Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (1): 107-117.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2024.01.013
• Physiology and Ecology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Boyi SONG1,2,3,4, Mingming WANG1,2,3,4, Weiwei ZHUANG1,2,3,4( )
)
Received:2023-06-14
Online:2024-01-20
Published:2023-12-27
Contact:
Weiwei ZHUANG
E-mail:zww8611@sina.com
CLC Number:
Boyi SONG, Mingming WANG, Weiwei ZHUANG. Physiological Responses of Three Bryophytes to Simulated Atmospheric Nitrogen Deposition[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(1): 107-117.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://bbr.nefu.edu.cn/EN/10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2024.01.013
Table 1
Basic information of mosses in this study
科 Family | 物种 Species | 采样地 Sampling site | 生境 Habitat | 经纬度 Latitude and longitude | 海拔 Altitude/m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
丛藓科 Pottiaceae | 齿肋赤藓 S. caninervis | 古尔班通古特沙漠 Gurbantunggut Desert | 沙漠土壤 Desert soil | 44°22ˊN,87°55ˊE | 395 |
真藓科 Bryaceae | 真藓 B. argenteum | 喀纳斯自然保护区 Kanas Nature Reserve | 湿润沃土 Wet fertile soil | 48°51ˊN,87°13ˊE | 1 340 |
提灯藓科 Mniaceae | 尖叶匐灯藓 P. acutum | 西天山自然保护区 West Tianshan Nature Reserve | 云杉林下 Under spruce understory | 43°10ˊN,82°52ˊE | 2 240 |
Table 2
Meteorological and soil nutrient information of the three habitats
采样地 Sampling site | 养分信息 Nutrient information | 气象信息 Meteorological information | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
有机碳 Organic carbon /(g·kg-1) | 全氮 Total N/(g·kg-1) | 全磷 Total P/(g·kg-1) | 年均温 Mean annual temperature/℃ | 年降水 Mean annual precipitation/mm | 干旱程度 Aridity | |
古尔班通古特沙漠 Gurbantunggut Desert | 7.725 | 0.667 | 0.630 | 10.60 | 123.02 | 0.895 |
喀纳斯自然保护区 Kanas Nature Reserve | 83.243 | 3.091 | 0.892 | 8.20 | 150.30 | 0.725 |
西天山自然保护区 West Tianshan Nature Reserve | 40.970 | 1.948 | 0.827 | 9.50 | 136.60 | 0.822 |

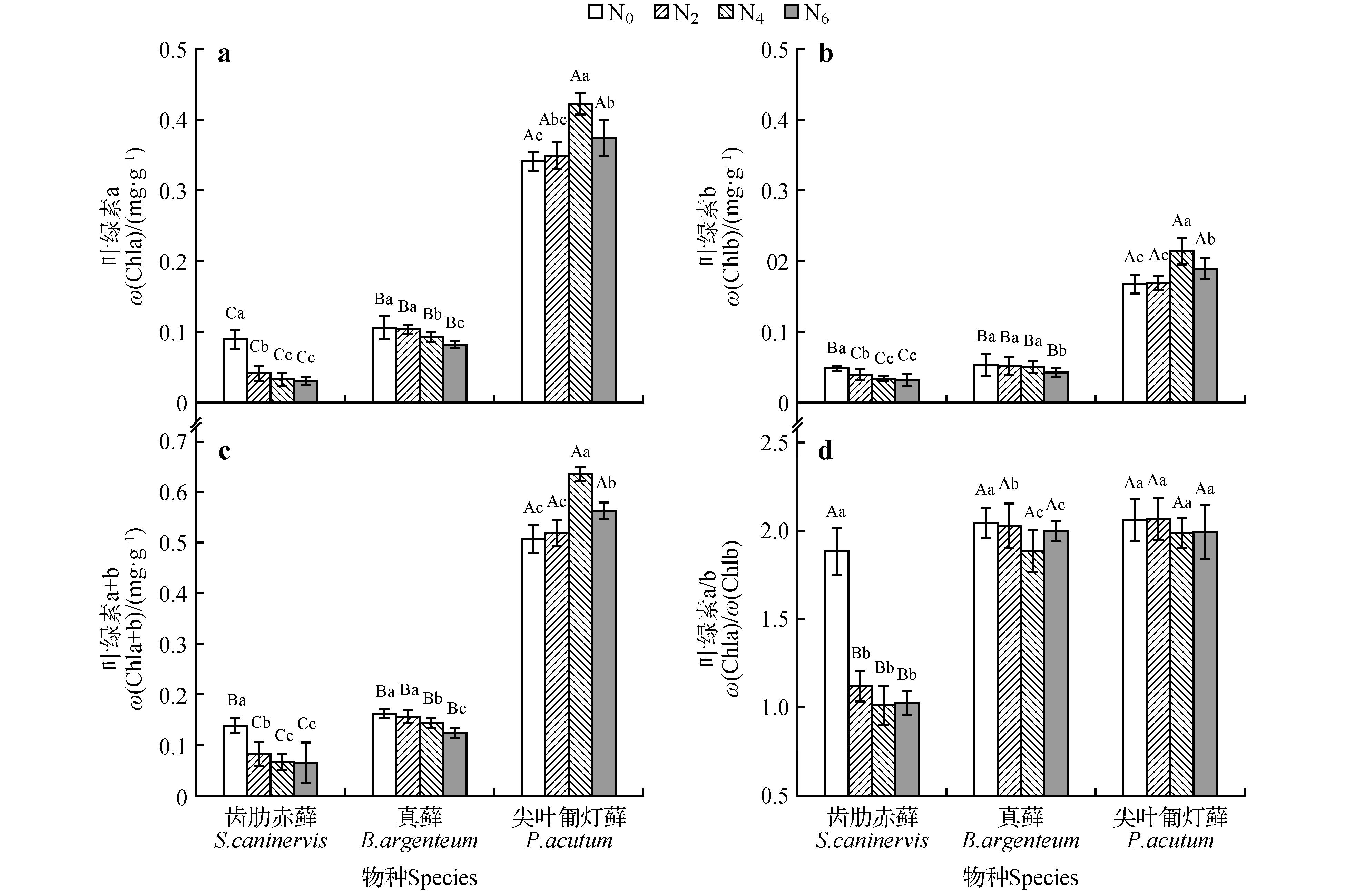
Fig.2
Effect of different nitrogen levels on chlorophyll mass fraction of three mossesDifferent capital letters indicated significant differences between the same treatments for different species, and different lowercase letters indicated significant differences between different treatments of the same species(P<0.05);the same as below.
| 1 | GAO Y, JIA Y L, YU G R,et al.Anthropogenic reactive nitrogen deposition and associated nutrient limitation effect on gross primary productivity in inland water of China[J].Journal of Cleaner Production,2019,208:530-540. |
| 2 | XU W, ZHAO Y H, LIU X J,et al.Atmospheric nitrogen deposition in the Yangtze River basin:spatial pattern and source attribution[J].Environmental Pollution,2018,232:546-555. |
| 3 | LI K H, LIU X J, SONG W,et al.Atmospheric Nitrogen Deposition at Two Sites in an Arid Environment of Central Asia[J].PLoS One,2013,8(6):e67018. |
| 4 | BAI Y F, WU J G, CLARK C M,et al.Tradeoffs and thresholds in the effects of nitrogen addition on biodiversity and ecosystem functioning:evidence from inner Mongolia Grasslands[J].Global Change Biology,2010,16(1):358-372. |
| 5 | ZHANG Y, ZHENG L X, LIU X J,et al.Evidence for organic N deposition and its anthropogenic sources in China[J].Atmospheric Environment,2008,42(5):1035-1041. |
