Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (6): 870-878.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2024.06.008
• Physiology and Ecology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Hao ZHANG1, Wansheng LIU1, Yanqi WANG2, Xi CHEN1, Liqiang MU1( )
)
Received:2024-07-29
Online:2024-11-20
Published:2024-11-22
Contact:
Liqiang MU
E-mail:mlq0417@163.com
CLC Number:
Hao ZHANG, Wansheng LIU, Yanqi WANG, Xi CHEN, Liqiang MU. Intraspecific and Interspecific Competitions of the Three Hardwood Tree species in Northeast China[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(6): 870-878.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://bbr.nefu.edu.cn/EN/10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2024.06.008
Table 1
Important values of tree species in the sample plot
树种 Species | 株数 Number | 相对优势度 Relative dominance | 相对多度 Relative abundance | 相对频度 Relative frequency | 重要值 Important value/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 共计Total | 781 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 100.0 |
白桦 Betula platyphylla | 38 | 0.059 | 0.049 | 0.070 | 5.9 |
紫椴 Tilia amurensis | 55 | 0.023 | 0.070 | 0.123 | 7.2 |
胡桃楸 Juglans mandshurica | 128 | 0.365 | 0.164 | 0.134 | 22.1 |
黄檗 Phellodendron amurense | 79 | 0.146 | 0.101 | 0.118 | 12.2 |
蒙古栎 Quercus mongolica | 31 | 0.011 | 0.040 | 0.069 | 4.0 |
五角槭 Acer truncatum | 72 | 0.015 | 0.092 | 0.101 | 6.9 |
山杨 Populus davidiana | 85 | 0.144 | 0.109 | 0.085 | 11.3 |
水曲柳 Fraxinus mandshurica | 82 | 0.106 | 0.105 | 0.123 | 11.1 |
春榆 Ulmus davidiana var. japonica | 199 | 0.121 | 0.255 | 0.134 | 17.0 |
| 其他Other | 12 | 0.010 | 0.015 | 0.043 | 2.3 |
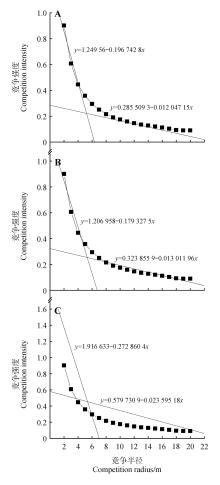
Fig.1
Competition intensity of three species under different competition radiusA.Competition intensity of Juglans mandshurica under different competition radius;B.Competition intensity of Phellodendron amurense under different competition radius;C.Competition intensity of Fraxinus mandshurica under different competition radius.
Table 2
Intraspecific and interspecific competition intensity of Juglans mandshurica
径级 Diameter class/cm | 种内竞争 Intraspecific competition | 种间竞争 Interspecific competition | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
株数 Number | 竞争指数 Competition index | 平均竞争指数 Average competition index | 株数 Number | 竞争指数 Competition index | 平均竞争指数 Average competition index | |
| 合计Total | 68 | 50.25 | 89 | 95.09 | ||
| 5≤DBH<10 | 0 | 1 | 10.71 | 10.71 | ||
| 10≤DBH<15 | 4 | 4.19 | 1.05 | 4 | 15.87 | 3.97 |
| 15≤DBH<20 | 9 | 7.59 | 0.84 | 10 | 10.52 | 1.05 |
| 20≤DBH<25 | 19 | 17.26 | 0.91 | 18 | 17.96 | 1.00 |
| 25≤DBH<30 | 16 | 10.71 | 0.67 | 21 | 19.95 | 0.95 |
| 30≤DBH<35 | 13 | 7.93 | 0.61 | 21 | 13.58 | 0.65 |
| 35≤DBH<40 | 3 | 1.01 | 0.34 | 8 | 4.15 | 0.52 |
| DBH≥40 | 4 | 1.56 | 0.39 | 6 | 2.35 | 0.39 |
Table 3
Intraspecific and interspecific competition intensity of Phellodendron amurense
