Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (6): 840-850.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2025.06.002
• Review Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xueyi ZHAO, Mingyu YANG, Xiang LI, Linhan SI, Nan WANG, Weican LIU, Yuanyuan DONG, Xiaowei LI, Fawei WANG( )
)
Received:2025-04-10
Online:2025-11-20
Published:2025-11-27
Contact:
Fawei WANG
E-mail:wangfawei@jlau.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Xueyi ZHAO, Mingyu YANG, Xiang LI, Linhan SI, Nan WANG, Weican LIU, Yuanyuan DONG, Xiaowei LI, Fawei WANG. Research Progress on Inositol Phosphate Kinases in Plants[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(6): 840-850.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://bbr.nefu.edu.cn/EN/10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2025.06.002
Fig.1
The phosphorylation network of inositol phosphate kinase in plantIPK2 phosphorylates the 6-hydroxyl group of Ins(1,4,5)P3 to synthesize Ins(1,4,5,6)P4, and subsequently catalyzes 3-hydroxyl phosphorylation to generate Ins(1,3,4,5,6)P5; IPK1 phosphorylates the 2-hydroxyl group of Ins(1,3,4,5,6)P5 to produce InsP6; ITPK further catalyzes InsP6 to synthesize InsP7; VIH mediates the pyrophosphorylation of InsP7 to InsP8.
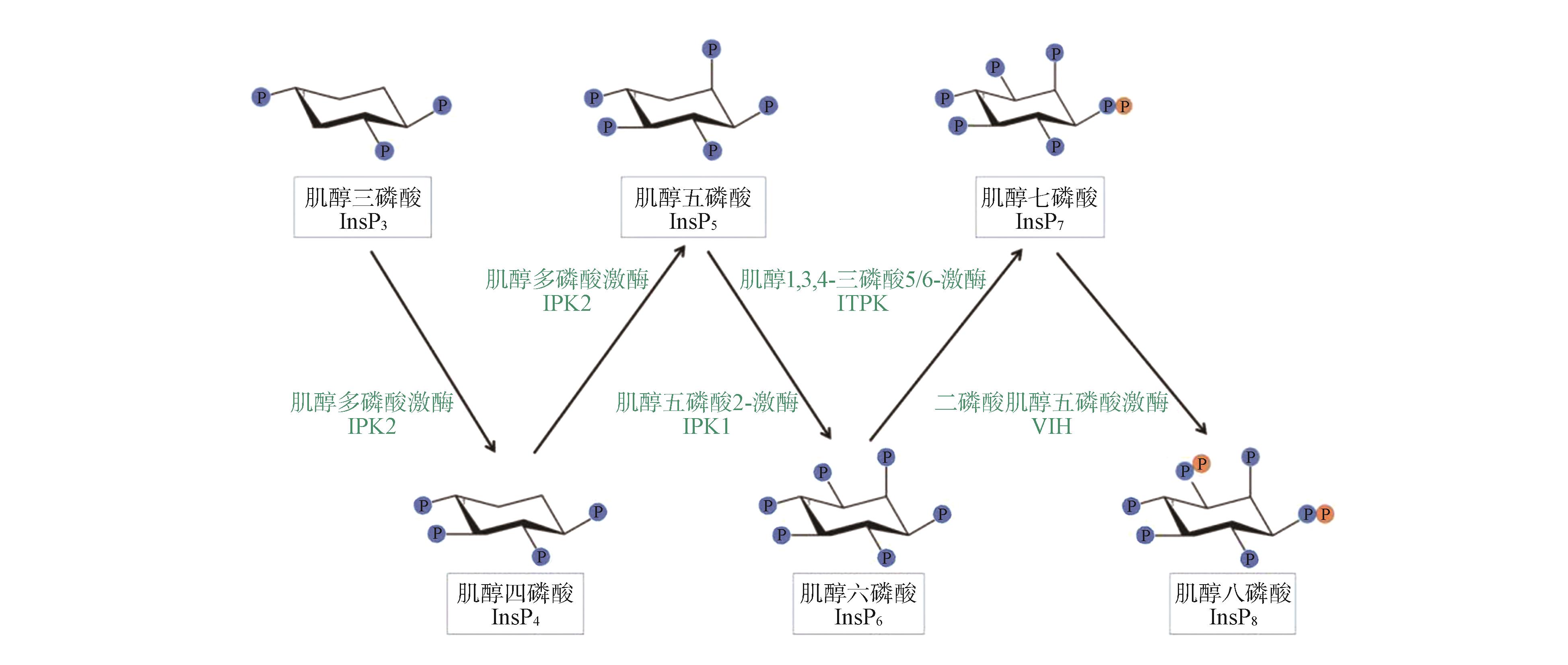
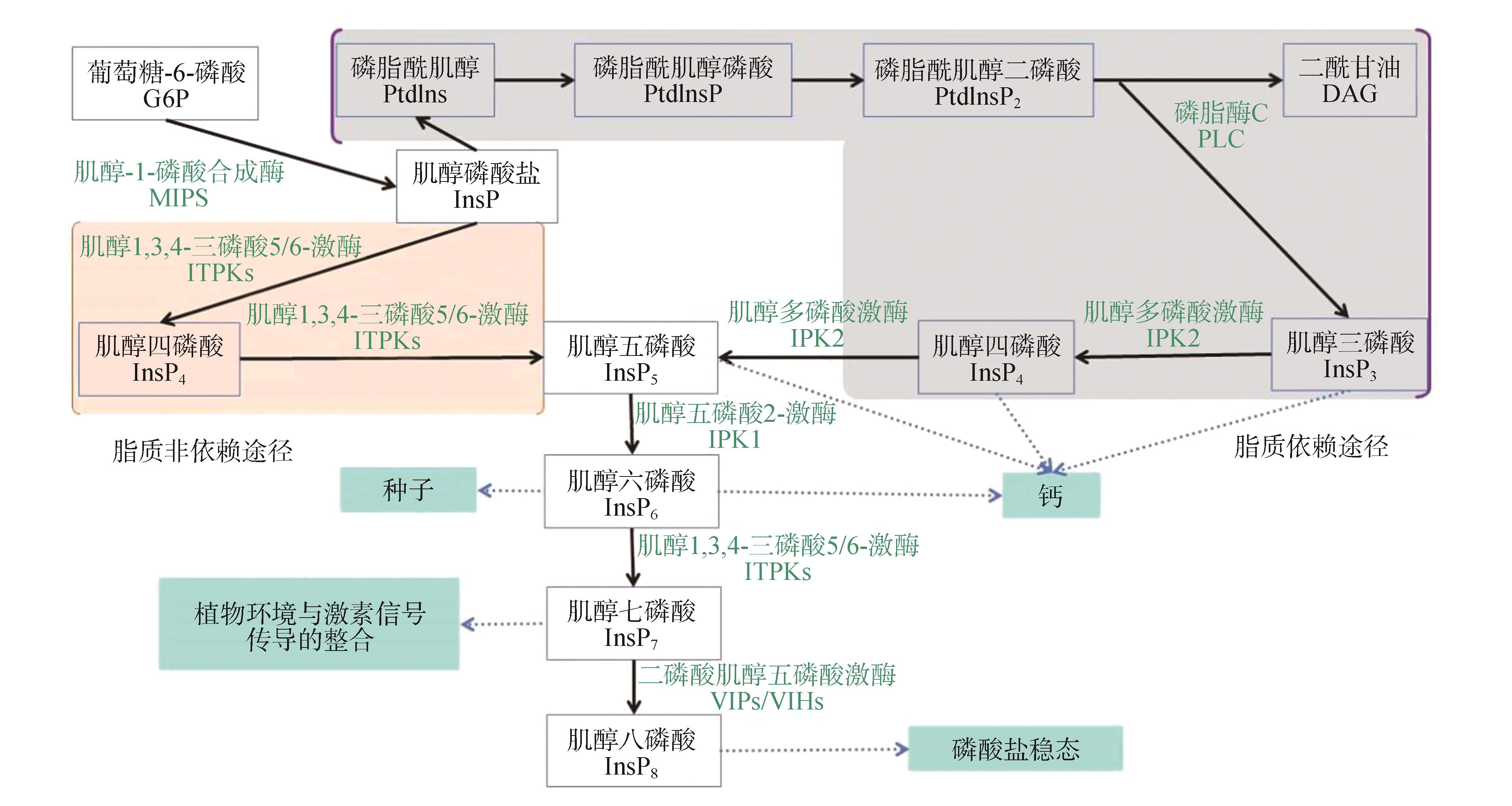
Fig.2
Mechanism of inositol phosphate kinase in plantInsP4, as a phosphorylated product of InsP3, indirectly modulates cytosolic calcium ion concentration in plant cells. In contrast, InsP3, InsP5, and InsP6 directly participate in the regulation of calcium ion dynamics. InsP6 additionally serves as phytic acid, functioning as a major phosphorus reservoir in seeds. InsP7 acts as a signaling hub, integrating environmental cues and hormonal signals to orchestrate plant developmental programs and metabolic adaptations. InsP8 regulates the activity of the phosphate signaling mediator PHR1, thereby controlling phosphate homeostasis and nutrient allocation.