| 6 | XU W, LUO X S, PAN Y P,et al.Quantifying atmospheric nitrogen deposition through a nationwide monitoring network across China[J].Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics,2015,15(21):12345-12360. |
| 7 | JING Y L, GUAN D X, WU J B,et al.Photosynthate supply drives soil respiration of Fraxinus mandshurica seedlings in northeastern China:evidences from a shading and nitrogen addition experiment[J].Journal of Forestry Research,2016,27(6):1271-1276. |
| 8 | LI G, ZHANG Z S, GAO H Y,et al.Effects of nitrogen on photosynthetic characteristics of leaves from two different stay-green corn(Zea mays L.) varieties at the grain-filling stage[J].Canadian Journal of Plant Science,2012,92(4):671-680. |
| 9 | WANG C, LI X N, HU Y X,et al.Nitrogen addition weakens the biodiversity-multifunctionality relationships across soil profiles in a grassland assemblage[J].Agriculture,Ecosystems and Environment,2023,342:108241. |
| 10 | 朱瑞良,马晓英,曹畅,等.中国苔藓植物多样性研究进展[J].生物多样性,2022,30(7):22378. |
| ZHU R L,MA X Y,CAO C,et al,Advances in research on bryophyte diversity in China[J].Biodiversity Science,2022,30(7):22378. | |
| 11 | POTT U, TURPIN D H.Changes in atmospheric trace element deposition in the Fraser Valley,B.C.,Canada from 1960 to 1993 measured by moss monitoring with Isothecium stoloniferum[J].Canadian Journal of Botany,1996,74(8):1345-1353. |
| 12 | WOLTERBEEK H T, KUIK P, VERBURG T G,et al.Moss interspecies comparisons in trace element concentrations[J].Environmental Monitoring and Assessment,1995,35(3):263-286. |
| 13 | STORKEY J, MACDONALD A J, POULTON P R,et al.Grassland biodiversity bounces back from long-term nitrogen addition[J].Nature,2015,528(7582):401-404. |
| 14 | GONZÁLEZ-MIQUEO L, ELUSTONDO D, LASHERAS E,et al.Spatial trends in heavy metals and nitrogen deposition in Navarra(Northern Spain) based on moss analysis[J].Journal of Atmospheric Chemistry,2010,62(1):59-72. |
| 15 | AGNAN Y, SÉJALON-DELMAS N, CLAUSTRES A,et al.Investigation of spatial and temporal metal atmospheric deposition in France through lichen and moss bioaccumulation over one century[J].Science of the Total Environment,2015,529:285-296. |
| 16 | 董向楠.氮素添加对山西太岳山苔藓植物的影响[D].北京:北京林业大学,2016:29-31. |
| DONG X N.Effects of nitrogen addition on bryophytes in Taiyue Mountain of Shanxi[D].Beijing:Beijing Forestry University,2016:29-31. | |
| 17 | BRITTON A J, MITCHELL R J, FISHER J M,et al.Nitrogen deposition drives loss of moss cover in alpine moss-sedge heath via lowered C∶N ratio and accelerated decomposition[J].New Phytologist,2018,218(2):470-478. |
| 18 | 周晓兵,尹本丰,张元明.模拟氮沉降对不同类型生物土壤结皮生长和光合生理的影响[J].生态学报,2016,36(11):3197-3205. |
| ZHOU X B, YIN B F, ZHANG Y M.The effects of simulated nitrogen deposition on growth and photosynthetic physiology of three types of biocrusts[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2016,36(11):3197-3205 | |
| 19 | 刘滨扬,刘蔚秋,雷纯义,等.三种苔藓植物对模拟N沉降的生理响应[J].植物生态学报,2009,33(1):141-149. |
| LIU B Y, LIU W Q, LEI C Y,et al.Physiological responses of three bryophyte species of south china to simulated nitrogen deposition[J].Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology,2009,33(1):141-149. | |
