Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2021, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (1): 138-144.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2021.01.017
Previous Articles Next Articles
Xu-Fu WANG1, Long-Fei HAO1, Jia-Xin HAO1, Wen-Ying HAO1, Hui-Ga BAO2, Shu-Lan BAI1( )
)
Received:2019-11-25
Online:2021-01-20
Published:2021-01-05
Contact:
Shu-Lan BAI
E-mail:baishulan2004@163.com
About author:WANG Xu-Fu(1992—),male,master candidates,engaged in mycorrhizal biotechnology research.
Supported by:CLC Number:
Xu-Fu WANG, Long-Fei HAO, Jia-Xin HAO, Wen-Ying HAO, Hui-Ga BAO, Shu-Lan BAI. Growth Responses of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica Seedlings under Simulated Nitrogen Deposition and Different Inoculation of Ectomycorrhizal Fungi Treatments[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(1): 138-144.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://bbr.nefu.edu.cn/EN/10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2021.01.017

Fig.1
Mycorrhizal colonization rate of P.sylvestris var. mongolica seedlings under different nitrogen concentration treatmentsDifferent capital letters indicate significant differences between different inoculation treatments in the same nitrogen concentration treatment(P<0.05).Different small letters indicate significant differences between different nitrogen concentration in the same inoculation treatments(P<0.05)
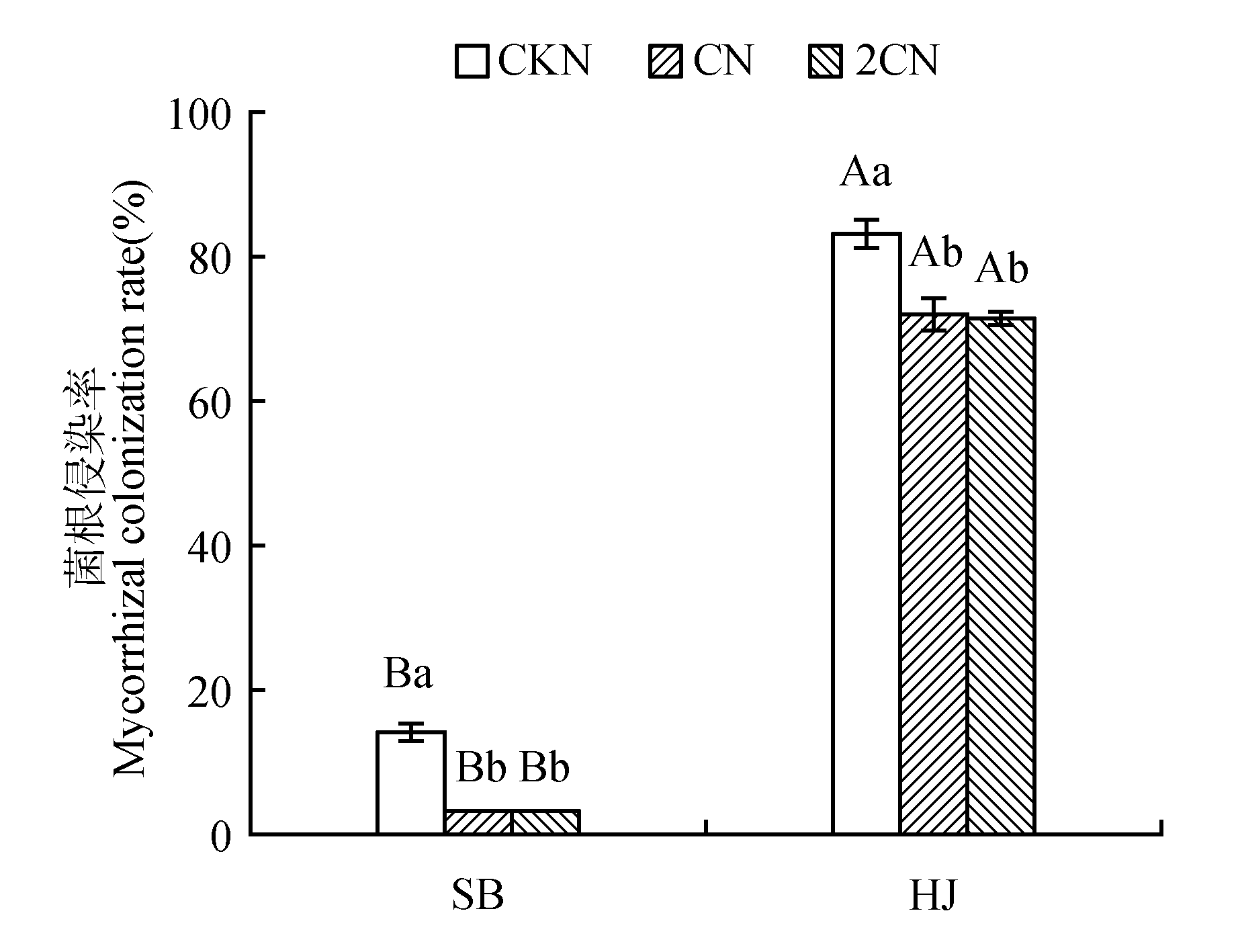
Table 1
Growth and biomass of P.sylvestris var.mongolica seedlings under different treatments(13 months old)
接种 Inoculation | 氮浓度 Nitrogen concentration | 苗高 Seedling height (mm) | 地径 Ground diameter (mm) | 地上生物量 Aboveground biomass (g) | 地下生物量 Underground biomass (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | CKN | 52.527±1.232Aa | 0.570±0.035Bb | 0.009±0.001Cb | 0.007±0.000Ca |
| CN | 53.397±1.814Aa | 0.700±0.000Ba | 0.017±0.001Ca | 0.008±0.001Ca | |
| 2CN | 51.083±0.483Ba | 0.770±0.012Aa | 0.016±0.001Ca | 0.010±0.002Ca | |
| SB | CKN | 51.620±3.333Aa | 0.750±0.084ABa | 0.047±0.002Ba | 0.020±0.001Ba |
| CN | 52.567±2.169Aa | 0.690±0.029Ba | 0.025±0.002Bb | 0.020±0.005Ba | |
| 2CN | 55.737±0.507Aa | 0.823±0.033Aa | 0.030±0.001Bb | 0.025±0.001Ba | |
| HJ | CKN | 58.123±2.584Aa | 0.827±0.067Aa | 0.067±0.002Aa | 0.039±0.006Aa |
| CN | 56.413±1.137Aa | 0.860±0.040Aa | 0.057±0.003Ab | 0.039±0.001Aa | |
| 2CN | 57.357±1.575Aa | 0.760±0.000Aa | 0.056±0.001Ab | 0.052±0.002Aa | |
| ECFM | ** | ** | *** | *** | |
| N | NS | NS | *** | * | |
| FM×N | NS | * | *** | NS | |
Table 2
Root morphology of P. sylvestris var. mongolica seedlings under different treatments