| [1] | GONZÁLEZ B, BAÑOS-SANZ J I, VILLATE M,et al.Inositol 1,3,4,5,6-pentakisphosphate 2-kinase is a distant IPK member with a singular inositide binding site for axial 2-OH recognition[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2010,107(21):9608-9613. |
| [2] | LAHA N P, GIEHL R F H, RIEMER E,et al.Inositol(1,3,4) triphosphate 5/6 KINASE1-dependent inositol polyphosphates regulate auxin responses in Arabidopsis [J].Plant Physiology,2022,190(4):2722-2738. |
| [3] | SHEARS S B, WANG H C.Inositol phosphate kinases:expanding the biological significance of the universal core of the protein kinase fold[J].Advances in Biological Regulation,2019,71:118-127. |
| [4] | SCHELL M J.Inositol trisphosphate 3-kinases:focus on immune and neuronal signaling[J].Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences,2010,67(11):1755-1778. |
| [5] | LI X Y, GU C F, HOSTACHY S,et al.Control of XPR1-dependent cellular phosphate efflux by InsP8 is an exemplar for functionally-exclusive inositol pyrophosphate signaling[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2020,117(7):3568-3574. |
| [6] | SAIARDI A, AZEVEDO C, DESFOUGÈRES Y,et al.Microbial inositol polyphosphate metabolic pathway as drug development target[J].Advances in Biological Regulation,2018,67:74-83. |
| [7] | NAGY R, GROB H, WEDER B,et al.The Arabidopsis ATP-binding cassette protein AtMRP5/AtABCC5 is a high affinity inositol hexakisphosphate transporter involved in guard cell signaling and phytate storage[J].Journal of Biological Chemistry,2009,284 (48):33614-33622. |
| [8] | DESFOUGÈRES Y, WILSON M S C, LAHA D,et al. ITPK1 mediates the lipid-independent synthesis of inositol phosphates controlled by metabolism[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2019,116(49):24551-24561. |
| [9] | MILLER G J, WILSON M P, MAJERUS P W,et al.Specificity determinants in inositol polyphosphate synthesis:crystal structure of inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate 5/6-kinase[J].Molecular Cell,2005,18(2):201-212. |
| [10] | KUO H F, HSU Y Y, LIN W C,et al. Arabidopsis inositol phosphate kinases IPK1 and ITPK1 constitute a metabolic pathway in maintaining phosphate homeostasis[J].The Plant Journal,2018,95(4):613-630. |
| [11] | LAHA D, PARVIN N, HOFER A,et al. Arabidopsis ITPK1 and ITPK2 have an evolutionarily conserved phytic acid kinase activity[J].ACS Chemical Biology,2019,14(10):2127-2133. |
| [12] | RANDALL T A, GU C F, LI X Y,et al.A two-way switch for inositol pyrophosphate signaling:evolutionary history and biological significance of a unique,bifunctional kinase/phosphatase[J].Advances in Biological Regulation,2020,75:100674. |
| [13] | WILSON M S, JESSEN H J, SAIARDI A.The inositol hexakisphosphate kinases IP6K1 and -2 regulate human cellular phosphate homeostasis,including XPR1-mediated phosphate export[J].Journal of Biological Chemistry,2019,294(30):11597-11608. |
| [14] | LAHA D, JOHNEN P, AZEVEDO C,et al.VIH2 regulates the synthesis of inositol pyrophosphate InsP8 and jasmonate-dependent defenses in Arabidopsis [J].The Plant Cell,2015,27(4):1082-1097. |
| [15] | ZHU J S, LAU K, PUSCHMANN R,et al.Two bifunctional inositol pyrophosphate kinases/phosphatases control plant phosphate homeostasis[J].eLife,2019,8:e43582. |
| [16] | LAHA D, PORTELA-TORRES P, DESFOUGÈRES Y,et al.Inositol phosphate kinases in the eukaryote landscape[J].Advances in Biological Regulation,2021,79:100782. |
