Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2026, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (1): 51-66.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2026.01.005
• Original Paper • Previous Articles Next Articles
Mengmeng CHENG1,2,3, Bin GE1,2,3, Beisen KOU1,2,3, Wenbin GUAN4, Hai LU1,2,3, Huihong GUO1,2,3, Hui LI1,2,3( )
)
Received:2025-08-12
Online:2026-01-20
Published:2026-01-20
Contact:
Hui LI
E-mail:lihui830@bjfu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Mengmeng CHENG, Bin GE, Beisen KOU, Wenbin GUAN, Hai LU, Huihong GUO, Hui LI. Identification and Expression Analysis of HDAC and HAT gene families in Xanthoceras sorbifolium[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2026, 46(1): 51-66.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://bbr.nefu.edu.cn/EN/10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2026.01.005
Table 1
Information of primers’ sequences used
基因名称 Gene name | 正向引物(5′→3′) Forward primer(5′→3′) | 反向引物(5′→3′) Reverse primer(5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| XsGAPDHF | GCCAAGACTATCCAACCT | GCAACCACATCAACATCAT |
| XsHDA5 | ACGCTGCCATTCCTCAAAGA | ATGCAGACTCCGATGAACCC |
| XsHDA6 | AGATCAACCGTCCCTTCCCT | AGAAGCCGAAAAGCCCATCA |
| XsHDA8 | CCGGGCTTTCTTGACGTTCT | CCCGCTTTGTCTGCTTCAAC |
| XsHDA9 | GTCTACTTTGGGCCCAACCA | GTCAGCTGAGTGGAATTGCG |
| XsHDA14 | AGTCACTTGTTGCAGCTGGA | AGCCCATGTACACGTTGAGT |
| XsHDA15 | TGCTGGGTGAAAATCCTGGA | GCCCGCCGTACCTTCTTAAT |
| XsHDA19a | GCACTTGGTATGGACGTGGA | TGGACACTAGGTGCATGCTG |
| XsHDA19b | ACCTGGTGCTGTGGTTCTTC | TCCACGTCCATACCAAGTGC |
| XsSRT2 | ACGATATTGGGCAAGGAGCT | ACAGTCCCATGCAACTCAAGT |
| XsSRT4 | TGTCGGATCTCAGTTCCTGG | GGGCTTTCACTTGGTCCTGA |
| XsSRT6a | TGCACCTGTAAACGCCACTA | TGTCGGATCTCAGTTCCTGG |
| XsSRT6b | AGGCTACGCAGAGAAGCTCT | ATACCTGCACCCGTGAACAC |
| XsHDT1a | AGTCGTGAGGTTGAAAGTGACA | AGCCTTCTTATCAGGAACCGG |
| XsHDT1b | AAAGCAGGCACTCCTCAGAC | TAGAGCACCATCAGACCCGA |
| XsHDT3 | GCCCAGAACATAAGCCAGGA | ACTTTTCTCCTCTGCCAGCT |
| XsHAG1 | GCCACCTCTTCCATCCACAA | AGTCCTCAGCATCAGAGTCG |
| XsHAG2 | ATTTGTCCCTCCTGCCAGTG | GCTTCCCAGCAGTTCCTGAA |
| XsHAG3 | TTGATGGAAGAGGCAGAGCG | TCGGGTTGGTTGAGGCATTT |
| XsHAM1 | TTGGCATGCATCCTCACCTT | ACTCAACAGCCCAAGGTCAG |
| XsHAM2 | AGGAGGCTTGATGAATGGGTG | GTTCACGTAAACTGGCAGCA |
| XsHAC1 | GAGTAATGCCGGGTGATGGA | GATGGAGGCTTTACATGCGC |
| XsHAF1 | CGTGGGAAGCAGGAGAACTT | TCAGCAAGCATTTCTCGCTC |
| XsHAF2 | GGTGAGTGTGTGGCAGTTCT | TGGAAGCGGTGTGGAAACTT |
Table2
Physicochemical properties of proteins encoded by XsHDACs and XsHATs gene family members
亚家族 Subfamily | 基因名称 Gene name | 基因编号 Gene ID | 基因序列长度 Gene sequence length/bp | 氨基酸数目 Amino acids number | 染色体 Chromosome | 等电点 pI | 疏水性 Hydroph- obicity | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 编号No. | 起始位置 Starting | 结束位置 Ending | ||||||||
