Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (6): 952-964.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2025.06.012
• Original Paper • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yingying FU1,2, Jiahui LAI1, Huayi YUAN1,2, Hongya YU1,2, Guanghua LIU1, Furong XU1,2( )
)
Received:2024-12-20
Online:2025-11-20
Published:2025-11-27
Contact:
Furong XU
E-mail:xfrong99@163.com
CLC Number:
Yingying FU, Jiahui LAI, Huayi YUAN, Hongya YU, Guanghua LIU, Furong XU. Analysis of Physiological and Biochemical Indexes Changes During Seed Germination of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(6): 952-964.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://bbr.nefu.edu.cn/EN/10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2025.06.012
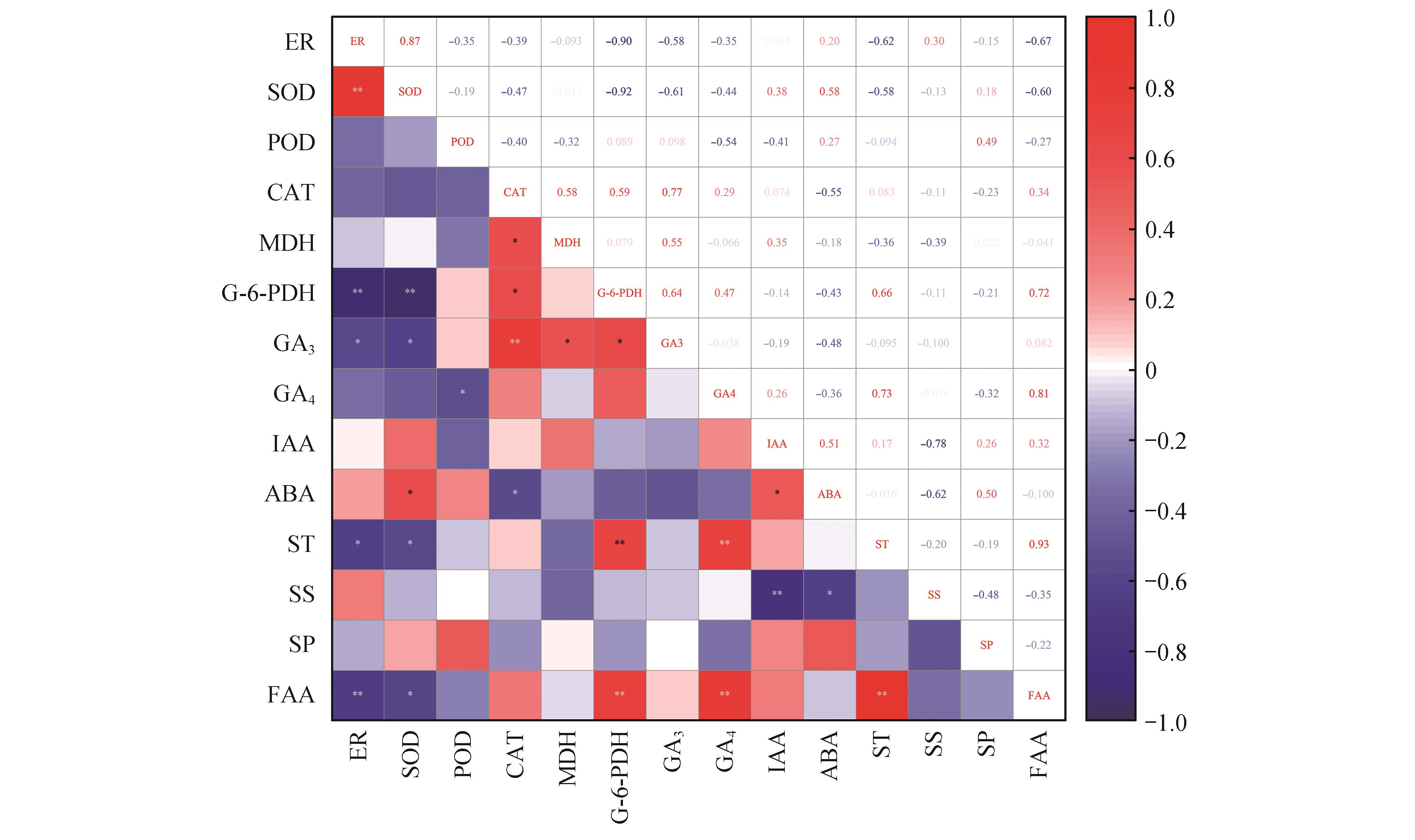
Fig.7
Correlation matrix diagram of each index of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis seeds at different germination stages* indicated significant correlation at the P<0.05 level, and ** indicated extremely significant correlation at the P<0.01 level. ER. Embryo rate; SOD. Superoxide dismutase; POD. Peroxidase; CAT. Catalase; MDH. Malate dehydrogenase; G-6-PDH. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase; GA3. Gibberellin A3; GA4. Gibberellin A4; IAA. Indole-3-acetic acid; ABA. Abscisic acid; ST. Starch; SS. Soluble sugar; SP. Soluble protein; FAA. Free amino acids.
