Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (5): 679-689.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2023.05.005
• Genetic and Breeding • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2023-07-18
Online:2023-09-20
Published:2023-09-05
Contact:
Dezong SUI
E-mail:535122107@qq.com
About author:SUI Dezong(1978—),male,research fellow,mainly engaged in salt-tolerant tree breeding and coastal shelterbelt construction technology research.
Supported by:CLC Number:
Dezong SUI, Baosong WANG. Comparative Proteomics on Leaves of Triadica sebifera Clones under Salt Stress[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(5): 679-689.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://bbr.nefu.edu.cn/EN/10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2023.05.005
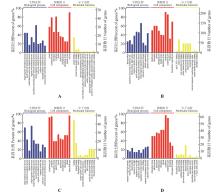
Fig.1
GO enrichment analysis of DEPs in T. sebifera leaves under salt stressA.GO analysis of DEPs in SS18 leaves after 24 h salt stress,compared with 0 h no salt stress;B.GO analysis of DEPs in SS18 leaves after 72 h salt stress,compared with 0 h no salt stress;C.GO analysis of DEPs in ST21 leaves after 24 h salt stress,compared with 0 h no salt stress;D.GO analysis of DEPs in ST21 leaves after 72 h salt stress,compared with 0 h no salt stress
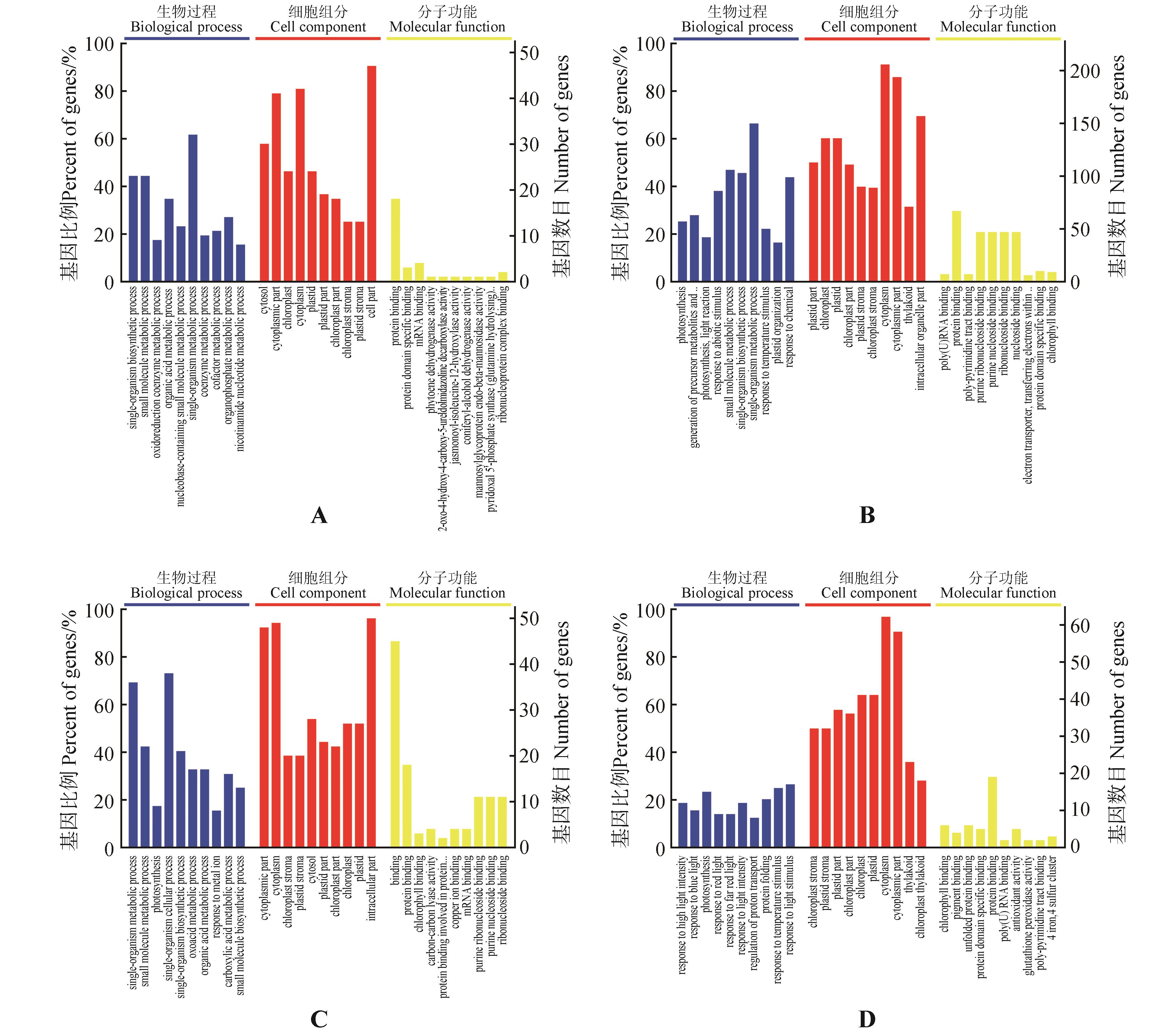
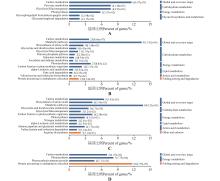
Fig.2
KEGG analysis of DEPs in T. sebifera leaves under salt stressA.KEGG analysis of DEPs in SS18 leaves after 24 h salt stress,compared with 0 h no salt stress;B.KEGG analysis of DEPs in SS18 leaves after 72 h salt stress,compared with 0 h no salt stress;C.KEGG analysis of DEPs in ST21 leaves after 24 h salt stress,compared with 0 h no salt stress; D.KEGG analysis of DEPs in ST21 leaves after 72 h salt stress,compared with 0 h no salt stress


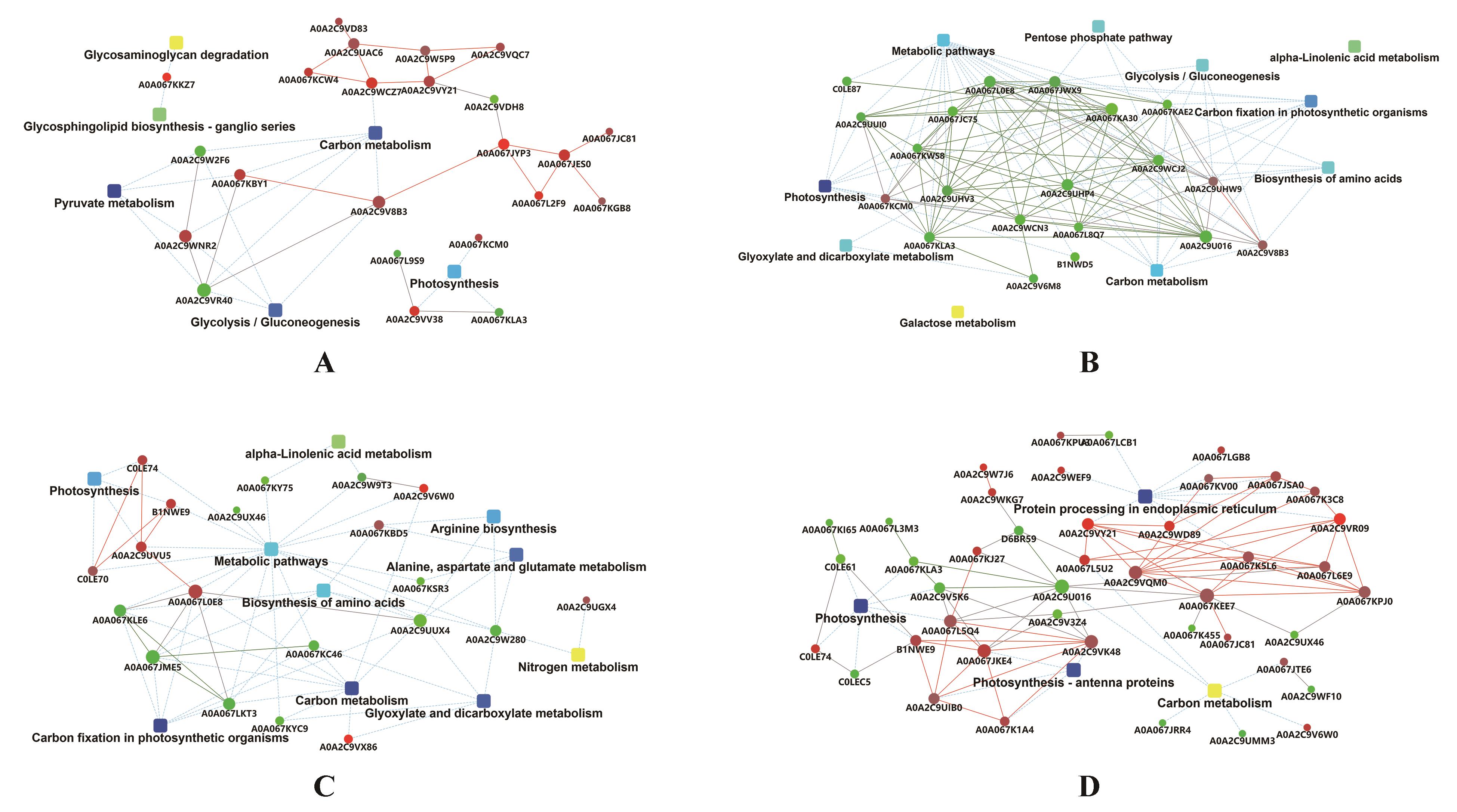
Fig.3
PPI analysis of DEPs in T. sebifera leaves under salt stressThe nodes represented the different proteins,the size of node represented the relative abundance,the green nodes meant the low change fold,and the red nodes meant the high change fold,the square nodes represented the KEGG pathways,the blue nodes meant greater value of -log(P),and the yellow nodes meant smaller value of -log(P),the red lines meant the significantly positive correlations,the green lines meant the significantly negative correlations,and the black lines meant the significant correlations;A.PPI analysis of DEPs in SS18 leaves after 24 h salt stress, compared with 0 h no salt stress;B.PPI analysis of DEPs in SS18 leaves after 72 h salt stress, compared with 0 h no salt stress;C.PPI analysis of DEPs in ST21 leaves after 24 h salt stress,compared with 0 h no salt stress;D.PPI analysis of DEPs in ST21 leaves after 72 h salt stress, compared with 0 h no salt stress