径级 Diameter class/cm | 种内竞争 Intraspecific competition | 种间竞争 Interspecific competition | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
株数 Number | 竞争指数 Competition index | 平均竞争指数 Average competition index | 株数 Number | 竞争指数 Competition index | 平均竞争指数 Average competition index | |
| 合计Total | 39 | 35.76 | 53 | 93.53 | ||
| 5≤DBH<10 | 0 | 3 | 16.36 | 5.45 | ||
| 10≤DBH<15 | 2 | 5.12 | 2.56 | 3 | 4.48 | 1.49 |
| 15≤DBH<20 | 10 | 12.57 | 1.26 | 10 | 26.92 | 2.69 |
| 20≤DBH<25 | 20 | 14.97 | 0.75 | 25 | 35.35 | 1.41 |
| 25≤DBH<30 | 6 | 2.51 | 0.42 | 10 | 9.75 | 0.98 |
| 30≤DBH<35 | 1 | 0.59 | 0.59 | 1 | 0.29 | 0.29 |
| 35≤DBH<40 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| DBH≥40 | 0 | 1 | 0.38 | 0.38 | ||
Table 4
Intraspecific and interspecific competition intensity of Fraxinus mandshurica
径级 Diameter class/cm | 种内竞争 Intraspecific competition | 种间竞争 Interspecific competition | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
株数 Number | 竞争指数 Competition index | 平均竞争指数 Average competition index | 株数 Number | 竞争指数 Competition index | 平均竞争指数 Average competition index | |
| 合计Total | 32 | 26.24 | 59 | 216.75 | ||
| 5≤DBH<10 | 14 | 17.33 | 1.24 | 23 | 158.01 | 6.87 |
| 10≤DBH<15 | 2 | 0.75 | 0.38 | 7 | 20.31 | 2.90 |
| 15≤DBH<20 | 4 | 1.84 | 0.46 | 8 | 13.49 | 1.69 |
| 20≤DBH<25 | 4 | 1.32 | 0.33 | 5 | 9.02 | 1.80 |
| 25≤DBH<30 | 3 | 0.95 | 0.32 | 7 | 7.48 | 1.07 |
| 30≤DBH<35 | 3 | 3.03 | 1.01 | 6 | 6.28 | 1.05 |
| 35≤DBH<40 | 1 | 0.85 | 0.85 | 2 | 1.72 | 0.86 |
| DBH≥40 | 1 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 1 | 0.44 | 0.44 |
Table 5
Competition intensity between the three hardwood tree species and different tree species
树种 Species | 胡桃楸 Juglans mandshurica | 黄檗 Phellodendron amurense | 水曲柳 Fraxinus mandshurica | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
株数 Number | 竞争指数 Competition index | 平均竞争指数 Average competition index | 株数 Number | 竞争指数 Competition index | 平均竞争指数 Average competition index | 株数 Number | 竞争指数 Competition index | 平均竞争指数 Average competition index | |
| 共计Total | 342 | 145.36 | 234 | 129.27 | 290 | 242.98 | |||
白桦 Betula platyphylla | 13 | 4.39 | 0.34 | 4 | 1.91 | 0.48 | 10 | 5.80 | 0.58 |
紫椴 Tilia amurensis | 19 | 4.75 | 0.25 | 17 | 3.61 | 0.21 | 19 | 8.61 | 0.45 |
胡桃楸 Juglans mandshurica | 71 | 50.25 | 0.71 | 27 | 33.84 | 1.25 | 50 | 70.84 | 1.42 |
黄檗 Phellodendron amurense | 37 | 25.76 | 0.70 | 51 | 35.75 | 0.70 | 31 | 46.47 | 1.50 |
蒙古栎 Quercus mongolica | 14 | 3.20 | 0.23 | 10 | 3.13 | 0.31 | 13 | 4.72 | 0.36 |
五角槭 Acer truncatum | 26 | 5.46 | 0.21 | 22 | 4.05 | 0.18 | 23 | 11.55 | 0.50 |
山杨 Populus davidiana | 17 | 8.04 | 0.47 | 23 | 14.47 | 0.63 | 28 | 37.82 | 1.35 |
水曲柳 Fraxinus mandshurica | 46 | 17.36 | 0.38 | 28 | 11.19 | 0.40 | 34 | 26.22 | 0.77 |
春榆 Ulmus davidiana var. japonica | 94 | 24.64 | 0.26 | 51 | 21.14 | 0.41 | 76 | 28.43 | 0.37 |
| 其他Other | 5 | 1.51 | 0.30 | 1 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 6 | 2.52 | 0.42 |
Table 6