| [17] | SHAH A, GANGULI S,SEN J,et al.Inositol pyrophosphates:energetic,omnipresent and versatile signalling molecules[J].Journal of the Indian Institute of Science,2017,97(1):23-40. |
| [18] | COUSO I, SMYTHERS A L, FORD M M,et al.Inositol polyphosphates and target of rapamycin kinase signalling govern photosystem II protein phosphorylation and photosynthetic function under light stress in Chlamydomonas [J].New Phytologist,2021,232(5):2011-2025. |
| [19] | AZEVEDO C, SAIARDI A.Eukaryotic phosphate homeostasis:the inositol pyrophosphate perspective[J].Trends in Biochemical Sciences,2017,42(3):219-231. |
| [20] | LÓPEZ-SÁNCHEZ U, TURY S, NICOLAS G,et al.Interplay between primary familial brain calcification-associated SLC20A2 and XPR1 phosphate transporters requires inositol polyphosphates for control of cellular phosphate homeostasis[J].Journal of Biological Chemistry,2020,295(28):9366-9378. |
| [21] | BLIND R D.Structural analyses of inositol phosphate second messengers bound to signaling effector proteins[J].Advances in Biological Regulation,2020,75:100667. |
| [22] | QIU D Y, WILSON M S, EISENBEIS V B,et al.Analysis of inositol phosphate metabolism by capillary electrophoresis electrospray ionization mass spectrometry[J].Nature Communications,2020,11(1):6035. |
| [23] | KOMATSU H, TANABE K, NISHIMOTO S I.(13)C-labeled indolequinone-DTPA-Gd conjugate for NMR probing cytochrome:P450 reductase-mediated one-electron reduction[J].Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters,2011,21(2):790-793. |
| [24] | ITO M, FUJII N, WITTWER C,et al.Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for the quantitative analysis of mammalian-derived inositol poly/pyrophosphates[J].Journal of Chromatography A,2018,1573:87-97. |
| [25] | WILSON M S C, BULLEY S J, PISANI F,et al.A novel method for the purification of inositol phosphates from biological samples reveals that no phytate is present in human plasma or urine[J].Open Biology,2015,5(3):150014. |
| [26] | SHEARS S B, BAUGHMAN B M, GU C F,et al.The significance of the 1-kinase/1-phosphatase activities of the PPIP5K family[J].Advances in Biological Regulation,2017,63:98-106. |
| [27] | KUO H F, CHANG T Y, CHIANG S F,et al. Arabidopsis inositol pentakisphosphate 2-kinase,AtIPK1,is required for growth and modulates phosphate homeostasis at the transcriptional level[J].The Plant Journal,2014,80(3):503-515. |
| [28] | PERERA I, SENEWEERA S, HIROTSU N.Manipulating the phytic acid content of rice grain toward improving micronutrient bioavailability[J].Rice,2018,11:4. |
| [29] | TAKAGI D, MIYAGI A, TAZOE Y,et al.Phosphorus toxicity disrupts rubisco activation and reactive oxygen species defence systems by phytic acid accumulation in leaves[J].Plant,Cell & Environment,2020,43(9):2033-2053. |
| [30] | ZHAN H D, ZHONG Y J, YANG Z G,et al.Enzyme activities of Arabidopsis inositol polyphosphate kinases AtIPK2α and AtIPK2β are involved in pollen development,pollen tube guidance and embryogenesis[J].The Plant Journal,2015,82(5):758-771. |
| [31] | ZHU J Q, ZHANG J T, TANG R J,et al.Molecular characterization of ThIPK2,an inositol polyphosphate kinase gene homolog from Thellungiella halophila,and its heterologous expression to improve abiotic stress tolerance in Brassica napus [J].Physiologia Plantarum,2009,136(4):407-425. |