| 1 | 刘微,李佳薇,徐若瑄,等.NaCl胁迫对辣椒种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响[J/OL].分子植物育种[2021-10-29].. |
| LIU W, LI J W, XU R X,et al.Effect of NaCl stress on seed germination and seedling growth of pepper[J/OL].Molecular Plant Breeding[2021-10-29].. | |
| 2 | 缪李飞,于晓晶,张秋悦,等.4个杜梨半同胞家系苗期耐盐性分析[J].南京林业大学学报(自然科学版),2020,44(5):157-166. |
| MIAO L F, YU X J, ZHANG Q Y,et al.Salt tolerance of four half-sib families of Pyrus betulaefolia Bunge from coastal areas[J].Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition),2020,44(5):157-166. | |
| 3 | 崔士友,张蛟,翟彩娇,等.江苏沿海滩涂快速改良与高效利用研究进展[J].农学学报,2017,7(3):42-46. |
| CUI S Y, ZHANG J, ZHAI C J.Fast amelioration and efficient utilization of coastal beach in Jiangsu province[J].Journal of Agriculture,2017,7(3):42-46. | |
| 4 | 刘鹏,龚伟,陈鑫,等.乌桕经霜满树红:乌桕园林观赏价值及应用[J].现代园艺,2020,43(14):90-92. |
| LIU P, GONG W, CHEN X,et al.The ornamental value and application of Triadica sebifera [J].Modern Horticulture,2020,43(14):90-92. | |
| 5 | 李冬林,黄栋,王瑾,等.乌桕研究综述[J].江苏林业科技,2009,36(4):43-47. |
| LI D L, HUANG D, WANG J,et al.The review of research on Triadica sebifera [J].Journal of Jiangsu Forestry Science and Technology,2009,36(4):43-47. | |
| 6 | 张广涛,包厚天,黄卫和,等.不同氮素施肥处理对乌桕容器苗和根系生长的影响[J].江苏农业科学,2022,50(9):135-142. |
| ZHANG G T, BAO H T, HUANG W H,et al.Effects of different nitrogen application treatments on growth and root architecture of Sapium sebiferum container seedlings[J].Jiangsu Agricultural Science,2022,50(9):135-142. | |
| 7 | 陈百强,曹受金,沈鑫,等.观赏乌桕品种表型多样性分析及综合评价[J].分子植物育种,2022,20(12):4108-4120. |
| CHEN B Q, CAO S J, SHEN X,et al.Phenotypic diversity analysis and comprehensive evaluation of ornamental Triadica sebiferum varieties[J].Molecular Plant Breeding,2022,20(12):4108-4120. | |
| 8 | 李立君,赵婷婷,钱存梦,等.内源抑制物对乌桕种子萌发的影响[J].东北林业大学学报,2022,50(12):9-14. |
| LI L J, ZHAO T T, QIAN C M,et al.Effect of endogenous inhibitors on seed germination of Sapium sebiferum [J].Journal of Northeast Forestry University,2022,50(12):9-14. | |
| 9 | 李因刚,沈凤强,徐永勤,等.观赏乌桕新品种‘红紫佳人’[J].园艺学报,2020,47(S2):3137-3138. |
| LI Y G, SHEN F Q, XU Y Q,et al.A new ornamental Triadica sebifera cultivar‘Hongzi Jiaren’[J].Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2020,47(S2):3137-3138. | |
| 10 | 许中秋,隋德宗,谢寅峰,等.两个乌桕新品种苗木光合特性比较[J].南京林业大学学报(自然科学版),2021,45(1):93-100. |