Correlation analysis of intraspecific and interspecific competition index with DBH of Juglans mandshurica, Phellodendron amurense and Fraxinus mandshurica
树种 Species | 指标 Index | 种内竞争指数 Intraspecific competition index | 种间竞争指数 Interspecific competition index | 总的林分竞争指数 General stand competition index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
胡桃楸 Juglans mandshurica | 相关系数 Correlation coefficient | -0.262 | -0.497 | -0.559 |
相对显著度 Relative prominence | <0.050 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
黄檗 Phellodendron amurense | 相关系数 Correlation coefficient | -0.434 | -0.448 | -0.508 |
相对显著度 Relative prominence | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
水曲柳 Fraxinus mandshurica | 相关系数 Correlation coefficient | -0.367 | -0.631 | -0.634 |
相对显著度 Relative prominence | <0.050 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
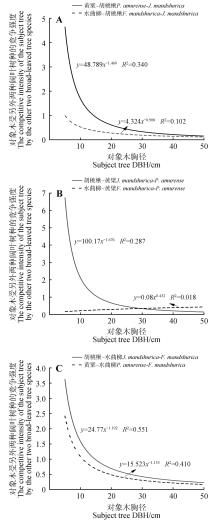
Fig.2
Correlations between subject tree DBH and competition index of the competing tree speciesA.The fitting curve of competition index and DBH of Juglans mandshurica with Phellodendron amurense and Fraxinus mandshurica;B.The fitting curve of competition index and DBH of Phellodendron amurense with Juglans mandshurica and Fraxinus mandshurica;C.The fitting curve of competition index and DBH of Fraxinus mandshurica with Juglans mandshurica and Phellodendron amurense.
| 1 | 张树森,董利虎.张广才岭三大硬阔树高曲线的研究[J].森林工程,2017,33(4):15-20. |
| ZHANG S S, DONG L H.Tree height-diameter model for three hardwood tree species in the Zhangguangcai Mountains[J].Forest Engineering,2017,33(4):15-20. | |
| 2 | SABATIA C O, BURKHART H E.Competition among loblolly pine trees:does genetic variability of the trees in a stand matter?[J].Forest Ecology and Management,2012,263(9):122-130. |
| 3 | CONTRERAS M A, AFFLECK D, CHUNG W.Evaluating tree competition indices as predictors of basal area increment in western Montana forests[J].Forest Ecology and Management,2011,262(11):1939-1949. |
| 4 | BENGTSSON J, FAGERSTRÖM T, RYDIN H.Competition and coexistence in plant communities[J].Trends in Ecology and Evolution,1994,9(7):246-250. |
| 5 | 姚慧芳,卢杰,曾加芹,等.藏东南川滇高山栎天然林的种内与种间竞争指数的海拔差异[J].林业科学,2022,58(8):53-62. |
| YAO H F, LU J, ZENG J Q,et al.Altitudinal differences in intraspecific and interspecific competition index of natural forests of Quercus aquifolioides in southeast Tibet[J].Scientia Silvae Sinicae,2022,58(8):53-62. | |
| 6 | 项小燕,吴甘霖,段仁燕,等.大别山五针松种内和种间竞争强度[J].生态学报,2015,35(2):389-395. |
| XIANG X Y, WU G L, DUAN R Y,et al.Intraspecific and interspecific competition of Pinus dabeshanesis [J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2015,35(2):389-395. | |
| 7 | 苏金娟,王晓春.张广才岭北部三大硬阔树木生长-气候关系的时空变异[J].生态学报,2017,37(5):1484-1495. |
| SU J J, WANG X C.Spatio-temporal variations in climate-growth relationships of three hardwood tree species across the north Zhangguangcai mountains,northeast China[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2017,37(5):1484-1495. | |
| 8 | 董莉莉,赵济川,汪成成,等.辽东山区胡桃楸次生林垂直结构特征研究[J].西南林业大学学报(自然科学),2023,43(6):91-96. |