接种 Inoculation | 氮浓度 Nitrogen concentration | 平均直径 Average diameter (mm) | 总根长 Total root length (cm) | 总表面积 Total surface area (cm2) | 总分叉数 Total bifurcation number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | CKN | 0.372±0.010Bb | 79.366±11.107Bb | 9.273±1.546Bc | 214.000±77.942Ba |
| CN | 0.367±0.004Bb | 111.724±22.247Cab | 12.873±2.590Cb | 304.333±21.341Aa | |
| 2CN | 0.414±0.005Aa | 139.166±13.632Ba | 17.185±0.647Ba | 242.000±24.826Aa | |
| SB | CKN | 0.364±0.001Bb | 127.379±20.887Bb | 14.855±1.882Bb | 173.667±25.115Bb |
| CN | 0.396±0.004Aa | 170.950±20.872Ba | 21.360±2.791Ba | 333.000±8.660Aa | |
| 2CN | 0.392±0.011Ba | 196.641±21.362Aa | 24.630±2.854Aa | 255.667±38.394Aab | |
| HJ | CKN | 0.409±0.004Aa | 226.221±55.761Aab | 27.948±7.880Aab | 813.000±17.898Aa |
| CN | 0.407±0.013Aa | 292.103±32.688Aa | 34.810±2.654Aa | 376.667±60.911Ab | |
| 2CN | 0.388±0.003Bb | 154.268±6.520Bb | 19.592±1.318Bb | 175.667±4.910Ac | |
| ECFM | *** | *** | *** | *** | |
| N | ** | *** | *** | *** | |
| FM×N | *** | *** | *** | *** | |
| 1 | 龚振平.春大豆氮代谢机制及相关酶活性的研究[D].哈尔滨:东北农业大学,2004. |
| Gong Z P.Study on nitrogen metabolism mechanism and relative enzymatic activity of soybean[D].Harbin:Northeast Agricultural University,2004. | |
| 2 | Stevens C J,Dise N B,Mountford J O,et al.Impact of nitrogen deposition on the species richness of grasslands[J].Science,2004,303(5665):1876-1879. |
| 3 | Aber J,Mcdowell W,Nadelhoffer K,et al.Nitrogen saturation in temperate forest ecosystems:Hypotheses revisited[J].Bioscience,1998,48(11):921-934. |
| 4 | 刘双娥,李义勇,方熊,等.不同氮添加量和添加方式对南亚热带4个主要树种幼苗生长的影响[J].植物生态学报,2015,39(10):950-961. |
| Liu S E,Li Y Y,Fang X,et al.Effects of the level and regime of nitrogen addition on seedling growth of four major tree species in subtropical China[J].Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology,2015,39(10):950-961. | |
| 5 | 陶晨悦,邵珊璐,史文辉,等.氮沉降对干旱胁迫下毛竹实生苗生物量和保护酶活性的影响[J].林业科学,2019,55(9):31-40. |
| Tao C Y,Shao S L,Shi W H,et al.Effects of nitrogen deposition on biomass and protective enzyme activities of Phyllostachysedulis seedlings under drought stress[J].Scientia Silvae Sinicae,2019,55(9):31-40. | |
| 6 | 吕超群,田汉勤,黄耀.陆地生态系统氮沉降增加的生态效应[J].植物生态学报,2007,31(2):205-218. |
| Lv C Q,Tian H Q,Huang Y.Ecological effects of increased nitrogen deposition in terrestrial ecosystems[J].Journal of Plant Ecology,2007,31(2):205-218. | |
| 7 | Galloway J N,Dentener F J,Capone D G,et al.Nitrogen cycles:past,present,and future[J].Biogeochemistry,2004,70(2):153-226. |
| 8 | Liu X J,Zhang Y,Han W X,et al.Enhanced nitrogen deposition over China[J].Nature,2013,494(7438):459-462. |
| 9 | Li Y,Schichtel B A,Walker J T,et al.Increasing importance of deposition of reduced nitrogen in the United States[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,2016,113(21):5874-5879. |