| 20 | 热比也木·吾甫,艾尼瓦尔·阿布都热衣木,玛尔孜亚·阿不力米提,等.新疆苔藓植物的研究进展[J].新疆大学学报(自然科学版),2014,31(3):335-340,362. |
| RABIYE GUPUR, ANWAR ABDUREHIM, MARZIYA ABLIMIT,et al.Recent advances in Xinjiang Bryoligical Research[J].Journal of Xinjiang University(Natural Science Edition),2014,31(3):335-340,362. | |
| 21 | KIDRON G J.The negative effect of biocrusts upon annual-plant growth on sand dunes during extreme droughts[J].Journal of Hydrology,2014,508(1):128-136. |
| 22 | ZHUANG W W, DOWNING A, ZHANG Y M.The influence of biological soil crusts on 15N translocation in soil and vascular plant in a temperate desert of Northwestern China[J].Journal of Plant Ecology,2015,8(4):420-428. |
| 23 | 李俊柯,杜家豪,邓章轩,等.铀胁迫对不同苔藓生长及抗氧化系统的影响[J].广东农业科学,2020,47(8):65-73. |
| LI J K, DU J H, DENG Z X,et al.Effects of Uranium stress on growth and antioxidant system of different Bryophytes[J].Guangdong Agricultural Sciences,2020,47(8):65-73. | |
| 24 | 刘滨扬,刘蔚秋,张以顺,等.低温胁迫后苔藓植物对模拟氮沉降条件的生理响应[J].植物生态学报,2011,35(3):268-274. |
| LIU B Y, LIU W Q, ZHANG Y C,et al.Physiological responses of bryophytes experienced low temperature stress to simulated nitrogen deposition[J].Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology,2011,35(3):268-274. | |
| 25 | ASGHAR T, JAMIL Y, IQBAL M,et al.Laser light and magnetic field stimulation effect on biochemical,enzymes activities and chlorophyll contents in soybean seeds and seedlings during early growth stages[J].Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B:Biology,2016,165:283-290. |
| 26 | BATES L S, WALDREN R P, TEARE I D.Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies[J].Plant and Soil,1973,39:205-207. |
| 27 | GIANNAKOULA A, MOUSTAKAS M, SYROS T,et al.Aluminum stress induces up-regulation of an efficient antioxidant system in the Al-tolerant maize line but not in the Al-sensitive line[J].Environmental and Experimental Botany,2010,67(3):487-494. |
| 28 | LASSOUANE N, AÏD F, LUTTS S.Water stress impact on young seedling growth of Acacia arabica [J].Acta Physiologiae Plantarum,2013,35:2157-2169. |
| 29 | HEATH R L, PACKER L.Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts:I.Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation[J].Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics,1968,125(1):189-198. |
| 30 | WU H L, WU X L, LI Z H,et al.Physiological evaluation of drought stress tolerance and recovery in cauliflower (Brassica oleracea L.) seedlings treated with methyl jasmonate and coronatine[J].Journal of Plant Growth Regulation,2012,31(1):113-123. |
| 31 | ZHOU X B, ZHANG Y M, JI X H,et al.Combined effects of nitrogen deposition and water stress on growth and physiological responses of two annual desert plants in northwestern China[J].Environmental and Experimental Botany,2011,74:1-8. |
| 32 | OCHOA-HUESO R, MEJÍAS-SANZ V, PÉREZ-CORONA M E,et al.Nitrogen deposition effects on tissue chemistry and phosphatase activity in Cladonia foliacea (Huds.) Willd.,a common terricolous lichen of semi-arid Mediterranean shrublands[J].Journal of Arid Environments,2013,88:78-81. |