| RPD3/HDA1 | XsHDA5 | XS13G0000300.1 | 31 469 | 1 346 | 13 | 42 083 | 73 551 | 7.04 | -0.231 | 细胞核 |
| XsHDA6 | XS13G0205600.1 | 6 511 | 715 | 13 | 18 440 192 | 18 446 702 | 5.88 | -0.281 | 叶绿体 | |
| XsHDA8 | XS10G0208600.1 | 4 094 | 378 | 10 | 27 324 779 | 27 328 872 | 5.38 | -0.181 | 细胞骨架 | |
| XsHDA9 | XS10G0189900.1 | 9 672 | 459 | 10 | 25 563 436 | 25 573 107 | 5.16 | -0.343 | 细胞质 | |
| XsHDA14 | XS08G0082900.1 | 1 687 | 175 | 8 | 10 694 904 | 10 696 590 | 5.28 | 0.054 | 细胞质 | |
| XsHDA15 | XS13G0012000.1 | 110 820 | 581 | 13 | 999 640 | 1 010 459 | 6.09 | -0.423 | 细胞核 | |
| XsHDA19a | XS06G0265200.1 | 6 258 | 499 | 6 | 31 591 565 | 31 597 822 | 5.11 | -0.567 | 细胞核 | |
| XsHDA19b | XS06G0266100.1 | 11 068 | 467 | 6 | 31 988 618 | 31 999 685 | 5.79 | -0.397 | 细胞质 | |
| SIR | XsSRT2 | XS01G0117000.1 | 11 080 | 447 | 1 | 13 708 191 | 13 719 270 | 8.17 | -0.159 | 细胞核 |
| XsSRT4 | XS08G0254700.1 | 6 286 | 372 | 8 | 29 422 597 | 29 428 882 | 8.72 | -0.219 | 无 | |
| XsSRT6a | XS01G0117200.1 | 7 465 | 472 | 1 | 1 374 249 | 13 749 961 | 7.88 | 0.107 | 细胞质膜 | |
| XsSRT6b | XS15G0181700.1 | 6 828 | 448 | 15 | 18 691 280 | 18 698 107 | 9.11 | -0.260 | 细胞核 | |
| HD2 | XsHDT1a | XS12G0010700.1 | 4 221 | 326 | 12 | 1 014 407 | 1 018 627 | 4.87 | -1.055 | 细胞核 |
| XsHDT1b | XS10G0185900.1 | 3 539 | 274 | 10 | 25 235 716 | 25 239 254 | 5.3 | -0.821 | 细胞核 | |
| XsHDT3 | XS13G0226100.1 | 4 773 | 608 | 13 | 21 330 954 | 21 335 726 | 5.14 | -0.977 | 细胞核 | |
| GNAT | XsHAG1 | XS01G0275100.1 | 9 344 | 616 | 1 | 28 219 065 | 28 228 408 | 5.99 | -0.603 | 细胞核 |
| XsHAG2 | XS04G0216600.1 | 3 258 | 466 | 4 | 27 534 203 | 27 537 460 | 5.55 | -0.246 | 细胞骨架 | |
| XsHAG3 | XS13G0078200.1 | 5 775 | 1 005 | 13 | 7 261 674 | 7 267 448 | 7.13 | -0.255 | 细胞骨架 | |
| MYST | XsHAM1 | XS07G0161100.1 | 1 674 | 456 | 7 | 14 445 643 | 14 453 353 | 6.99 | -0.613 | 细胞核 |
| XsHAM2 | XS07G0161400.1 | 5 973 | 456 | 7 | 14 513 828 | 14 521 582 | 8.23 | -0.436 | 细胞核 | |
| CBP | XsHAC1 | XS13G0220600.1 | 2 360 | 1 793 | 13 | 20 139 040 | 20 151 359 | 8.36 | -0.678 | 细胞核 |
| TAFII250 | XsHAF1 | XS13G0224500.1 | 9 596 | 1 101 | 13 | 20 139 040 | 20 151 359 | 9.17 | -0.734 | 无 |
| XsHAF2 | XS12G0000500.1 | 5 412 | 1 803 | 12 | 20 139 040 | 20 151 359 | 5.81 | -0.675 | 无 | |
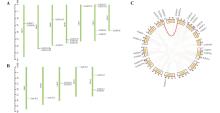
Fig.1
Chromosomal localization and synteny analysis(C) of the XsHDACs(A) and XsHATs(B) gene families of Xanthoceras sorbifoliumIn Fig. 1C, the chromosomal positions of XsHDACs and XsHATs genes were indicated by short red lines on the circles. Gray lines represented all synteny blocks in the Xanthoceras sorbifolium genome, while red lines indicated the duplicated gene pairs in XsHDACs and XsHATs.
