Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (3): 459-469.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2024.03.015
• Plant synecology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Huadong DU1,2, Penghui FAN1, Yinli BI2, Shanshan XIE1, Yan LIU1, Yunlong LIU1
Received:2023-09-04
Online:2024-05-20
Published:2024-05-14
CLC Number:
Huadong DU, Penghui FAN, Yinli BI, Shanshan XIE, Yan LIU, Yunlong LIU. Plant Community Characteristics and Their Relationship with Environmental Factors in Different Geomorphic Units in Arid Gravel Desert[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(3): 459-469.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://bbr.nefu.edu.cn/EN/10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2024.03.015
Table 1
Soil physical and chemical properties in different geomorphic units in arid gravel area
微地貌单元 Geomorphic units | 土壤容重 Soil bulk density/ (g·cm-3) | 土壤酸碱度 pH | 土壤含水率 Soil moisture content/% | 可溶性盐 Soluble salt/% | 有机质 Soil organic matter/ (g·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
砾漠戈壁 GG | 1.29±0.09a | 8.46±0.74a | 2.90±0.09b | 18.40±3.86b | 6.88±1.22b |
风蚀残丘 WU | 1.25±0.10a | 8.36±0.49ab | 3.30±0.05ab | 33.10±4.17a | 3.73±1.58c |
河谷 RV | 1.25±0.23a | 8.07±0.43b | 6.20±0.12a | 21.70±3.28b | 9.60±1.90a |
风沙地 AL | 1.24±0.17a | 8.52±0.37a | 2.50±0.08c | 15.30±2.94c | 6.27±1.23b |
微地貌单元 Geomorphic units | 有效钾 Available potassium/ (mg·kg-1) | 有效磷 Available phosphorus/ (mg·kg-1) | 空气湿度 Air humidity/% | 地表风速 Surface wind speed/ (m·s-1) | 地表温度 Surface temperature/℃ |
砾漠戈壁 GG | 214.80±34.50b | 6.30±1.41b | 20.22±8.07b | 4.14±2.82b | 42.90±6.80a |
风蚀残丘 WU | 151.40±25.80d | 4.30±0.80d | 23.90±5.69a | 6.05±2.00a | 37.40±10.30b |
河谷 RV | 274.20±34.00a | 8.67±1.10a | 25.60±8.86a | 4.3±2.05b | 33.05±6.90b |
风沙地 AL | 176.04±33.20c | 5.10±0.84c | 18.90±4.34b | 6.70±2.50a | 44.60±7.36a |
Table 2
Plant community structure and composition in different geomorphic units in arid gravel area
微地貌单元 Geomorphic units | 群落垂直结构层数 Vertical structure layers | 群落高度 Plant community high/m | 植株密度 Plant density/ (株·m-2) | 生活型占比 The proportion of living type/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1年生植物 Annual | 多年生草本 Perennial herb | 多年生禾草 Perennial grasses | 灌木 Shrub | 乔木 Tree | 藤本植物 Liana | ||||
| GG | 1 | 0.32±0.09d | 8.5±1.2b | 20.1±3.6c | 19.6±3.6a | 15.1±2.9a | 45.2±6.7a | — | — |
| WU | 2 | 0.87±0.12c | 12.5±3.6ab | 52.7±5.6a | 3.4±0.70c | 5.7±1.8c | 38.2±5.8ab | — | — |
| RV | 2 | 1.68±0.18b | 35.8±4.5a | 35.2±4.2ab | 15.9±4.8ab | 12.2±3.7a | 30.7±4.3b | 1.2±0.3 | 4.8±0.8 |
| AL | 2 | 2.57±0.36a | 3.8±0.7c | 48.1±6.8a | 6.7±1.6b | 8.3±2.3b | 36.9±7.6ab | — | — |
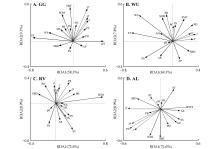
Fig.4
RDA sequence plots for plant community characteristics and environmental factors in different geomorphic units in arid gravel areaSBD.Soil bulk density; pH.Soil pH; SMC.Soil moisture content; SS.Soluble salt; SOM.Soil organic matter; AK.Available potassium; AP.Available phosphorus; AH.Air humidity; WS.Surface wind speed; ST.Surface temperature; PD.Plant density; PC.Plant cover; PB.Plant biomass; PS.Plant community stability; H′.Shannon-Wiener; J.Pielou; R.Margalef; The solid lines indicated ecological indicators; the dotted lines indicated vegetation features.