| 33 | ZHOU X B, ZHANG Y M, NIKLAS K J.Sensitivity of growth and biomass allocation patterns to increasing nitrogen:a comparison between ephemerals and annuals in the Gurbantunggut Desert,north-western China[J].Annals of Botany,2014,113(3):501-511. |
| 34 | REICH P B.Elevated CO2 reduces losses of plant diversity caused by nitrogen deposition[J].Science,2009,326(5958):1399-1402. |
| 35 | JOHANSSON O, OLOFSSON J, GIESLER R,et al.Lichen responses to nitrogen and phosphorus additions can be explained by the different symbiont responses[J].New Phytologist,2011,191(3):795-805. |
| 36 | LANGE O L, NOBEL P S, OSMOND C B,et al.Physiological plant ecology I:Responses to the physical environment[M].New York:Springer,1981. |
| 37 | KITAJIMA K, HOGAN K P.Increases of chlorophyll a/b ratios during acclimation of tropical woody seedlings to nitrogen limitation and high light[J].Plant,Cell & Environment,2003,26(6):857-865. |
| 38 | LIU B Y, LEI C Y, JIN J H,et al.Physiological responses of two moss species to the combined stress of water deficit and elevated N deposition (II):Carbon and nitrogen metabolism[J].Ecology and Evolution,2016,6(21):7596-7609. |
| 39 | ZHANG Y M, ZHOU X B, YIN B F,et al.Sensitivity of the xerophytic moss Syntrichia caninervis to prolonged simulated nitrogen deposition[J].Annals of Botany,2016,117(7):1153-1161. |
| 40 | BELNAP J, PHILLIPS S L, FLINT S,et al.Global change and biological soil crusts:effects of ultraviolet augmentation under altered precipitation regimes and nitrogen additions[J].Global Change Biology,2008,14(3):670-686. |
| 41 | 周晓兵,张元明,陶冶,等.新疆古尔班通古特沙漠土壤N2O、CH4和CO2通量及其对氮沉降增加的响应[J].植物生态学报,2017,41(3):290-300. |
| ZHOU X B, ZHANG Y M, TAO Y,et al.Effluxes of nitrous oxide,methane and carbon dioxide and their responses to increasing nitrogen deposition in the Gurbantünggüt Desert of Xinjiang,China[J].Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology,2017,41(3):290-300. | |
| 42 | BOBBINK R, HORNUNG M, ROELOFS J G M.The effects of air-borne nitrogen pollutants on species diversity in natural and semi-natural European vegetation[J].Journal of Ecology,1998,86(5):717-738. |
| 43 | 匡鹤凌,汪贵斌,曹福亮.氮素对喜树光合作用、营养元素和喜树碱含量的影响[J].南京林业大学学报(自然科学版),2016,40(3):15-20. |
| KANG H L, WANG G B, CAO F L.Influence of nitrogen levels on photosynthesis,nutrient elements and camptothecin content of Camptotheca acuminata [J].Journal of Nanjing Forestry University(Natural Sciences Edition),2016,40(3):15-20. |
| [1] | Li CAO, Yunli YANG, Tianfang LI, Jing JIANG. Analysis on Leaf Color and Growth Variation of Transgenic BpGLK Betula pendula ‘Dalecarlica' [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(3): 351-360. |
| [2] | Mingyang CONG, Yongkun LI, Wenjing YANG, Puqing CHEN. Bryophyte Diversity of Underground Forests in Craters of Jingpohu Global Geopark [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(3): 361-369. |
| [3] | Zhenggang XU, Hang XU, Xiutao PENG, Shijun LIANG, Rong LIU, Shanghua LUO, Juan XIAO. Effects of N addition on Root Exudates and Their Mediated Nutrient Rransformation Processes in a Betula albosinensis Burk Forest in Southwest China [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(2): 194-206. |