| [32] | STILES A R, QIAN X, SHEARS S B,et al.Metabolic and signaling properties of an Itpk gene family in Glycine max .FEBS Letters,2008,582(13):1853-1858. |
| [33] | CHEN Y, HAN J M, WANG X Y,et al. OsIPK2,a rice inositol polyphosphate kinase gene,is involved in phosphate homeostasis and root development[J].Plant and Cell Physiology,2023,64(8):893-905. |
| [34] | SONG J H, SHIN G, KIM H J,et al.Mutation of GmIPK1 gene using CRISPR/Cas9 reduced phytic acid content in soybean seeds[J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2022,23(18):10583. |
| [35] | STEPHENS L R, IRVINE R F.Stepwise phosphorylation of myo-inositol leading to myo-inositol hexakisphosphate in Dictyostelium [J].Nature,1990,346(6284):580-583. |
| [36] | BREARLEY C A, HANKE D E.Metabolic evidence for the order of addition of individual phosphate esters in the myo-inositol moiety of inositol hexakisphosphate in the duckweed Spirodela polyrhiza L.[J].Biochemical Journal,1996,314(1):227-233. |
| [37] | WAKEEL A, ARIF S, BASHIR M A,et al.Perspectives of folate biofortification of cereal grains[J].Journal of Plant Nutrition,2018,41(19):2507-2524. |
| [38] | SHI J R, WANG H Y, WU Y S,et al.The maize low-phytic acid mutant lpa2 is caused by mutation in an inositol phosphate kinase gene[J].Plant Physiology,2003,131(2):507-515. |
| [39] | JOSEFSEN L, BOHN L, SORENSEN M B,et al.Characterization of a multifunctional inositol phosphate kinase from rice and barley belonging to the ATP-grasp superfamily[J].Gene,2007,397(1/2):114-125. |
| [40] | SWEETMAN D, STAVRIDOU I, JOHNSON S,et al. Arabidopsis thaliana inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate 5/6-kinase 4 (AtITPK4) is an outlier to a family of ATP-grasp fold proteins from Arabidopsis [J].FEBS Letters,2007,581(22):4165-4171. |
| [41] | SAIARDI A, ERDJUMENT-BROMAGE H, SNOWMAN A M,et al.Synthesis of diphosphoinositol pentakisphosphate by a newly identified family of higher inositol polyphosphate kinases[J].Current Biology,1999,9(22):1323-1326. |
| [42] | FREED C, ADEPOJU O, GILLASPY G.Can inositol pyrophosphates inform strategies for developing low phytate crops?[J].Plants,2020,9(1):115. |
| [43] | RIEMER E, QIU D Y, LAHA D,et al.ITPK1 is an InsP6/ADP phosphotransferase that controls phosphate signaling in Arabidopsis [J].Molecular Plant,2021,14(11):1864-1880. |
| [44] | DONG J S, MA G J, SUI L Q,et al.Inositol pyrophosphate InsP8 acts as an intracellular phosphate signal in Arabidopsis [J].Molecular Plant,2019,12(11):1463-1473. |
| [45] | DESAI M, RANGARAJAN P, DONAHUE J L,et al.Two inositol hexakisphosphate kinases drive inositol pyrophosphate synthesis in plants[J].The Plant Journal,2014,80(4):642-653. |
| [46] | LEMTIRI-CHLIEH F, MACROBBIE E A C, BREARLEY C A.Inositol hexakisphosphate is a physiological signal regulating the K+-inward rectifying conductance in guard cells[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2000,97(15):8687-8692. |
| [47] | DORSCH J A, COOK A, YOUNG K A,et al.Seed phosphorus and inositol phosphate phenotype of barley low phytic acid genotypes[J].Phytochemistry,2003,62(5):691-706. |
| [48] | MULUGU S, BAI W L, FRIDY P C,et al.A conserved family of enzymes that phosphorylate inositol hexakisphosphate[J].Science,2007,316(5821):106-109. |
| [49] | WILD R, GERASIMAITE R, JUNG J Y,et al.Control of eukaryotic phosphate homeostasis by inositol polyphosphate sensor domains[J].Science,2016,352(6288):986-990. |