Table 3
Secondary structure analysis of XsHDACs和XsHATs protein family members
蛋白名称 Protein name | α-螺旋 α-helix/% | 延伸链 Extended strand/% | β-转角 β-sheet/% | 不规则卷曲 Random coil/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| XsHDA5 | 34.18 | 10.25 | 0 | 55.57 |
| XsHDA6 | 36.22 | 13.43 | 0 | 50.35 |
| XsHDA8 | 37.83 | 15.87 | 0 | 46.30 |
| XsHDA9 | 34.89 | 11.56 | 0 | 53.56 |
| XsHDA14 | 30.29 | 21.14 | 0 | 48.57 |
| XsHDA15 | 37.52 | 11.19 | 0 | 51.29 |
| XsHDA19a | 37.68 | 11.02 | 0 | 51.30 |
| XsHDA19b | 34.69 | 11.19 | 0 | 53.75 |
| XsSRT2 | 30.65 | 11.02 | 0 | 58.17 |
| XsSRT4 | 29.84 | 11.56 | 0 | 59.14 |
| XsSRT6a | 28.18 | 13.35 | 0 | 58.47 |
| XsSRT6b | 29.24 | 9.38 | 0 | 61.38 |
| XsHDT1a | 11.04 | 12.58 | 0 | 76.38 |
| XsHDT1b | 8.76 | 16.79 | 0 | 74.45 |
| XsHDT3 | 9.54 | 13.98 | 0 | 76.48 |
| XsHAG1 | 29.71 | 7.63 | 0 | 62.66 |
| XsHAG2 | 44.42 | 13.09 | 0 | 42.49 |
| XsHAG3 | 46.67 | 12.04 | 0 | 41.29 |
| XsHAM1 | 32.24 | 13.16 | 0 | 54.61 |
| XsHAM2 | 38.28 | 15.91 | 0 | 45.81 |
| XsHAC1 | 26.49 | 5.13 | 0 | 68.38 |
| XsHAF1 | 47.23 | 4.09 | 0 | 48.68 |
| XsHAF2 | 40.82 | 4.83 | 0 | 54.35 |
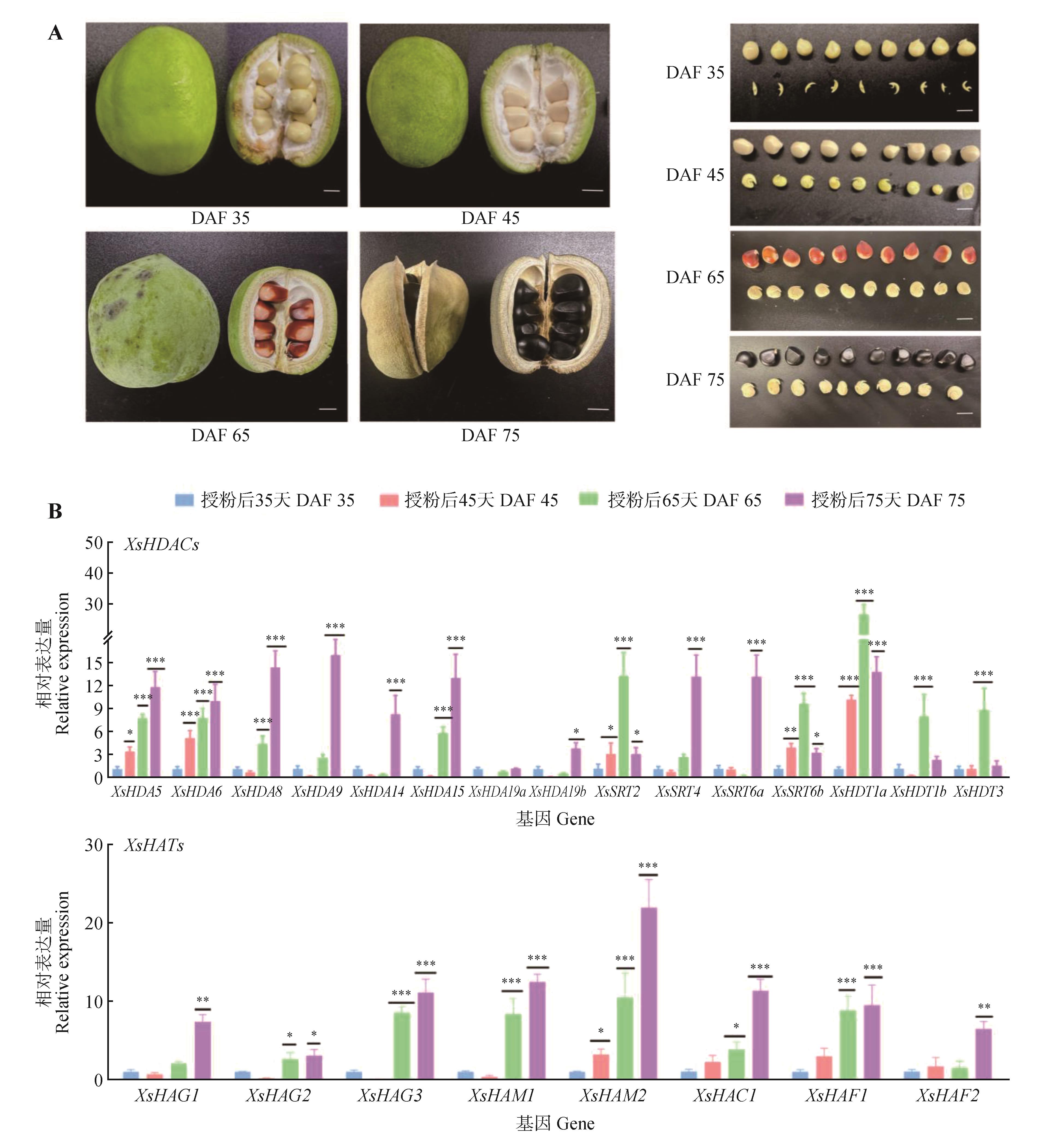
Fig.8
Characteristics of Xanthoceras sorbifolium fruits,seeds(A) and expression pattern analysis of XsHDACs and XsHATs genefamily members during development(B)Gene relative expression of each stage was compared with that of the DAF35 group using Student’s t-test (*.P<0.05; **.P<0.01; ***.P<0.001).
| [1] | 顾玉红.文冠果体细胞胚胎发生及形态建成机理的研究[D].北京:北京林业大学,2005. |
| GU Y H.Mechanisms of somatic embryogenesis and morphogenesis of Xanthoceras sorbifolia Bunge[D].Beijing:Beijing Forestry University,2005. | |
| [2] | ZHAO N, ZHANG Y, LI Q Q,et al.Identification and expression of a stearoyl-ACP desaturase gene responsible for oleic acid accumulation in Xanthoceras sorbifolia seeds[J].Plant Physiology and Biochemistry,2015,87:9-16. |
| [3] | XIAO W, WANG Y, ZHANG P,et al.Bioactive barrigenol type triterpenoids from the leaves of Xanthoceras sorbifolia Bunge[J].European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry,2013,60:263-270. |
| [4] | BANNISTER A J, KOUZARIDES T.Regulation of chromatin by histone modifications[J].Cell Research,2011,21(3):381-395. |
| [5] | PANDEY R, MÜLLER A, NAPOLI C A,et al.Analysis of histone acetyltransferase and histone deacetylase families of Arabidopsis thaliana suggests functional diversification of chromatin modification among multicellular eukaryotes[J].Nucleic Acids Research,2002,30(23):5036-5055. |
| [6] | 韩召奋,王秋苹,罗鑫娟.植物组蛋白去乙酰化酶的特性及功能[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报,2017,33(10):1008-1013. |