| XU Z Q, SUI D Z, XIE Y F,et al.Comparison of photosynthetic characteristics of two new Triadica sebifera varieties[J].Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition),2021,45(1):93-100. | |
| 11 | 倪正.观叶乌桕优株选择及其叶片呈色生理生化分析[D].合肥:安徽农业大学,2022. |
| NI Z.Physiological and biochemical analysis of superior selection and leaves discoloration of ornamental leaves Sapium sebiferum [D].Hefei:Anhui Agricultural University,2022. | |
| 12 | 吴飞洋,柳新红,王成龙,等.土壤水分对乌桕秋叶生理指标及观赏效果的影响[J].东北林业大学学报,2021,49(5):19-23,44. |
| WU F Y, LIU X H, WANG C L,et al.Effects of soil water content on physiological indexes and ornamental effects of Triadica sebifera leaves in autumn[J].Journal of Northeast Forestry University,2021,49(5):19-23,44. | |
| 13 | 王乔健.独脚金内酯调控乌桕抗旱耐盐的分子机理研究[D].合肥:安徽农业大学,2019. |
| WANG Q J.Molecular mechanism of strigolactons in the regulation of drought and salt resistance in the S .sebiferum[D].Hefei:Anhui Agricultural University,2019. | |
| 14 | 隋德宗,许中秋,王俊毅.4个乌桕新品种对NaCl胁迫的生理响应及耐盐性评价[J].安徽农业大学学报,2021,48(6):889-894. |
| SUI D Z, XU Z Q, WANG J Y.Physiological response and salt tolerance evaluation of four new Triadica sebifera varieties to salt stress[J].Journal of Anhui Agricultural University,2021,48(6):889-894. | |
| 15 | 董峰平,李海波,柳新红,等.基于转录组序列的乌桕SSR分子标记开发[J].分子植物育种,2020,18(19):6449-6455. |
| DONG F P, LI H B, LIU X H,et al.Development of SSR markers based on transcriptome sequences of Triadica sebifera [J].Molecular Plant Breeding,2020,18(19):6449-6455. | |
| 16 | 王东东.SsGA2o×1和Ssga20o×1调控乌桕木质部发育的功能研究[D].合肥:安徽农业大学,2019. |
| WANG D D.Functional study of SsGA2o×1 and Ssga20o×1 on the regulation of tallow xylem development[D].Hefei:Anhui Agricultural University,2019. | |
| 17 | 吴影.乌桕花芽转录组测序分析及花发育调控机制研究[D].合肥:中国科学技术大学,2015. |
| WU Y.Floral bud transcriptome analysis and research on floral development regulation mechanism of Sapium sebiferum [D].Hefei:University of Science and Technology of China,2015. | |
| 18 | LUO J, REN W Y, CAI G H. et al.The chromosome-scale genome sequence of Triadica sebifera provides insight into fatty acids and anthocyanin biosynthesis[J].Communications Biology,2022,5(1):786. |
| 19 | YE Z C, YU J, YAN W P,et al.Integrative iTRAQ-based proteomic and transcriptomic analysis reveals the accumulation patterns of key metabolites associated with oil quality during seed ripening of Camellia oleifera [J].Horticulture Research,2021,8(1):157. |
| 20 | FENG Z M, GAO P, ZHAO J H,et al.iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomics analysis of defense responses triggered by the pathogen Rhizoctonia solani infection in rice[J].Journal of Integrative Agriculture,2022,21(1):139-152. |