| 1 | BIRHANU L, BEKELE T, TESFAW B,et al.Relationships between topographic factors,soil and plant communities in a dry Afromontane forest patches of Northwestern Ethiopia[J].PLoS One,2021,16(3):e0247966. |
| 2 | HORN S, HEMPEL S, RISTOW M,et al.Plant community assembly at small scales:spatial vs.environmental factors in a European grassland[J].Acta Oecologica,2015,63:56-62. |
| 3 | THUILLER W, ALBERT C, ARAÚJO M B,et al.Predicting global change impacts on plant species’ distributions:future challenges[J].Perspectives in Plant Ecology,Evolution and Systematics,2008,9(3/4):137-152. |
| 4 | 秦洁,司建华,贾冰,等.巴丹吉林沙漠植被群落特征与土壤水分关系研究[J].干旱区研究,2021,38(1):207-222. |
| QIN J, SI J H, JIA B,et al.Study on the relationship between vegetation community characteristics and soil moisture in Badain jaran desert[J].Arid Zone Research,2021,38(1):207-222. | |
| 5 | YANG Q C, ZHANG H H, WANG L H,et al.Topography and soil content contribute to plant community composition and structure in subtropical evergreen-deciduous broadleaved mixed forests[J].Plant Diversity,2021,43(4):264-274. |
| 6 | 强方方,魏天兴,刘崴.晋西黄土区土壤水分动态变化与植被群落关系研究[J].植物研究,2019,39(1):61-68. |
| QIANG F F, WEI T X, LIU W.Relationship between soil moisture dynamics and vegetation community in the loess area of western Shanxi Province[J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2019,39(1):61-68. | |
| 7 | 张和钰.天山南麓中段戈壁区植被空间分布格局及其形成机制研究[D].北京:中国林业科学研究院,2023. |
| ZHANG H Y.The spatial distribution pattern and formation mechanism of vegetation in the Gobi region in the middle section of the southern piedmont of Tianshan mountains[D].Beijing:Chinese Academy of Forestry,2023. | |
| 8 | 安永梅,杜维波,周晓雷,等.兴隆山自然保护区种子植物的垂直分布格局研究[J].西北植物学报,2023,43(6):1017-1025. |
| AN Y M, DU W B, ZHOU X L,et al.Vertical distribution pattern of seed plants in Xinglong Mountain Nature Reserve[J].Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica,2023,43(6):1017-1025. | |
| 9 | NADAL-ROMERO E, PETRLIC K, VERACHTERT E,et al.Effects of slope angle and aspect on plant cover and species richness in a humid Mediterranean badland[J].Earth Surface Processes and Landforms,2014,39(13):1705-1716. |
| 10 | YAIR A, KOSSOVSKY A.Climate and surface properties:hydrological response of small arid and semi-arid watersheds[J].Geomorphology,2002,42(1/2):43-57. |
| 11 | MATA-GONZÁLEZ R, AVERETT J P, ABDALLAH M A B,et al.Variations in groundwater level and microtopography influence desert plant communities in shallow aquifer areas[J].Environmental Management,2022,69(1):45-60. |
| 12 | 段义忠,杜忠毓,亢福仁.西北干旱区孑遗濒危植物蒙古沙冬青群落特征及与环境因子的关系[J].植物研究,2018,38(6):834-842. |
| DUAN Y Z, DU Z Y, KANG F R.Community characteristics of endangered plant of Ammopiptanthus mongolicus to environmental factors in northwest arid area of China[J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2018,38(6):834-842 | |
| 13 | 张瑞红,蔡文涛,来利明,等.鄂尔多斯高原弃耕农田植物群落演替过程中物种多样性的变化[J].干旱区资源与环境,2018,32(10):178-183. |
| ZHANG R H, CAI W T, LAI L M,et al.Changes of species diversity in plant community succession of abandoned cropland in Ordos Plateau[J].Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment,2018,32(10):178-183. | |
| 14 | 杜忠毓,安慧,文志林,等.荒漠草原植物群落结构及其稳定性对增水和增氮的响应[J].生态学报,2021,41(6):2359-2371. |
| DU Z Y, AN H, WEN Z L,et al.Response of plant community structure and its stability to water and nitrogen addition in desert grassland[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2021,41(6):2359-2371. | |