| 10 | 郑丹楠,王雪松,谢绍东,等.2010年中国大气氮沉降特征分析[J].中国环境科学,2014,34(5):1089-1097. |
| Zheng D N,Wang X S,Xie S D,et al.Simulation of atmospheric nitrogen deposition in China in 2010[J].China Environmental Science,2014,34(5):1089-1097. | |
| 11 | Belford R K,Klepper B,Rickman R W.Studies of intact shoot-root systems of field-grown winter wheat.Ⅱ.root and shoot developmental patterns as related to nitrogen fertilizer[J].Agronomy Journal,1987,79(2):310-319. |
| 12 | Sun T,Dong L L,Mao Z J.Simulated atmospheric nitrogen deposition alters decomposition of ephemeral roots[J].Ecosystems,2015,18(7):1240-1252. |
| 13 | 郝龙飞,王庆成,刘婷岩,等.指数施肥对斑叶稠李苗木生物量分配、光合作用及根系形态的影响[J].林业科学,2014,50(11):175-181. |
| Hao L F,Wang Q C,Liu T Y,et al.Effect of exponential fertilization on biomass allocation,photosynthesis and root morphology of Padusmaackii seedlings[J].Scientia Silvae Sinicae,2014,50(11):175-181. | |
| 14 | 白淑兰,阎伟,胡永建,等.菌根研究及内蒙古大青山外生菌根资源[M].呼和浩特:内蒙古人民出版社,2011:41-42. |
| Bai S L,Yan W,Hu Y J,et al.Mycorrhizal research and ectomycorrhizal resources of Da Qing Shan Mountain in Inner Mongolia[M].Hohehot:Inner Mongolia people's Publishing House,2011:41-42. | |
| 15 | Averill C,Turner B L,Finzi A C.Mycorrhiza-mediated competition between plants and decomposers drives soil carbon storage[J].Nature,2014,505(7484):543-545. |
| 16 | Mollavali M,Perner H,Rohn S,et al.Nitrogen form and mycorrhizal inoculation amount and timing affect flavonol biosynthesis in onion(Allium cepa L.)[J].Mycorrhiza,2018,28(1):59-70. |
| 17 | Termorshuizen A J,Ket P C.Effects of ammonium and nitrate on mycorrhizal seedlings of Pinus sylvestris[J].European Journal of Forest Pathology,2007,21(6-7):404-413. |
| 18 | Bauma C,Weihb M,Verwijstb T,et al.The effects of nitrogen fertilization and soil properties on mycorrhizal formation of Salix viminalis[J].Forest Ecology and Management,2002,160(1-3):35-43. |
| 19 | 许美玲,朱教君,孙军德,等.树木外生菌根菌与环境因子关系研究进展[J].生态学杂志,2004,23(5):212-217. |
| Xu M L,Zhu J J,Sun J D,et al.A review on the relationships between forest Ectomycorrhizal fungi and environmental factors[J].Chinese Journal of Ecology,2004,23(5):212-217. | |
| 20 | 薛璟花,莫江明,李炯,等.氮沉降对外生菌根真菌的影响[J].生态学报,2004,24(8):1785-1792. |
| Xue J H,Mo J M,Li J,et al.Effects of nitrogen deposition on ectomycorrhizal fungi[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2004,24(8):1785-1792. | |
| 21 | 郭米山,高广磊,丁国栋,等.呼伦贝尔沙地樟子松外生菌根真菌多样性[J].菌物学报,2018,37(9):1133-1142. |
| Guo M S,Gao G L,Ding G D,et al.Diversity of ectomycorrhizal fungi associated with Pinus sylvestris var.mongolica in Hulunbuir Sandy Land[J].Mycosystema,2018,37(9):1133-1142. | |
| 22 | Sun Y,Gu J C,Zhuang H F,et al.Effects of ectomycorrhizal colonization and nitrogen fertilization on morphology of root tips in a Larix gmelinii plantation in northeastern China[J].Ecological Research,2010,25(2):295-302. |