| DONG L L, ZHAO J C, WANG C C. et al.Analysis on vertical structure characteristics of Juglans mandshurica secondary forest in eastern Liaoning mountainous area[J].Journal of Southwest Forestry University(Natural Sciences),2023,43(6):91-96. | |
| 9 | 王泳腾,黄治昊,王俊,等.燕山山脉黄檗种群结构与动态特征[J].生态学报,2021,41(7):2826-2834. |
| WANG Y T, HUANG Z H, WANG J,et al.The population structure and dynamic characteristics of Phellodendron amurense in Yanshan mountains[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2021,41(7):2826-2834. | |
| 10 | 许恒,刘艳红.珍稀濒危植物梓叶槭种群径级结构与种内种间竞争关系[J].西北植物学报,2018,38(6):1160-1170. |
| XU H, LIU Y H.Relationship between diameter class structure and intraspecific and interspecific competitions of precious and endangering Plant Acer catalpifolium [J].Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica,2018,38(6):1160-1170. | |
| 11 | 孙红阳,王庆成.张广才岭西坡45年生不同起源林分碳储量研究[J].植物研究,2015,35(3):378-383. |
| SUN H Y, WANG Q C.Carbon storage of 45-year-old stands in different origins on the west slope of Zhangguangcai mountain[J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2015,35(3):378-383. | |
| 12 | 罗梅,陈绍志.不同龄组长白落叶松种内及种间竞争研究[J].北京林业大学学报,2018,40(9):33-44. |
| LUO M, CHEN S Z.Intraspecific and interspecific competition of Larix olgensis plantations in different age groups[J].Journal of Beijing Forestry University,2018,40(9):33-44. | |
| 13 | 杨倩,李宁云,陈丽,等.大山包湿地植被群落数量分类及主要种生态位特征研究[J].西部林业科学,2020,49(2):36-42. |
| YANG Q, LI N Y, CHEN L,et al.Quantitative classification of plant community and niche characteristics of main species in Dashanbao wetland[J].Journal of West China Forestry Science,2020,49(2):36-42. | |
| 14 | 于达勇,樊智丰,马长乐,等.云南榧树群落种内与种间竞争研究[J].西北林学院学报,2022,37(1):47-52. |
| YU D Y, FAN Z F, MA C L,et al.Intra- and inter-specific competition of Torreya yunnanensis community[J].Journal of Northwest Forestry University,2022,37(1):47-52. | |
| 15 | 汪清,潘萍,欧阳勋志,等.马尾松-木荷不同比例混交林种内和种间竞争强度[J].生态学杂志,2021,40(1):49-57. |
| WANG Q, PAN P, OUYANG X Z,et al.Intraspecific and interspecific competition intensity in mixed plantation with different proportion of Pinus massoniana and Schima superba [J].Chinese Journal of Ecology,2021,40(1):49-57. | |
| 16 | HEGYI F.A simulation model for managing jack-pine stands[M]//Fries J.Growth models for tree and stand simulation.Stockholm:Royal College of Forestry,1974:74-90. |
| 17 | 刘万生,李想,陈福元,等.蒙古栎林种内和种间竞争研究[J].植物研究,2020,40(4):552-558. |
| LIU W S, LI X, CHEN F Y,et al.Intraspecific and interspecific competition of Quercus mongolica forest[J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2020,40(4):552-558. | |
| 18 | 段仁燕,王孝安.太白红杉种内和种间竞争研究[J].植物生态学报,2005,29(2):242-250. |
| DUAN R Y, WANG X A.Intraspecific and interspecific competition in Larix chinensis [J].Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology,2005,29(2):242-250. | |
| 19 | 辛营营,韦新良.青山湖针阔混交林优势树种竞争的数量研究[J].浙江农林大学学报,2011,28(4):601-606. |