| [50] | ZHU A Q, IBRAHIM J G, LOVE M I.Heavy-tailed prior distributions for sequence count data:removing the noise and preserving large differences[J].Bioinformatics,2019,35(12):2084-2092. |
| [51] | NAGPAL L, HE S N, RAO F,et al.Inositol pyrophosphates as versatile metabolic messengers[J].Annual Review of Biochemistry,2024,93:317-338. |
| [52] | STEGER D J, HASWELL E S, MILLER A L,et al.Regulation of chromatin remodeling by inositol polyphosphates[J].Science,2003,299(5603):114-116. |
| [53] | WILSON M S C, LIVERMORE T M, SAIARDI A.Inositol pyrophosphates:between signalling and metabolism[J].Biochemical Journal,2013,452(3):369-379. |
| [54] | BLOOT A P M, KALSCHNE D L, AMARAL J A S,et al.A review of phytic acid sources,obtention,and applications[J].Food Reviews International,2023,39(1):73-92. |
| [55] | SHAMSUDDIN A K, Bose S.IP6(inositol hexaphosphate) as a signaling molecule[J].Current Signal Transduction Therapy,2012,7(3):289-304. |
| [56] | BROUNS F.Phytic acid and whole grains for health controversy[J].Nutrients,2022,14(1):25. |
| [57] | XU L L, CUI M Q, XU C,et al.A clade of receptor-like cytoplasmic kinases and 14-3-3 proteins coordinate inositol hexaphosphate accumulation[J].Nature Communications,2024,15:5107. |
| [58] | PERERA I, SENEWEERA S, HIROTSU N.Manipulating the phytic acid content of rice grain toward improving micronutrient bioavailability[J].Rice,2018,11:4. |
| [59] | LIU H T, GAO F, CUI S J,et al.Primary evidence for involvement of IP3 in heat-shock signal transduction in Arabidopsis [J].Cell Research,2006,16(4):394-400. |
| [60] | WANG LN, CUI J, ZHANG N,et al. OsIPK1 frameshift mutations disturb phosphorus homeostasis and impair starch synthesis during grain filling in rice[J].Plant Molecular Biology,2024,114(5):91. |
| [61] | XIA H J, YANG G.Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinases:functions and regulations[J].Cell Research,2005,15(2):83-91. |
| [62] | YADAV R, LIU G Z, RANA P,et al.Conservation of heat stress acclimation by the inositol polyphosphate multikinase,IPMK responsible for 4/6-InsP7 production in land plants[EB/OL].bioRxiv,(2023-11-18)[2025-03-30].. |
| [63] | JIANG M, LIU Y H, LI R Q,et al.An inositol 1,3,4,5,6-pentakisphosphate 2-kinase 1 mutant with a 33-nt deletion showed enhanced tolerance to salt and drought stress in rice[J].Plants,2021,10(1):23. |
| [64] | WANG W, XIE Y W, LIU L,et al.Genetic control of seed phytate accumulation and the development of low-phytate crops:a review and perspective[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2022,70(11):3375-3390. |
| [65] | ALI N, PAUL S, GAYEN D,et al.Development of low phytate rice by RNAi mediated seed-specific silencing of inositol 1,3,4,5,6-pentakisphosphate 2-kinase gene (IPK1)[J].PLoS One,2013,8(7):e68161. |
| [66] | AGGARWAL S, KUMAR A, BHATI K K,et al.RNAi-mediated downregulation of inositol pentakisphosphate kinase(IPK1) in wheat grains decreases phytic acid levels and increases Fe and Zn accumulation[J].Frontiers in Plant Science,2018,9:259. |
| [67] | ZHANG Y, LIANG Z, ZONG Y,et al.Efficient and transgene-free genome editing in wheat through transient expression of CRISPR/Cas9 DNA or RNA[J].Nature Communications,2016,7:12617. |
| [68] | WHITFIELD H, WHITE G, SPRIGG C,et al.An ATP-responsive metabolic cassette comprised of inositol tris/tetrakisphosphate kinase 1 (ITPK1) and inositol pentakisphosphate 2-kinase(IPK1) buffers diphosphosphoinositol phosphate levels[J].Biochemical Journal,2020,477(14):2621-2638. |