| 23 | Kou L,Guo D L,Yang H,et al.Growth,morphological traits and mycorrhizal colonization of fine roots respond differently to nitrogen addition in a slash pine plantation in subtropical China[J].Plant and Soil,2015,391(1-2):207-218. |
| 24 | Wallenda T,Kottke I.Nitrogen deposition and ectomycorrhizas[J].New Phytologist,1998,139(1):169-187. |
| 25 | Corkidi L,Rowland D L,Johnson N C,et al.Nitrogen fertilization alters the functioning of arbuscular mycorrhizas at two semiarid grasslands[J].Plant and Soil,2002,240(2):299-310. |
| 26 | 祁金玉,邓继峰,尹大川,等.外生菌根菌对油松幼苗抗氧化酶活性及根系构型的影响[J].生态学报,2019,39(8):2826-2832. |
| Qi J Y,Deng J F,Yin D C,et al.Effects of inoculation of exogenous mycorrhizal fungi on the antioxidant and root configuration enzyme activity of Pinus tabulaeformis seedlings[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2019,39(8):2826-2832. | |
| 27 | 吴小芹,郑玲,叶建仁.黑松三种菌根苗根系构型差异及其与生长的关系[J].生态学报,2009,29(10):5493-5499. |
| Wu X Q,Zheng L,Ye J R.Root architecture differences and their relationships with the growth of Pinus thunbergii seedlings with three kinds of ectomycorrhizae[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2009,29(10):5493-5499. | |
| 28 | 辛月,尚博,陈兴玲,等.氮沉降对臭氧胁迫下青杨光合特性和生物量的影响[J].环境科学,2016,37(9):3642-3649. |
| Xin Y,Shang B,Chen X L,et al.Effects of elevated ozone and nitrogen deposition on photosynthetic characteristics and biomass of Populus cathayana[J].Environmental Science,2016,37(9):3642-3649. | |
| 29 | 李树庭,于捷,岳钉伊,等.不同密度和氮素水平对设施袋培番茄产量、品质及冠层结构的影响[J].西北农业学报,2016,25(6):903-911. |
| Li S T,Yu J,Yue D Y,et al.Effect of plant density and nitrogen fertilizer rate on yield,quality and canopy structure of greenhouse tomato cultivated on organic substrate bag[J].Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica,2016,25(6):903-911. | |
| 30 | Wang G L,Fahey T J,Xue S,et al.Root morphology and architecture respond to N addition in Pinus tabulaeformis,west China[J].Oecologia,2013,171(2):583-590. |
| 31 | 闫国永.模拟氮沉降对兴安落叶松细根动态和形态结构的影响[D].哈尔滨:东北林业大学,2017. |
| Yan G Y.Effected of simulated nitrogen deposition on fine root dynamics and morphological structure of Larix gmelinii[D].Harbin:Northeast Forestry University,2017. |
| [1] | Zhenggang XU, Hang XU, Xiutao PENG, Shijun LIANG, Rong LIU, Shanghua LUO, Juan XIAO. Effects of N addition on Root Exudates and Their Mediated Nutrient Rransformation Processes in a Betula albosinensis Burk Forest in Southwest China [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(2): 194-206. |
| [2] | Zhaoyi LI, Longfei HAO, Tingyan LIU, Yanhong HE, You ZHANG, Shulan BAI, Xinyu YANG. AM Fungi Inoculation on Root Morphology and Nutrient Loading of Clematis fruticosa Seedlings under Simulated Atmospheric Nitrogen Deposition [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(5): 886-895. |