| 21 | ZHANG Y X, CHEN Y, GUO Y Y,et al.iTRAQ-based proteomic analysis reveals that energy waste caused by transmembrane transport disruption accelerated the ripening and senescence of postharvest broccoli heads under high O2 stress[J].Scientia Horticulturae,2022,301:111125. |
| 22 | LI J J, NADEEM M, CHEN L Y,et al.Differential proteomic analysis of soybean anthers by iTRAQ under high-temperature stress[J].Journal of Proteomics,2020,229:103968. |
| 23 | TENG R M, WU Z J, MA H Y,et al.Differentially expressed protein are involved in dynamic changes of catechins contents in postharvest tea leaves under different temperatures[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2019,67(26):7547-7560. |
| 24 | 姜志磊,金峰学,李毅丹.基于iTRAQ技术的干旱胁迫下玉米苗期蛋白质组学研究[J].玉米科学,2020,28(1):51-58. |
| JIANG Z L, JIN X F, LI Y D.iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomic analysis of maize seedlings in response to drought stress[J].Journal of Maize Sciences,2020,28(1):51-58. | |
| 25 | WU Z J, MA H Y, ZHUANG J.iTRAQ-based proteomics monitors the withering dynamics in postharvest leaves of tea plant (Camellia sinensis)[J].Molecular Genetics and Genomics,2018,293(1):45-59. |
| 26 | 齐琪,马书荣,徐维东.盐胁迫对植物生长的影响及耐盐生理机制研究进展[J].分子植物育种,2020,18(8):2741-2746. |
| QI Q, MA S R, XU W D.Advances in the effects of salt stress on plant growth and physiological mechanisms of salt tolerance[J].Molecular Plant Breeding,2020,18(8):2741-2746. | |
| 27 | 李正丽,张丽,文林宏,等.盐胁迫对两个基因型辣椒生理特性的影响[J].分子植物育种,2022,20(5):1658-1663. |
| LI Z L, ZAHNG L, WEN L H,et al.Effects of salt stress on the physiological characteristics of two pepper genotypes[J].Molecular Plant Breeding,2022,20(5):1658-1663. | |
| 28 | 尚晓蕊,红格日其其格,雷艳红,等.盐胁迫下拟南芥角果蛋白质组学分析[J/OL].分子植物育种[2023-02-02].. |
| SHANG X R, HONG GERI Q, LEI H Y,et al.Proteomic analysis of Arabidopsis silique under salt stress[J/OL].Molecular Plant Breeding[2023-02-02].. | |
| 29 | 王强,刘会芳,韩宏伟,等.基于TMT和PRM技术筛选番茄响应盐胁迫差异表达蛋白[J].新疆农业科学,2022,59(6):1418-1428. |
| WANG Q, LIU H F, HAN H W,et al.Screening differentially expressed proteins in response to salt stress of tomato leaves based on TMT and PRM techniques[J].Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences,2022,59(6):1418-1428. | |
| 30 | 梁敏,许兴,丁向真,等.盐胁迫下宁夏枸杞Na+吸收及Na+/H+转运蛋白与H+-ATPase基因表达的研究[J].核农学报,2020,34(4):745-751. |
| LIANG M, XU X, DING X Z,et al.Effects of salt stress on Na+ uptake and expression of Na+ /H+ transporter and H+-ATPase genes in Lycium barbarum L.[J].Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences,2020,34(4):745-751. | |