| [1] | 李世昌,彭寿杰,王一博,等.重楼本草考证[J].中成药,2023,45(8):2662-2670. |
| LI S C, PENG S J, WANG Y B,et al.Textual research on medicinal plants of the genus Paris [J].Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine,2023,45(8):2662-2670. | |
| [2] | 王宇飞,江媛,杨成金,等.滇重楼化学成分、药理作用和临床应用研究进展[J].中草药,2022,53(23):7633-7648. |
| WANG Y F, JIANG Y, YANG C J,et al.Research progress on chemical constituents,pharmacological actities,and clinical applications of Paris polyphylla var.yunnanensis [J].Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2022,53(23):7633-7648. | |
| [3] | 张保得,蔡吹,谢准,等.气候变化情景下滇重楼在中国的适生性分析[J].植物遗传资源学报,2024,25(9):1601-1612. |
| ZHANG B D, CAI C, XIE Z,et al.Ecological suitability of Paris polyphylla var.yunnanensis in China under the situation of climate change[J].Journal of Plant Genetic Resources,2024,25(9):1601-1612. | |
| [4] | 黄娟,王涛,徐德,等.重楼种子繁殖研究进展[J].四川农业科技,2024(5):35-38. |
| HUANG J, WANG T, XU D,et al.Research progress on seed reproduction of Paris polyphylla [J].Sichuan Agricultural Science and Technology,2024(5):35-38. | |
| [5] | 赖佳辉,赵艳丽,蔡吹,等.重楼属植物种子休眠特性的研究进展[J].分子植物育种,(2023-09-12)[2024-12-19].. |
| LAI J H, ZHAO Y L, CAI C,et al.Research progress on seed dormancy characteristics of Paris L.[J].Molecular Plant Breeding,(2023-09-12)[2024-12-19].. | |
| [6] | 陈疏影,尹品训,杨艳琼,等.变温层积对解除滇重楼种子休眠及其内源激素变化的研究[J].中草药,2011, 42(4):793-795. |
| CHEN S Y, YIN P X, YANG Y Q,et al.Rule of breaking Paris polyphylla var.yunnanensis seed dormancy under fluctuating temperature stratification and content changes of endogenous hormone[J].Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2011,42(4):793-795. | |
| [7] | 汪佳维,王华磊,赵致,等.不同试剂及温度对解除滇重楼种子休眠的影响[J].河南农业科学,2020,49(3):47-53. |
| WANG J W, WANG H L, ZHAO Z,et al.Effects of different reagents and temperature on removing seed dormancy of Paris polyphylla var.yunnanensis [J].Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences,2020,49(3):47-53. | |
| [8] | 孟繁蕴,汪丽娅,张文生,等.滇重楼种胚休眠和发育过程中内源激素变化的研究[J].中医药学报,2006,34(4):36-38. |
| MENG F Y, WANG L Y, ZHANG W S,et al.Dynamic changes of several endohormones in embryogenic cell of Paris polyphylla var.yunnanensis during dormancy and different development stages[J].Acta Chinese Medicine and Pharmacology,2006,34(4):36-38. | |
| [9] | 黄玮,孟繁蕴,张文生,等.滇重楼种子休眠机理研究[J].中国农学通报,2008,24(12):242-246. |
| HUANG W, MENG F Y, ZHANG W S,et al.Study on seed dormancy mechanism of Paris polyphylla var.yunnanensis [J].Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin,2008,24(12):242-246. | |
| [10] | 浦梅,孙永玉,高成杰,等.滇重楼种子内源激素含量与种胚长度和萌发的关系[J].林业科学研究,2016,29(2):268-273. |
| PU M, SUN Y Y, GAO C J,et al.Relationship between endogenous hormone content and embryo growth and the seed germination of Paris polyphylla var.yunnanensis [J].Forest Research,2016,29(2):268-273. | |
| [11] | 浦梅.滇重楼种子发芽过程中生理生化特征研究[D].北京:中国林业科学研究院,2016. |
| PU M.Study on the physiological and biochemical characteristic during the seed germination of Paris polyphylla var.yunnanensis[D].Beijing:Chinese Academy of Forestry,2016. | |
| [12] | FINKELSTEIN R, REEVES W, ARIIZUMI T,et al.Molecular aspects of seed dormancy[J].Annual Review of Plant Biology,2008,59(1):387-415. |
| [13] | 任艳君,郭晓瑞,于子煊,等.变温层积不同阶段刺五加种子萌发生理及代谢特点[J].植物研究,2024,44(4):576-589. |
| REN Y J, GUO X R, YU Z X,et al.Characteristics of temperature stratification on germination physiology and metabolism of Acanthopanax senticosus seeds at different stages[J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2024,44(4):576-589. | |
| [14] | 康亮,卢覃培,王德宝,等.七叶一枝花种子萌发过程中内源激素含量及酶活性变化研究[J].广西植物,2024,44(6):1118-1128. |