| 15 | VAN DE VEN C M, WEISS S B, ERNST W G.Plant species distributions under present conditions and forecasted for warmer climates in an arid mountain range[J].Earth Interactions,2007,11(9):1-33. |
| 16 | 杨学亭,樊军,盖佳敏,等.祁连山不同类型草地的土壤理化性质与植被特征[J].应用生态学报,2022,33(4):878-886. |
| YANG X T, FAN J, GE J M,et al.Soil physical and chemical properties and vegetation characteristics of different types of grassland in Qilian Mountains,China[J].Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2022,33(4):878-886. | |
| 17 | 中国科学院新疆综合考察队.新疆地貌[M].北京:科学出版社,1978. |
| Xinjiang Comprehensive Investigation Team of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.Geomorphology of Xinjiang[M].Beijing:Science Press,1978. | |
| 18 | 张甘霖,龚子同.土壤调查实验室分析方法[M].北京:科学出版社,2012:8-141. |
| ZHANG G L, GONG Z T.Methods for laboratory analysis of soil investigation[M].Beijing:Science Press,2012:8-141. | |
| 19 | 新疆植物志编辑委员会.新疆植物志:第5卷[M].乌鲁木齐:新疆科技卫生出版社,1999. |
| Xinjiang Flora Editorial Committee.Flora of Xinjiang:Vol.5[M].Urumqi:Xinjiang Science and Technology Health Press,1999. | |
| 20 | 张金屯.数量生态学[M].3版.北京:科学出版社,2018:87-97. |
| ZHANG J T.Quantitative ecology[M].3rd ed.Beijing:Science Press,2018:87-97. | |
| 21 | BEGON M, TOWNSEND C R.Ecology:from individuals to ecosystems[M].Hoboken:John Wiley & Sons,2021:575-576. |
| 22 | DU H D, CAO Y C, ZHANG Y Y,et al.Plant community development in a coal mining subsidence area:active versus passive revegetation[J].Écoscience,2021,28(2):185-197. |
| 23 | 郑元润.森林群落稳定性研究方法初探[J].林业科学,2000,36(5):28-32. |
| ZHENG Y R.Comparison of methods for studying stability of forest community[J].Scientia Silvae Sinicae,2000,36(5):28-32. | |
| 24 | 费诚,董乙强,安沙舟.新疆北疆荒漠群落植被的物种多样性及影响因素研究[J].中国草地学报,2023,45(7):49-59. |
| FEI C, DONG Y Q, AN S Z,et al.Study on species diversity and influencing factors of desert community vegetation in northern Xinjiang[J].Chinese Journal of Grassland,2023,45(7):49-59. | |
| 25 | VON WEHRDEN H, WESCHE K, MIEHE G.Plant communities of the southern Mongolian Gobi[J].Phytocoenologia,2009,39(3):331-376. |
| 26 | 张俊杰,白中科,杨博宇.新疆荒漠露天矿区生态受损及砾幕层重构方法研究[J].地学前缘,2021,28(4):142-152. |
| ZHANG J J, BAI Z K, YANG B Y.Gravel curtain layer in the desert open-pit mining area of Xinjiang:ecological damage and reconstruction method[J].Earth Science Frontiers,2021,28(4):142-152. | |
| 27 | KATO H, ONDA Y, TANAKA Y,et al.Field measurement of infiltration rate using an oscillating nozzle rainfall simulator in the cold,semiarid grassland of Mongolia[J].Catena,2009,76(3):173-181. |
| 28 | 王胜,刘洪兰.肃北县戈壁过渡带降水量对气候变化的响应[J].干旱区研究,2014,31(5):898-904. |
| WANG S, LIU H L.Response of precipitation to climate change in desert ecotone in Subei County[J].Arid Zone Research,2014,31(5):898-904. | |
| 29 | 廖晗茹, TUVSHINTOGTOKH I,郭通,等.围封对蒙古荒漠草原和高山草原植物群落组成及稳定性的影响[J].北京大学学报(自然科学版),2020,56(3):471-478. |
| LIAO H R, TUVSHINTOGTOKH I, GUO T,et al.Effects of grazing exclusion on the vegetation community composition and the community stability of dry steppe and mountain steppe ecosystems in Mongolia[J].Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis,2020,56(3):471-478. | |
| 30 | HENRY H A L.Soil freeze–thaw cycle experiments:trends,methodological weaknesses and suggested improvements[J].Soil Biology and Biochemistry,2007,39(5):977-986. |
| 31 | TUGWELL-WOOTTON T, SKRZYPEK G, DOGRAMACI S,et al.Soil moisture evaporative losses in response to wet-dry cycles in a semiarid climate[J].Journal of Hydrology,2020,590:125533. |