| 31 | 孔伟伟.花生质膜H+-ATPase基因AhHA1在盐胁迫响应中的功能研究[D].济南:山东师范大学,2020. |
| KONG W W.Role of peanut plasma membrane H+-ATPase gene AhHA1 in salt stress response[D].Jinan:Shandong Normal University,2020. | |
| 32 | 田林.比拉底白刺响应盐胁迫的生理生化与分子机制研究[D].北京:北京林业大学,2019. |
| TIAN L.Physiological and molecular mechanisms of Nitraria billardieri in response to salt stress[D].Beijing:Beijing Forestry University,2019. | |
| 33 | 麻莹,王晓苹,姜海波,等.盐碱胁迫下碱地肤体内的有机酸积累及其草酸代谢特点[J].草业学报,2017,26(7):158-165. |
| MA Y, WANG X P, JIANG H B,et al.Characteristics of organic acids accumulation and oxalate metabolism in Kochia sieversiana under salt and alkali stresses[J].Acta Prataculturae Sinica,2017,26(7):158-165. | |
| 34 | 王哲,柴里昂,樊怀福,等.植物响应盐胁迫蛋白质组学研究进展[J].浙江农业学报,2019,31(6):1021-1028. |
| WANG Z, CHAI L A, FAN H F,et al.Progress in proteomics analysis of plant response to salt stress[J].Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis,2019,31(6):1021-1028. | |
| 35 | LUO M J, ZHAO Y X, WANG Y D,et al.Comparative proteomics of contrasting maize genotypes provides insights into salt-stress tolerance mechanisms[J].Journal of Proteome Research,2018,17(1):141-153. |
| 36 | PRINSI B, FAILLA O, SCIENZA A,et al.Root proteomic analysis of two grapevine rootstock genotypes showing different susceptibility to salt stress[J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2020,21(3):1-22. |
| 37 | 王强,王娟,张慧君,等.番茄幼苗盐胁迫响应蛋白质组分析[J].西北植物学报,2016,36(11):2226-2232. |
| WANG Q, WANG J, ZHANG H J,et al.Proteome analysis of tomato seedlings in response to salt stress[J].Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica,2016,36(11):2226-2232. | |
| 38 | 张恒,刘晓婷,陈嵩,等.盐胁迫下三倍体小黑杨杂种无性系叶片蛋白质差异表达分析[J].南京林业大学学报(自然科学版),2020,44(2):59-66. |
| ZHANG H, LIU X T, CHEN S,et al.Analysis of differentially expressed proteins in leaves of triploid Populus simonii × P.nigra hybrid clones under salt stress[J].Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Science Edition),2020,44(2):59-66. | |
| 39 | KAV N N V, SRIVASTAVA S, GOONEWARDENE L,et al.Proteome-level changes in the roots of Pisum sativum in response to salinity[J].Annals of Applied Biology,2004,145(2):217-230. |
| 40 | 赵海燕,魏宁,孙聪聪,等.NaCl胁迫对银杏幼树组织解剖结构和光合作用的影响[J].北京林业大学学报,2018,40(11):28-41. |
| ZHAO H Y, WEI N, SUN C C,et al.Effects of salt stress on anatomic structure of tissue and photosynthesis in Ginkgo biloba seedlings[J].Journal of Beijing Forestry University,2018,40(11):28-41. | |
| 41 | 张若溪,蔡亚南,李庆卫.混合盐胁迫对栾树光合生理指标的影响[J].西北植物学报,2022,42(1):98-106. |