| KANG L, LU Q P, WANG D B,et al.Changes of endogenous hormone content and enzyme activities during seed germination of Paris polyphylla [J].Guihaia,2024,44(6):1118-1128. | |
| [15] | 张娟,其乐木格,段海婧,等.层积过程中羌活种子种胚形态及生理生化变化[J].植物资源与环境学报,2023,32(1):61-68. |
| ZHANG J, QI L M G, DUAN H J,et al.Embryo morphology and physiological and biochemical variations of Notopterygium incisum seeds during stratification[J].Journal of Plant Resources and Environment,2023,32(1):61-68. | |
| [16] | 苏海兰,牛雨晴,成建华,等.多花黄精种子生理后熟过程的生理变化及基因表达模式分析[J].福建农业学报,2024,39(6):662-670. |
| SU H L, NIU Y Q, CHENG J H,et al.Physiobiochemical changes and gene expressions of Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua seeds undergone post-ripening treatment[J].Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences,2024,39(6):662-670. | |
| [17] | 管岳,申文靖,宋晓萌,等.巴尔鲁克山野扁桃种子萌发特性[J].植物研究,2024,44(3):400-409. |
| GUAN Y, SHEN W J, SONG X M,et al.Seed germination characteristics of Amygdalus ledebouriana in Barluk Mountain[J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2024,44(3):400-409. | |
| [18] | 李昭玲,童凯,闫燊,等.变温层积过程中华重楼种胚后熟生理生化的变化[J].中国中药杂志,2015,40(4):629-633. |
| LI Z L, TONG K, YAN S,et al.Physiological and biochemical change of Paris seed in after-ripening during variable temperature stratification[J].China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2015,40(4):629-633. | |
| [19] | WATERS M T, LANGDALE J A.The making of a chloroplast[J].The EMBO Journal,2009,28(19):2861-2873. |
| [20] | ZHAO M, ZHANG H X, YAN H,et al.Mobilization and role of starch,protein,and fat reserves during seed germination of six wild grassland species[J].Frontiers in Plant Science,2018,9:234. |
| [21] | 陆沁怡,沈永宝,史锋厚.芍药种胚发育及物质代谢的探究[J].分子植物育种,(2022-05-18) [2024-12-19].. |
| LU Q Y, SHEN Y B, SHI F H.Study on embryo development and material metabolism of Paeonia lactiflora Pall.[J].Molecular Plant Breeding,(2022-05-18) [2024-12-19].. | |
| [22] | 孙瑞敏,王蕾,王佳琪,等.裕民贝母破除种子生理休眠营养物质的变化[J].分子植物育种,2021,19(15):5143-5149. |
| SUN R M, WANG L, WANG J Q,et al.The changes of nutrients in breaking seed physiological dormancy of Fritillaria yuminensis X.Z.Duan[J].Molecular Plant Breeding,2021,19(15):5143-5149. | |
| [23] | LI M, LI Q F, LI S,et al.SHORT-ROOT specifically functions in the chalazal region to modulate assimilate partitioning into seeds[J].The Plant Journal,2024,120(5):2031-2044. |
| [24] | ZHENG G W, LI W C, ZHANG S Z,et al.Multiomics strategies for decoding seed dormancy breakdown in Paris polyphylla [J].BMC Plant Biology,2023,23(1):247. |
| [25] | LIU S Y, WANG W, LU H Y,et al.New perspectives on physiological,biochemical and bioactive components during germination of edible seeds:a review[J].Trends in Food Science & Technology,2022,123:187-197. |
| [26] | 李玛,王玲,杨生超,等.滇重楼种子后熟期间生理生化变化的研究[J].云南农业大学学报(自然科学),2015,30(5):766-770. |
| LI M, WANG L, YANG S C,et al.Physiological and biochemical changes during post-maturation of seeds in Paris polyphylla Smith var.yunnanensis [J].Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University (Natural Science),2015,30(5):766-770. | |
| [27] | 张春椿,年慧慧,李石清,等.激素加变温层积法处理南方红豆杉种子生理生化变化研究[J].中华中医药杂志,2012,27(10):2723-2726. |
| ZHANG C C, NIAN H H, LI S Q,et al.Study on physiological changes of break dormancy of Taxus mairei (Lemee et LevI.) S.Y.Hu ex Liu seeds[J].China Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy,2012,27(10):2723-2726. | |
| [28] | TAKÁČ T, PECHAN T, ŠAMAJ J.Differential proteomics of plant development[J].Journal of Proteomics,2011,74(5):577-588. |
