAPIN III F S, MATSON P A, VITOUSEK P M.Principles of terrestrial ecosystem ecology[M].2nd ed.New York:Springer-Verlag,2011. |
| 53 | 孙彩丽,王艺伟,王从军,等.喀斯特山区土地利用方式转变对土壤酶活性及其化学计量特征的影响[J].生态学报,2021,41(10):4140-4149. |
| SUN C L, WANG Y W, WANG C J,et al.Effects of land use conversion on soil extracellular enzyme activity and its stoichiometric characteristics in karst mountainous areas[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2021,41(10):4140-4149. |
| [1] | Jikang XU, Yanhong HE, Tingyan LIU, Longfei HAO, Shengxi ZHANG, Zhaoyi LI. Characteristics of Rhizosphere Soil Microecological Environment of Different Ecological Restoration Vegetation in Arsenic Sandstone Areas [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(4): 531-539. |
| [2] | Qingqing ZHANG, Zaizhi ZHOU, Guihua HUANG, Weiwei ZHAO, Xiyang WANG, Guang YANG, Gaofeng LIU. Effects of Fertilizing on Trees Growth and Understory Vegetation of Young Teak Plantation [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(4): 694-703. |
| [3] | ZHAO Chun-Jian, LI Yu-Zheng, GUAN Jia-Jing, SU Wei-Ran, TIAN Yao, WANG Ting-Ting, LI Shen, LI Chun-Ying. Effect of Interplanting Taxus cuspidata with Ficus carica on Growth of Two Plants and Activities of Soil Enzymes [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(5): 679-685. |
| [4] | MA Peng-Yu, ZHANG Hong-Guang, ZAN Peng, GU Wei-Ping, WEN Lu-Ning, ZHANG Zi-Jia, WENG Hai-Long, SUN Tao, MAO Zi-Jun. Effects of Long-term Nitrogen Addition on Soil Enzymes in Larix gmelinii Plantation in Northeast China [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2019, 39(4): 598-603. |
| [5] | ZHOU Shu-Ping, LIANG Kun-Nan, DU Jiang, LI Bi-Jun, ZHOU Zai-Zhi, HUANG Gui-Hua. Research on Understory Vegetation and Soil Physical-chemical Properties of Teak Plantation with Difference Stand Densities [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2017, 37(2): 200-210. |
| [6] | SUN Guo-Rong, PENG Yong-Zhen, YUE Zhong-Hui, YAN Xiu-Feng. Effect of different ameliorative ways on the nutrition status of nitrogen of basification soil [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2004, 24(3): 369-373. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||