| [4] | Wenhai HU, Yi’an XIAO. Quantitative Analysis of Leaf Photosynthetic Heterogeneity Based on Chlorophyll Fluorescence Imaging and Distribution Characteristics of Fluorescence Parameters [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(6): 1052-1061. |
| [5] | Zhaoyi LI, Longfei HAO, Tingyan LIU, Yanhong HE, You ZHANG, Shulan BAI, Xinyu YANG. AM Fungi Inoculation on Root Morphology and Nutrient Loading of Clematis fruticosa Seedlings under Simulated Atmospheric Nitrogen Deposition [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(5): 886-895. |
| [6] | Xiwu DU, Jun QIN, Kang YE, Yonghong HU, Yiwei TAO, Yongzheng PENG, Yanxiang SHEN, Yan LIANG, Li ZENG. Effects of Flooding Stress on Photosynthetic Characteristics of Yulania stellata and Its Cultivars [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(3): 483-491. |
| [7] | Kuang-Zheng SHI, Zhao-Hui ZHANG, Chun-Mei HE, Zhi-Hui WANG. Effects of Different Canopy Density on the Chlorophyll Fluorescence and Water Storage Capacity of Sphagnum palustre in the Edge of the Tuntianjing Sinkhole in Bijie City [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(2): 262-269. |
| [8] | Xin-Dan HU, Yao LI, Xiao-Hua ZHANG, Juan-Hong LIANG, Teng-Guo ZHANG. Effect of Exogenous ATP on Cold Tolerance of Brassica campestris Seedlings [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(2): 302-311. |
| [9] | Xu-Fu WANG, Long-Fei HAO, Jia-Xin HAO, Wen-Ying HAO, Hui-Ga BAO, Shu-Lan BAI. Growth Responses of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica Seedlings under Simulated Nitrogen Deposition and Different Inoculation of Ectomycorrhizal Fungi Treatments [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(1): 138-144. |
| [10] | Ting-Yan LIU, Long-Fei HAO, Xu-Fu WANG, Hai-Xia YAN, Shu-Lan BAI. Effects of Nitrogen Deposition and Ectomycorrhizal Fungi on Root Architecture and Rhizosphere Soil Enzyme Activities of Larix olgensis Seedlings [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(1): 145-151. |
| [11] | Wen-Hai HU, Xiao-Hong YAN, Xiao-Hong LI, Zao-Gui CAO. Effects of 24-Epibrassinolide on the Chlorophyll Fluorescence Transient in Leaves of Pepper under Drought Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(1): 53-59. |
| [12] | Yi-Di LI, Chen-Rui GU, Hui-Xin GANG, Gui-Feng LIU, Su CHEN, Jing JIANG. Leaf Color and Growth Variation of Transgenic Gold Leaf Poplar [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(6): 897-905. |
| [13] | LI Chan, ZHANG Xiang, ZHENG Lan, CHANG Cheng-Long, LIU Cai-Xia, ZHENG Mi, YOU Xiang-Ling. Genetic Transformation of PsnHB22 Gene from Populus simonii×P.nigra in Tobacco [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(5): 760-767. |
| [14] | SUN Wang-Wang, MENG Xian-Min, XU Xiu-Yuan, WU Min-Hua, QIN Meng-Yang, LIN Meng-Meng, ZHANG Xin-Yan, YUE Guo-Zhong. Contents of Pigments and Anatomical Structure in the Leaves of Forsythia koreana ‘Sun Gold’ [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(3): 321-329. |
| [15] | ZHAO Zhe, JIN Ze-Xin. Effects of Simulated Nitrogen Deposition on the Growth and the Content of Non-structure Carbohydrate of Sinocalycanthus chinensis Seedlings [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(1): 41-49. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||