| [29] | 岳贺伟,李连珍,王雨情,等.IAA对黄精种子萌发及生理特性的影响[J].河南农业科学,2023,52(3):64-72. |
| YUE H W, LI L Z, WANG Y Q,et al.Effect of IAA on seed germination and physiological characteristics of Polygonatum sibiricum Red.[J].Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences,2023,52(3):64-72. | |
| [30] | BAILLY C.ROS in seed germination[M]//MITTLER R,VAN BREUSEGEM F.Advances in Botanical Research:Vol.105.[S.l.]:Academic Press,2023:177-204. |
| [31] | XI D M, LIU W S, YANG G D,et al.Seed-specific overexpression of antioxidant genes in Arabidopsis enhances oxidative stress tolerance during germination and early seedling growth[J].Plant Biotechnology Journal,2010,8(7):796-806. |
| [32] | 李玉杰,刘少康,周涛,等.盐胁迫对芝麻萌发过程中活性成分、抗氧化性及抗氧化酶活性的影响[J].食品工业科技,2024,45(19):76-83. |
| LI Y J, LIU S K, ZHOU T,et al.Effects of salt stress on active components,antioxidant capacity and antioxidase activity of sesame during germination[J].Science and Technology of Food Industry,2024,45(19):76-83. | |
| [33] | BUETLER T M, KRAUSKOPF A, RUEGG U T.Role of superoxide as a signaling molecule[J].Physiology,2004,19(3):120-123. |
| [34] | ZIELIŃSKI H, FRIAS J, PISKUŁA M K,et al.The effect of germination process on the superoxide dismutase-like activity and thiamine,riboflavin and mineral contents of rapeseeds[J].Food Chemistry,2006,99(3):516-520. |
| [35] | 马旭俊,朱大海.植物超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)的研究进展[J].遗传,2003,25(2):225-231. |
| MA X J, ZHU D H.Functional roles of the plant superoxide dismutase[J].Hereditas (Beijing),2003,25(2):225-231. | |
| [36] | WANG S, SHEN Y B, BAO H P.Morphological,physiological and biochemical changes in Magnolia zenii Cheng seed during development[J].Physiologia Plantarum,2021,172(4):2129-2141. |
| [37] | 苏海兰,周先治,李希,等.云南重楼种子萌发过程内源激素含量及酶活性变化研究[J].核农学报,2018,32(1):141-149. |
| SU H L, ZHOU X Z, LI X,et al.Dynamic changes of enzyme and endogenous of Paris polyphylla Smith var. yunnanensis seed during different stages of germination[J].Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences,2018,32(1):141-149. | |
| [38] | LIU Z G, MA C Y, HOU L,et al.Exogenous SA affects rice seed germination under salt stress by regulating Na+/K+ balance and endogenous GAs and ABA homeostasis[J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2022,23(6):3293. |
| [39] | AYELE B T, OZGA J A, KUREPIN L V,et al.Developmental and embryo axis regulation of gibberellin biosynthesis during germination and young seedling growth of pea[J].Plant Physiology,2006,142(3):1267-1281. |
| [40] | 李振华.烟草种子萌发的激素效应研究进展[J].云南农业大学学报(自然科学),2013,28(3):416-423. |
| LI Z H.Advances in hormones during tobacco seed germination[J].Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University (Natural Science),2013,28(3):416-423. | |
| [41] | WOLTERS H, JÜRGENS G.Survival of the flexible:hormonal growth control and adaptation in plant development[J].Nature Reviews Genetics,2009,10(5):305-317. |
| [42] | BAWA G, FENG L Y, CHEN G P,et al.Gibberellins and auxin regulate soybean hypocotyl elongation under low light and high-temperature interaction[J].Physiologia Plantarum,2020,170(3):345-356. |
| [43] | 柳苗,高捍东,高燕,等.休眠解除过程中紫楠种子生理生化特征的变化[J].南京林业大学学报(自然科学版),2023,47(2):9-17. |
| LIU M, GAO H D, GAO Y,et al.Study on the physiological and biochemical changes of Phoebe sheareri seed during its dormancy breaking[J].Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition),2023,47(2):9-17. |
| [1] | Lan WANG, Di ZHOU, Zhao XUE, Dongxu WANG, Xiaofang GUO, Ji DE. Dynamics of Endophytic Bacterial Communities in Highland Barley Seeds at Different Growth Stages [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(6): 965-974. |