| HAN Z F, WANG Q P, LUO X J.Characteristic and function of histone deacetylases in plants[J].Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,2017,33(10):1008-1013. | |
| [7] | YU C W, LIU X C, LUO M,et al.HISTONE DEACETYLASE6 interacts with FLOWERING LOCUS D and regulates flowering in Arabidopsis [J].Plant Physiology,2011,156(1):173-184. |
| [8] | YU C W, CHANG K Y, WU K Q.Genome-wide analysis of gene regulatory networks of the FVE-HDA6-FLD complex in Arabidopsis [J].Frontiers in Plant Science,2016,7:555. |
| [9] | TANAKA M, KIKUCHI A, KAMADA H,et al.The Arabidopsis histone deacetylases HDA6 and HDA19 contribute to the repression of embryonic properties after germination[J].Plant Physiology,2008,146(1):149-161. |
| [10] | ZHOU Y, TAN B, LUO M,et al.HISTONE DEACETYLASE19 interacts with HSL1 and participates in the repression of seed maturation genes in Arabidopsis seedlings[J].The Plant Cell,2013,25(1):134-148. |
| [11] | HU Y N, HAN Z Y, WANG T,et al.Ethylene response factor MdERF4 and histone deacetylase MdHDA19 suppress apple fruit ripening through histone deacetylation of ripening-related genes[J].Plant Physiology,2022,188(4):2166-2181. |
| [12] | HAN Y T, GEORGII E, PRIEGO-CUBERO S,et al. Arabidopsis histone deacetylase HD2A and HD2B regulate seed dormancy by repressing DELAY OF GERMINATION 1[J].Frontiers in Plant Science,2023,14:1124899. |
| [13] | VALL-LLAURA N, TORRES R, LINDO-GARCÍA V,et al. PbSRT1 and PbSRT2 regulate pear growth and ripening yet displaying a species-specific regulation in comparison to other Rosaceae spp.[J].Plant Science,2021,308:110925. |
| [14] | ZHAO L M, LU J X, ZHANG J X,et al.Identification and characterization of histone deacetylases in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum)[J].Frontiers in Plant Science,2015,5:760. |
| [15] | LEE C Y, GRANT P A.Chapter 1-1-role of histone acetylation and acetyltransferases in gene regulation[M]//MCCULLOUGH S D,DOLINOY D C.Toxicoepigenetics.London:Academic Press,2019:3-30. |
| [16] | BERTRAND C, BERGOUNIOUX C, DOMENICHINI S,et al. Arabidopsis histone acetyltransferase AtGCN5 regulates the floral meristem activity through the WUSCHEL/AGAMOUS pathway[J].Journal of Biological Chemistry,2003,278(30):28246-28251. |
| [17] | XIAO J, ZHANG H, XING L J,et al.Requirement of histone acetyltransferases HAM1 and HAM2 for epigenetic modification of FLC in regulating flowering in Arabidopsis [J].Journal of Plant Physiology,2013,170(4):444-451. |
| [18] | HAN S K, SONG J D, NOH Y S,et al.Role of plant CBP/p300-like genes in the regulation of flowering time[J].The Plant Journal,2007,49(1):103-114. |
| [19] | DENG W W, LIU C Y, PEI Y X,et al.Involvement of the histone acetyltransferase AtHAC1 in the regulation of flowering time via repression of FLOWERING LOCUS C in Arabidopsis [J].Plant Physiology,2007,143(4):1660-1668. |