| ZHANG R X, CAI Y N, LI Q W.Effect of mixed salt stress on photosynthetic physiological indexes of Koelreuteria paniculata [J].Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica,2022,42(1):98-106. | |
| 42 | 张潭,唐达,李思思,等.盐碱胁迫对枸杞幼苗生物量积累和光合作用的影响[J].西北植物学报,2017,37(12):2474-2482. |
| ZHANG T, TANG D, LI S S,et al.Responses of growth and photosynthesis of Lycium barbarum L.seedling to salt-stress and alkali-stress[J].Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica,2017,37(12):2474-2482. | |
| 43 | 赵娟娟,孟瑛,朱海峰,等.NaCl胁迫对酸枣(Ziziphus acidojujuba)幼苗光合作用和荧光特性的影响[J].石河子大学学报(自然科学版),2017,35(3):319-325. |
| ZHAO J J, MENG Y, ZHU H F,et al.Effect of NaCl stress on the photosynthetic and chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics of sour jujube (Ziziphus acidojujuba) seedlings[J].Journal of Shihezi University (Natural Science),2017,35(3):319-325. | |
| 44 | 李俊良.基于多组学技术探究甜菜盐胁迫应答的分子机制[D].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学,2021. |
| LI J L.Research on exploring the molecular mechanism of salt stress response in sugar beet based on multi-omics technology[D].Harbin:Harbin Institute of Technology,2021. |
| [1] | Shuyao ZHUANG, Hengbo XU, Xiaoyu HU, Shang DAI, Yanni ZHANG. Effects of Saline-alkali Stress on Growth and Physiological Characteristics of Color Leaf Heuchera micrantha ‘Silver Fan’ Seedlings [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(4): 520-530. |
| [2] | Wenhong CHEN, Jinxiu LI, Quang-Hieu NGUYEN, Sinh-Khang NGUYEN, Van-The PHAM, Changli FAN, Jianying XIANG, Yumin SHUI. Begonia holostyla, A New Species of Peltate-leaved Begoniaceae from the Karst Region of Northern Vietnam [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(4): 521-527. |
| [3] | ZHU Ya-Wei, WANG Li-Tao, AN Juan-Yan, Lü Mu-Jie, SUN Jian-Hang, GUO Na, FU Yu-Jie. Response Surface Optimized Enzymatic Hydrolysis-microwave Assisted Extraction Process of Mulberry Leaf Polysaccharide [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(4): 635-640. |
| [4] | ZHANG Shu-Qi, XU Quan, YAO Hai-Rong, YANG Qiu, LIU Wen-Jie, WANG Meng. Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus Contents and Their Ecological Stoichiometry Characteristics in Leaves of Casuarina equisetifolia and Ipomoea pes-caprae in the Coastal Zone of Hainan Island [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(2): 224-232. |
| [5] | LI Xin-Lei, WANG Jia-Tong, SUN Zhen-Yuan, WANG Jie, YIN Heng-Fu, FAN Zheng-Qi, LI Ji-Yuan. UPLC-Q-TOF-MS Analysis of Flavonoids in Flowers and Leaves of Camellia chuangtsoensis [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2019, 39(3): 365-371. |