| XIN Y Y, WEI X L.Dominance in a mixed conifer and broadleaved forest of Qingshan lake,Zhejiang[J].Journal of Zhejiang A & F University,2011,28(4):601-606. | |
| 20 | 王欢,杜凡,林海晏,等.西双版纳望天树林主要树种的竞争关系研究[J].西部林业科学,2014,43(2):58-64. |
| WANG H, DU F, LIN H Y,et al.Study on the competitive relations of the main tree species of Parashorea chinensis forest in Xishuangbanna[J].Journal of West China Forestry Science,2014,43(2):58-64. | |
| 21 | 高浩杰,高平仕,王国明.舟山群岛红楠林种内和种间竞争研究[J].植物研究,2017,37(3):440-446. |
| GAO H J, GAO P S, WANG G M.Intraspecific and interspecific competition of Machilus thunbergii forest in Zhoushan islands[J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2017,37(3):440-446. | |
| 22 | 杜峰,梁宗锁,胡莉娟.植物竞争研究综述[J].生态学杂志,2004,23(4):157-163. |
| DU F, LIANG Z S, HU L J.A review on plant competition[J].Chinese Journal of Ecology,2004,23(4):157-163. | |
| 23 | 邹春静,王庆礼,韩士杰.长白山暗针叶林建群种竞争关系的研究[J].应用与环境生物学报,2001,7(2):101-105. |
| ZOU C J, WANG Q L, HAN S J.Study on competition relationship between dificators in dark conifer forest in the Changbai mountains[J].Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology,2001,7(2):101-105. |
| [1] | Hong HUANG, Yumin SHUI, Zhiming ZHANG, Jiawang LUO, Deming HE, Chong YANG, Wei WANG, Wenhong CHEN. Species Composition and Community Characteristics of Summit Mossy Dwarf Forests of Bozhu Mountain, Wenshan County, Yunnan Province, China [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(5): 738-752. |
| [2] | LIU Wan-Sheng, LI Xiang, CHEN Fu-Yuan, ZHU Meng-Ting, MU Li-Qiang. Intraspecific and Interspecific Competition of Quercus mongolica Forest [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(4): 552-558. |
| [3] | GAO Hao-Jie, GAO Ping-Shi, WANG Guo-Ming. Intraspecific and Interspecific Competition of Machilus thunbergii Forest in Zhoushan Islands [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2017, 37(3): 440-446. |
| [4] | LI Xue-Mei;WANG Shu-Li*. Tree Species Diversity and DBH Diversity of the Secondary Forests on the North Slope of Changbai Mountains [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2014, 34(4): 542-546. |
| [5] | LÜHai-Liang;MAO Zi-Jun*;LI Na. Response of Growth and Interspecific Competition of Pinus koraiensis and Quercus mongolica Seedlings to Drought [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2014, 34(3): 364-371. |
| [6] | YIN Dong-Sheng;GE Wen-Zhi;ZHANG Feng-Hai;SHEN Hai-Long. Competition Relationship of Populations of Natural Secondary Acer mono Forest [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2012, 32(1): 105-109. |
| [7] | LIU Hong-Run;LI Feng-Ri*. Relationship Between Intraspecific and Interspecific Competitions of Natural Pinus koraiensis Forests [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2010, 30(4): 479-484. |
| [8] | Jin Ze-xin. PRELIMINARY STUDY ON THE INTRASPECIFIC AND INTERSPECIFIC COMPETITIONS OF GORDONIA ACUMINATA IN ITS COMMUNITY [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 1997, 17(1): 110-118. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||