| [20] | LIU X, LUO M, ZHANG W,et al.Histone acetyltransferases in rice (Oryza sativa L.):phylogenetic analysis,subcellular localization and expression[J].BMC Plant Biology,2012,12(1):145. |
| [21] | PAPAEFTHIMIOU D, LIKOTRAFITI E, KAPAZOGLOU A,et al.Epigenetic chromatin modifiers in barley:Ⅲ.Isolation and characterization of the barley GNAT-MYST family of histone acetyltransferases and responses to exogenous ABA[J].Plant Physiology and Biochemistry,2010,48(2/3):98-107. |
| [22] | BERTRAND C, BENHAMED M, LI Y F,et al. Arabidopsis HAF2 gene encoding TATA-binding protein(TBP)- associated factor TAF1,is required to integrate light signals to regulate gene expression and growth[J].Journal of Biological Chemistry,2005,280(2):1465-1473. |
| [23] | LIANG Q, LIU J N, FANG H C,et al.Genomic and transcriptomic analyses provide insights into valuable fatty acid biosynthesis and environmental adaptation of yellowhorn[J].Frontiers in Plant Science,2022,13:991197. |
| [24] | LIU H, YAN X M, WANG X R,et al.Centromere-specific retrotransposons and very-long-chain fatty acid biosynthesis in the genome of yellowhorn (Xanthoceras sorbifolium,Sapindaceae),an oil-producing tree with significant drought resistance[J].Frontiers in Plant Science,2021,12:766389. |
| [25] | ALTSCHUL S F, MADDEN T L, SCHÄFFER A A,et al.Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST:a new generation of protein database search programs[J].Nucleic Acids Research,1997,25(17):3389-3402. |
| [26] | EL-GEBALI S, MISTRY J, BATEMAN A,et al.The Pfam protein families database in 2019[J].Nucleic Acids Research,2019,47(D1):D427-D432. |
| [27] | LU S N, WANG J Y, CHITSAZ F,et al.CDD/SPARCLE:the conserved domain database in 2020[J].Nucleic Acids Research,2020,48(D1):D265-D268. |
| [28] | LETUNIC I, KHEDKAR S, BORK P.SMART:recent updates,new developments and status in 2020[J].Nucleic Acids Research,2021,49(D1):D458-D460. |
| [29] | LI K B.ClustalW-MPI:ClustalW analysis using distributed and parallel computing[J].Bioinformatics,2003,19(12):1585-1856. |
| [30] | KUMAR S, STECHER G, LI M,et al.MEGA X:molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms[J].Molecular Biology and Evolution,2018,35(6):1547-1549. |
| [31] | TAMURA K, PETERSON D, PETERSON N,et al.MEGA5:molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood,evolutionary distance,and maximum parsimony methods[J].Molecular Biology and Evolution,2011,28(10):2731-2739. |
| [32] | BAILEY T L, JOHNSON J, GRANT C E,et al.The MEME Suite[J].Nucleic Acids Research,2015,43(W1):W39-W49. |
| [33] | CHEN C J, CHEN H, ZHANG Y,et al.TBtools:an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data[J].Molecular Plant,2020,13(8):1194-1202. |