| [2] | Shuanglong TANG, Shixin CHEN, Yu WANG, Danwei MA, Shihui YANG, Shenming NIE, Zhaxizeli, Zhengyou TIAN. Morphological Adaptation to Alpine Environment of a Chinese Endemic Species, Cynanchum forrestii [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(3): 389-399. |
| [3] | Yue GUAN, Wenjing SHEN, Xiaomeng SONG, Yanxin WANG, Nurgailide AKEJULIDEZI, Pengfei CHEN, Long ZHOU. Seed Germination Characteristics of Amygdalus ledebouriana in Barluk Mountain [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(3): 400-409. |
| [4] | Yingying TANG, Chuanchao GUO, Dang SHI, Nanlin JIANG, Zheng XU, Liqiang LIU. Effects of Pulp and Buried Depth on Seed Germination and Seedling Growth of Armeniaca vulgaris [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(2): 251-260. |
| [5] | Xingui LE, Zhengwei WANG, Xin NING, Xiqing SUN, Yigang SONG. The Germination Characteristics and Dormancy Type of the Seed of Castanopsis sclerophylla [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(4): 688-693. |
| [6] | GUO Zi-Jing, ZHAO Xiu-Hua, ZU Yuan-Gang, WANG Si-Ying, LIU Pei-Yan. Process Optimization of Sunflower Seeds Oil by Enzyme-assisted Pressing [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2019, 39(6): 964-969. |
| [7] | LI Lin-Yu, FANG Zi-Yan, Maola Aikebaier, ZHOU Long, LU Biao. Germination Obstacle Factors of Berberis Seeds of Different Natural Populations [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2018, 38(6): 894-901. |
| [8] | LÜ Dong, ZHANG Hong-Bin, LI Bing-Xin, ZHAO Hu. Phenotypic Traits of Half Sibs-seeds and Their Offspring Seddlings on Picea crassifolia Superior Individual Trees [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2018, 38(3): 377-383. |
| [9] | LIU Jin, XIA Qi-Ping, WANG Jian, LI Zhen, SHAO Jian-Wen. A Preliminary Study on the Application of Self Pollination in Primula merrilliana Flower Color Selection [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2018, 38(2): 232-237. |
| [10] | LIU Zhi-Xiong1,2;LI Feng-Lan2. Expression of A Floral Homeotic Gene PrseSTK from Prunus lannesiana in Single and Double Flower [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2015, 35(4): 535-539. |
| [11] | ZHAN Zhi-Yong;WANG Yang-Dong*;CHEN Yi-Cun;HAN Xiao-Jiao;CUI Qin-Qin. Comparison of Three Protein Extraction Methods for Tung trees (Vernicia fordii) Seed [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2013, 33(1): 91-97. |
| [12] | SONG Yi-Gang;LI Li*;ZHANG Xi-Ming;PAN Xiang-Liang;ZENG Xin-Hua;. Differences of Seed Coat Structure and Ions Content between Dimorphic Seeds of Borszczowia aralocaspica [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2012, 32(3): 290-295. |
| [13] | LANG Xue-Dong;SU Jian-Rong*;LU Shu-Gang;ZHANG Zhi-Jun;LI Shuai-Feng. Taxonomic Status of Cephalotaxus alpina(Li) L.K.Fu(Cephalotaxaceae) in the Views of Morphological Characteristics of Seeds and Leaves [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2012, 32(1): 4-9. |
| [14] | ZHOU Xiao-Mei;XU Jin;LI Jun-Jian*. Study on the Germination and Plant Regeneration of Lolium perenne [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2009, 29(3): 325-328. |
| [15] | CHEN Yan;XUE Xiao-Juan;ZHU Hong*. Analysis of the Volatile Constituents from Seeds of Polygonum orientale by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Coupled with Solid-phase Microextraction [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2008, 28(6): 770-774. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||