| [69] | GULABANI H, GOSWAMI K, WALIA Y,et al. Arabidopsis inositol polyphosphate kinases IPK1 andITPK1 modulate crosstalk between SA-dependent immunity and phosphate-starvation responses[J].Plant Cell Reports,2022,41(2):347-363. |
| [70] | COLOMBO F, PAOLO D, COMINELLI E,et al.MRP transporters and low phytic acid mutants in major crops:main pleiotropic effects and future perspectives[J].Frontiers in Plant Science,2020,11:1301. |
| [71] | CHIU C H, PASZKOWSKI U.Mechanisms and impact of symbiotic phosphate acquisition[J].Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology,2019,11(6):a034603. |
| [72] | POIRIER Y, JASKOLOWSKI A, CLÚA J.Phosphate acquisition and metabolism in plants[J].Current Biology,2022,32(12):R623-R629. |
| [73] | SHUKLA A, KAUR M, KANWAR S,et al.Wheat inositol pyrophosphate kinase TaVIH2-3B modulates cell-wall composition and drought tolerance in Arabidopsis [J].BMC Biology,2021,19(1):261. |
| [74] | SONG L Z, WANG Y N, GUO Z A,et al.NCP2/RHD4/SAC7,SAC6 and SAC8 phosphoinositide phosphatases are required for PtdIns4P and PtdIns(4,5)P2 homeostasis and Arabidopsis development[J].New Phytologist,2021,231(2):713-725. |
| [75] | YANG S L, FANG G N, ZHANG A P,et al.Rice EARLY SENESCENCE 2,encoding an inositol polyphosphate kinase,is involved in leaf senescence[J].BMC Plant Biology,2020,20(1):393. |
| [76] | CHEN Y, YANG Q F, SANG S H,et al.Rice inositol polyphosphate kinase(OsIPK2) directly interacts with OsIAA11 to regulate lateral root formation[J].Plant and Cell Physiology,2017,58(11):1891-1900. |
| [77] | CHEN Y, HAN J M, WANG X Y,et al. OsIPK2,a rice inositol polyphosphate kinase gene,is involved in phosphate homeostasis and root development[J].Plant and Cell Physiology,2023,64(8):893-905. |
| [78] | AOYAMA T.Phospholipid signaling in root hair development[M]//Emons A M C,Ketelaar T,et al.Root hairs.Plant Cell Monographs:Vol.12.Berlin:Springer,2009:171-189. |
| [79] | ZHAN H D, ZHONG Y J, YANG Z N,et al.Enzyme activities of Arabidopsis inositol polyphosphate kinases AtIPK2α and AtIPK2β are involved in pollen development,pollen tube guidance and embryogenesis[J].The Plant Journal,2015,82(5):758-771. |
| [80] | STEVENSON-PAULIK J, BASTIDAS R J, CHIOU S T,et al.Generation of phytate-free seeds in Arabidopsis through disruption of inositol polyphosphate kinases[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2005,102(35):12612-12617. |
| [81] | IBRAHIM S, SALEEM B, REHMAN N,et al.CRISPR/Cas9 mediated disruption of Inositol Pentakisphosphate 2-Kinase 1(TaIPK1) reduces phytic acid and improves iron and zinc accumulation in wheat grains[J].Journal of Advanced Research,2022,37:33-41. |
| [82] | CHEN Y, WEI Z Y, YANG Q F,et al.Rice inositol polyphosphate kinase gene(OsIPK2),a putative new player of gibberellic acid signaling,involves in modulation of shoot elongation and fertility[J].Plant Cell,Tissue and Organ Culture,2017,131(3):471-482. |
| [1] | Yuhu WU, Zhenning LENG, Congjia LI, Zelin ZHANG, Zhe PANG. Vertical Distribution of Wild Seed Plant Species from Qinghai, China [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(6): 861-872. |
| [2] | Shanshan ZHANG, Sunmei RUAN, Wenzhong YANG. Genetic Diversity Evaluation and Core Germplasm Construction of Camellia fascicularis [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(6): 909-918. |