| [34] | LESCOT M, DÉHAIS P, THIJS G,et al.PlantCARE,a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences[J].Nucleic Acids Research,2002,30(1):325-327. |
| [35] | LIANG Q, LI H Y, LI S K,et al.The genome assembly and annotation of yellowhorn(Xanthoceras sorbifolium Bunge)[J].GigaScience,2019,8(6):giz071. |
| [36] | 李晓斐,张舒婷,陈晓慧,等.龙眼HDAC家族成员的全基因组鉴定及表达分析[J].果树学报,2020,37(6):793-807. |
| LI X F, ZHANG S T, CHEN X H,et al.Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of HDAC gene family in Dimocarpus longan Lour[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2020,37(6):793-807. | |
| [37] | 李晓斐,张舒婷,申序,等.龙眼HAT家族的全基因组鉴定及表达模式[J].应用与环境生物学报,2021,27(5):1354-1363. |
| LI X F, ZHANG S T, SHEN X,et al.Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of HAT gene family in longan[J].Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology,2021,27(5):1354-1363. | |
| [38] | ROSSI V, LOCATELLI S, VAROTTO S,et al.Maize histone deacetylase hda101 is involved in plant development,gene transcription,and sequence-specific modulation of histone modification of genes and repeats[J].The Plant Cell,2007,19(4):1145-1162. |
| [39] | VAROTTO S, LOCATELLI S, CANOVA S,et al.Expression profile and cellular localization of maize Rpd3-type histone deacetylases during plant development[J].Plant Physiology,2003,133(2):606-617. |
| [40] | HU Y F, QIN F J, HUANG L M,et al.Rice histone deacetylase genes display specific expression patterns and developmental functions[J].Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,2009,388(2):266-271. |
| [41] | 赵娜,张媛,王静,等.文冠果种子发育及油脂累积与糖类、蛋白质累积之间的关系研究[J].植物研究,2015,35(1):133-140. |
| ZHAO N, ZHANG Y, WANG J,et al.Seed development,lipid accumulation and its relationship with carbohydrates and protein in Xanthoceras sorbifolia Bunge[J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2015,35(1):133-140. | |
| [42] | HE M, QIN C X, WANG X,et al.Plant unsaturated fatty acids:biosynthesis and regulation[J].Frontiers in Plant Science,2020,11:390. |
| [43] | CHEN Q S, ZHANG J, LI G.Dynamic epigenetic modifications in plant sugar signal transduction[J].Trends in Plant Science,2022,27(4):379-390. |
| [44] | WEBER H, BORISJUK L, WOBUS U.Molecular physiology of legume seed development[J].Annual Review of Plant Biology,2005,56:253-279. |
| [45] | LI G S, WANG D F, YANG R L,et al.Temporal patterns of gene expression in developing maize endosperm identified through transcriptome sequencing[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2014,111(21):7582-7587. |
| [46] | VERDIER J, THOMPSON R D.Transcriptional regulation of storage protein synthesis during dicotyledon seed filling[J].Plant and Cell Physiology,2008,49(9):1263-1271. |