| [6] | ZHAO Xin, BAI Wei. Screening and Identification of the Proteins Related to Drought Response in Leaves of Eucommia ulmoides [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2018, 38(3): 422-432. |
| [7] | LIN Chun-Song, XU Su-Xia, HUANG Qing-Yun. Caffeoylquinic Acid Derivatives in DAYE Kudingcha(Ilex latifolia Thunb.) Organs in Differently Developing Stage by Micellar Electrokinetic Chromatography [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2018, 38(3): 453-459. |
| [8] | YAN Dong, LIU Dian-Kun, SI Dong-Jing, ZHENG Mi, ZHAO Xi-Yang, QU Guan-Zheng, LI Ying. Optional Protein Extracting Methods of Poplar Leaves for Two-dimensional Gel Electrophoresis [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2016, 36(3): 469-475. |
| [9] | JIN Jian-Bang1,3;CHENG Long-Xia1,3;SHI Man1,3;ZHU Zun-Ling1,2,3*. Induction and Culture of Carpinus betulus Callus [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2015, 35(5): 684-691. |
| [10] | LUO Meng1,2;SONG Zhuo-Yue1,2;HU Jiao-Yang1,2;MU Fan-Song1,2*;QIAO Qi1,2;ZU Yuan-Gang1,2. Optimization of Ultrasonic-assisted Extraction of Total Flavonoids from Crataegus pinnatifida Leaves and Its Antioxidant Activities [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2015, 35(4): 632-637. |
| [11] | MA Fei-Yue;DUAN Kai-Fang;WANG Xi-Qing;QIN Ming-Cong;LI Ji;FU Yu-Jie*. Ionic Liquids-based Microwave-assisted Extraction of Biochanin A and Genistein from Dalbergia odorifera T.Chen Leaves [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2013, 33(4): 494-498. |
| [12] | WU Tian;YE Chang-Hui;HAN Wei-Dong*. Leaf Anatomical Structure and Its Ecological Adaptability of Five Species of Rhizophoraceae Plants [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2012, 32(2): 143-146. |
| [13] | LANG Xue-Dong;SU Jian-Rong*;LU Shu-Gang;ZHANG Zhi-Jun;LI Shuai-Feng. Taxonomic Status of Cephalotaxus alpina(Li) L.K.Fu(Cephalotaxaceae) in the Views of Morphological Characteristics of Seeds and Leaves [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2012, 32(1): 4-9. |
| [14] | ZHAO En-Ze;JIN Shi;WEI Zuo-Fu;WEI Wei;FU Yu-Jie;*. Comparison of the Determination Methods for Total Flavonoids in Pigeon Pea Leaves [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2011, 31(4): 499-502. |
| [15] | WANG Fang;ZHANG Dong-Yang;MA Fei-Yue;GAI Qing-Yan;JIAO Jiao;FU Yu-Jie;*. The Extraction Process of Biochanin A from Dalbergia odorifera T. Chen Leaves [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2011, 31(3): 367-370. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