| [3] | Lan DU, Tiejuan WANG, Xuemeng ZHOU, Rui ZHANG, Bingbing ZHANG, Jing FENG. Intraspecific and Interspecific Competition Relationship Between Ammopiptanthus mongolicus and Zygophyllum xanthoxylum in theEcotone [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(6): 997-1002. |
| [4] | Ziyu LONG, Zhicheng WANG, Rui ZHAO, Bing LIU, Gongxi CHEN. Herbaceous Plant Diversity in the Karst River Valley Headwater Waterfalls of Dehang Geopark [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(5): 707-721. |
| [5] | Zheng ZHANG, Peng ZHANG. Comparative Research on Growth and Physiological Characteristics of Three Poplar Varieties Grown in Western Heilongjiang [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(5): 807-815. |
| [6] | Zhuosui LI, Yilin GAO, Han LIU, Xulan SHANG. Callus Induction and Secondary Metabolites Accumulation of Diploid Cyclocarya paliurus [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(4): 533-545. |
| [7] | Yingying WANG, Dengli YU, Fengjin QIU, Rongrong YAN, Guoxiong HU. Tissue Culture and Rapid Propagation of Endangered Salvia petrophila [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(4): 558-568. |
| [8] | Minwei CHAI, Yifan WU, Ruili LI, Lin ZHOU, Xiaoxue SHEN. The Influence of Cadmium, Microplastics, and Their Combination on the Growth and Photosynthetic Characteristics of Kandelia obovata [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(4): 603-613. |
| [9] | Xi LIU, Hongyuan HUANG, Shengchang YI, Yadi YU, Hao WANG, Xiaokang NI, Yuli HU, Ling ZHANG. Progress on Interaction of Invasive Plants and Mycorrhizal Fungi and Its Effect on Soil Nitrogen Cycling [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(3): 371-385. |
| [10] | Yaxin WANG, Yuan ZHU, Sen MENG, Angang MING, Hongyan JIA, Fangcuo QIN, Junkun LU. The Effects of Mixed Eucalyptus Plantations with Different Mycorrhizal Tree Species on Soil Microbial Community [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(3): 447-459. |
| [11] | Ziteng SUN, Xinyu WANG, Lili HOU, Yueying LIU, Zhimin ZHENG. Identification and Preliminary Functional Analysis of the BpGRFs Gene in Betula Platyphylla [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(2): 191-201. |
| [12] | Yuwei GUO, Jing LIANG, Haibing WU, Chuanjie ZHOU, Linlin SUN, Zhibao WANG, Xiaoru LI, Xiangfeng CHEN, Mulan LI. Ecosystem Carbon Storage Distribution and Influencing Factors in Different-aged Poplar Plantations in the Yellow River Floodplain in Western Shandong, China [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(2): 241-253. |
| [13] | Yun LIN, Haiyan BI. Correction of Collecting Number Errors in the Protologues of Seven Taxon Names (Asteraceae) in China [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(1): 148-154. |
| [14] | Xiuqi LI, Wenjing LI, Bing LI, Xingzhong XIAO, Tao PENG. Advances in Biological Functions and Mechanisms of Pipecolic Acid in Plants [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(1): 15-21. |
| [15] | Qingqing XU, Dehui SUN, Wenmeng WANG, Dangdang LI, Xingguo LAN, Guangchao SUI. Research Progress of Plant Growth, Development and Stress Resistance Traits Regulated by Liquid-liquid Phase Separation-mediated Gene Expression [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(6): 805-811. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||