| [1] | Linlin HE, Lei WU, Xuesong REN, Jun SI, Qinfei LI, Hongyuan SONG. Progress in the Study on Stay-green Gene SGR [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2026, 46(1): 1-12. |
| [2] | Jianhui CHUN, Wenlong DONG, Yuanchao TU, Fang LIU, Yunjian XU. Identification of the Maize GLP Family Genes and Their Expression in Response to Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Symbiosis [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(3): 406-418. |
| [3] | Xueying WANG, Ruiqi WANG, Yang ZHANG, Cong LIU, Dean XIA, Zhigang WEI. Genome‑wide Identification and Stress Response Analysis of Cyclic Nucleotide-gated Channels(CNGC) Gene Family in Populus trichocarpa [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(4): 613-625. |
| [4] | Meng-Ke WANG, Meng-Ni TIAN, Quan-Xin BI, Xiao-Juan LIU, Hai-Yan YU, Li-Bing WANG. Evaluation of Drought Tolerance Based on Stomatal Characters and Selection of Germplasm Resources from Xanthoceras sorbifolia [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(6): 957-964. |
| [5] | Shuang-Hui TIAN, He CHENG, Yang ZHANG, Cong LIU, De-An XIA, Zhi-Gang WEI. Genome-wide Identification and Expressional Analysis of Carotenoid Cleavage Dioxygenases(CCD) Gene Family in Populus trichocarpa under Drought and Salt Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(6): 993-1005. |
| [6] | ZHU Li-Li, QING Jun, DU Qing-Xin, HE Feng, DU Hong-Yan. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Characteristics of LOX Gene Family in Eucommia ulmoides [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2019, 39(6): 927-934. |
| [7] | WANG Jia-Qi, ZHANG Xi, LI Li. Bioinformatic and Expression Analysis of HD-Zip Family Gene in Betula platyphylla [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2018, 38(6): 931-938. |
| [8] | GUAN Qing-Jie1,2;WANG Zhen-Juan1;ZHENG Heng1;LIU Guang-Tao3;LIU Shen-Kui3. OsLOL2 Gene Clone of Rice and the Salt Resistance Analysis of Overexpression Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2015, 35(2): 259-269. |
| [9] | WU Xiang-Yu;XU Zhi-Ru;QU Chun-Pu;LI Wei;SUN Qi;LIU Guan-Jun*. Genome-wide Identification and Characterization of NLP Gene Family in Populus trichocarpa [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2014, 34(1): 37-43. |
| [10] | LIU Juan;XU Yan-Hong;YANG Yong;LIANG Liang;GAO Zhi-Hui;YANG Yun;ZHANG Zheng;SUI Chun;WEI Jian-He;*. Cloning and Gene Expression of 3-Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaryl-CoA Synthase Gene(AsHMGS) from Aquilaria sinensis(Lour.) Gilg [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2014, 34(1): 75-84. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||