| [3] | Hai-Jun XU, Qin YAO, Xin-Yu CHENG, Xiao-Fei WANG. Interspecies Difference of Astragalus on Root Development, Component Accumulation and Apparent Growth in Northern China [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(6): 862-869. |
| [4] | Ting-Yan LIU, Long-Fei HAO, Xu-Fu WANG, Hai-Xia YAN, Shu-Lan BAI. Effects of Nitrogen Deposition and Ectomycorrhizal Fungi on Root Architecture and Rhizosphere Soil Enzyme Activities of Larix olgensis Seedlings [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(1): 145-151. |
| [5] | ZHAO Zhe, JIN Ze-Xin. Effects of Simulated Nitrogen Deposition on the Growth and the Content of Non-structure Carbohydrate of Sinocalycanthus chinensis Seedlings [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(1): 41-49. |
| [6] | ZHAO Min, HAO Wen-Ying, NING Xin-Zhe, HAO Long-Fei, YAN Hai-Xia, MU Ya-Nan, BAI Shu-Lan. Screening of Excellent Ectomycorrhizal Fungi-tree for Drought Resistant with Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(1): 133-140. |
| [7] | MA Peng-Yu, ZHANG Hong-Guang, ZAN Peng, GU Wei-Ping, WEN Lu-Ning, ZHANG Zi-Jia, WENG Hai-Long, SUN Tao, MAO Zi-Jun. Effects of Long-term Nitrogen Addition on Soil Enzymes in Larix gmelinii Plantation in Northeast China [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2019, 39(4): 598-603. |
| [8] | WAN Xue-Bing, WANG Qing-Gui, YAN Guo-Yong, XING Ya-Juan. Response of Ecological Stoichiometric Characteristics and Photosynthetic Characteristics of Plant Leaves to Long-term N Deposition in Natural Secondary Forest [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2019, 39(3): 407-420. |
| [9] | LI Yuan-Yuan, WANG Zheng-Wen, SUN Tao. Response of Fine Root Decomposition to Long-term Nitrogen Addition in the Temperate Forest [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2017, 37(6): 848-854. |
| [10] | LIU Jian-Cai;CHEN Jin-Ling;JIN Guang-Ze*. Response of Soil Organic Carbon and Nutrients to Simulated Nitrogen Deposition in Typical Mixed Broadleaved-Korean Pine Forest [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2014, 34(1): 121-130. |
| [11] | WANG Chuan-Hua;WANG Yuan;LI Jun-Qing*. Effects of Light and Nitrogen Supply on the Carbon Balance of Seedling of Platycarya strobilacea [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2012, 32(2): 177-182. |
| [12] | GUO Xiao-Rui;WANG Hong-Ling;WANG Hua-Nan;DUAN Xi-Hua*. The Effects of Supplementary UV-B Radiation and Nitrogen Levels on the Growth and Physiological Metabolism of Catharanthus roseus [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2011, 31(5): 592-596. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||