| 32 | AMEZKETA E.An integrated methodology for assessing soil salinization,a pre-condition for land desertification[J].Journal of Arid Environments,2006,67(4):594-606. |
| 33 | PADILLA F M, PUGNAIRE F I.The role of nurse plants in the restoration of degraded environments[J].Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment,2006,4(4):196-202. |
| 34 | GÓMEZ-APARICIO L, ZAMORA R, GÓMEZ J M,et al.Applying plant facilitation to forest restoration:a meta-analysis of the use of shrubs as nurse plants[J].Ecological Applications,2004,14(4):1128-1138. |
| 35 | 程维明.新疆地貌格局及其效应[M].北京:科学出版社,2018:69-72. |
| CHENG W M.Geomorphological pattern and effects in Xinjiang[M].Beijing:Science Press,2018:69-72. | |
| 36 | SHEN Q, GAO G Y, LÜ Y H,et al.River flow is critical for vegetation dynamics:lessons from multi-scale analysis in a hyper-arid endorheic basin[J].Science of the Total Environment,2017,603/604:290-298. |
| 37 | KEHR J M, MERRITT D M, STROMBERG J C.Linkages between primary seed dispersal,hydrochory and flood timing in a semi-arid region river[J].Journal of Vegetation Science,2014,25(1):287-300. |
| 38 | 于昊辰.新疆荒漠矿区土地生态系统退化评价及调控策略研究[D].徐州:中国矿业大学,2022. |
| YU H C.Measurement and regulation strategies of land ecosystem degradation for desert mining area in Xinjiang[D].Xuzhou:China University of Mining and Technology,2022. | |
| 39 | 武胜利,李志忠,肖晨曦,等.灌丛沙堆的研究进展与意义[J].中国沙漠,2006,26(5):734-738. |
| WU S L, LI Z Z, XIAO C X,et al.Research progress on nabkhas and research significance[J].Journal of Desert Research,2006,26(5):734-738. | |
| 40 | 李玉灵,王林和,董锦兰.乌兰布和沙漠东缘几种灌木林微气候特征比较[J].内蒙古林学院学报,1997(4):14-19. |
| LI Y L, WANG L H, DONG J L.The micro-climatic comparison among several kinds of shrub growing in the eastern adage of Wulanbuhe Desert[J].Journal of Inner Mongolia Forestry College,1997(4):14-19. | |
| 41 | 党晓宏,徐立杰,高永,等.采煤沉陷对地表土壤蒸发和植被蒸腾的影响[J].应用基础与工程科学学报,2022,30(6):1389-1401. |
| DANG X H, XU L J, GAO Y,et al.Effects of coal mining subsidence on soil evaporation and vegetation transpiration[J].Journal of Basic Science and Engineering,2022,30(6):1389-1401. | |
| 42 | 徐高兴,赵鹏,陈思航,等.民勤绿洲荒漠过渡带沙拐枣群落种间关联及生态位研究[J].西北林学院学报,2023,38(1):25-33. |
| XU G X, ZHAO P, CHEN S H,et al.Interspecific association and niche of Calligonum mongolicum community in Minqin Oasis-Desert transition zone[J].Journal of Northwest Forestry University,2023,38(1):25-33. |
| [1] | Shuzhen ZOU, Caijia YIN, Qian YANG, Long MA, Di KANG. Competition Pattern of Standing Trees in Secondary Pinus Forest in the Ziwuling Mountains, China [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(1): 140-149. |
| [2] | YANG Pan-Pan, LIU Yu, BU Zhao-Jun, MA Jin-Ze, WANG Sheng-Zhong, CHEN Xu, YANG Yun-He. Effects of Water Table Level Increase and Sphagnum Propagule Transplantation on Vegetation Restoration [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2019, 39(5): 699-706. |
| [3] | XUE Ou;WEI Tian-Xing*. Interspecific Association among Understory Species of the Low-efficiency Plantation in the Jiufeng National Forest Park [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2016, 36(1): 34-42. |
| [4] | SUN Ming-Xue;JIA Wei-Wei*. Effect of Forest Fire on Vegetation in Tahe Forestry Bureau [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2009, 29(4): 481-487. |
| [5] | Dong Hou-de, Zhao Li, Chen Zhong-lin, Shao Cheng. STUDIES ON THE CLASSIFICATION AND ECOLOGY OF ZOYSIA JAPONICA COMMUNITY INH LIAODONG PENINSULA [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 1995, 15(2): 230-245. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||