Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (1): 139-151.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2024.01.016
• Molecular biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Shanshan WANG1, Rui WANG1, Erqin FAN1, Pengyue FU1, Guanzheng QU1, Nan WANG2( )
)
Received:2023-05-12
Online:2024-01-20
Published:2023-12-27
Contact:
Nan WANG
E-mail:nanwang2019@caf.ac.cn
CLC Number:
Shanshan WANG, Rui WANG, Erqin FAN, Pengyue FU, Guanzheng QU, Nan WANG. Bioinformatics Analysis of CbuDELLAs Gene Family and Functional Analysis of CbuGRAS9[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(1): 139-151.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://bbr.nefu.edu.cn/EN/10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2024.01.016
Table 1
Basic information of CbuDELLAs
拟南芥蛋白名称 Protein names in Arabidopsis thaliana | 楸树蛋白名称 Protein names in Catalpa bungei | 编码区长度 Encoding length/bp | 氨基酸数目 Amino acid number | 等电点 Isoelectric point | 相对分子质量 Molecular weight/kDa | 亚细胞定位 Sub-cellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AtGAI(AT1G14920) | CbuGRAS22 | 1755 | 585 | 4.81 | 6.41 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| AtRGA1(AT2G01570) | CbuGRAS1 | 1767 | 588 | 4.99 | 6.43 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| AtRGL2(AT3G03450) | CbuGRAS9 | 1662 | 553 | 4.93 | 6.01 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| AtGAI(AT1G14920) | CbuGRAS2 | 1368 | 455 | 5.14 | 5.04 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| AtRGA1(AT2G01570) | CbuGRAS32 | 1755 | 584 | 5.08 | 6.40 | 细胞核Nucleus |
Table 2
Secondary structure analysis of CbuDELLAs
楸树蛋白名称 Protein names in Arabidopsis thaliana | α螺旋 | β转角 | 无规则卷曲 | 延伸链 Extended strand | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
数量 Number | 比例 Percent/% | 数量 Number | 比例 Percent/% | 数量 Number | 比例 Percent/% | 数量 Number | 比例 Percent/% | |
| CbuGRAS1 | 265 | 45.07 | 28 | 4.76 | 240 | 40.82 | 55 | 9.35 |
| CbuGRAS2 | 257 | 56.48 | 20 | 4.40 | 130 | 28.57 | 48 | 10.55 |
| CbuGRAS9 | 273 | 49.37 | 26 | 4.70 | 197 | 35.62 | 57 | 10.31 |
| CbuGRAS22 | 269 | 45.98 | 33 | 5.64 | 228 | 38.97 | 55 | 9.40 |
| CbuGRAS32 | 269 | 46.06 | 28 | 4.79 | 235 | 40.24 | 52 | 8.90 |
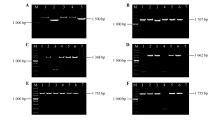
Fig.4
Cloning of the target sequence and PCR detection of the fragment linked to E.coli pEASY-T1M.DL5000 DNA Marker;7.Negative control;A.Sequences of Catalpa bungei DELLAs(1-5.CbuGRAS1,CbuGRAS2,CbuGRAS22,CbuGRAS32,CbuGRA9 PCR products);B.PCR detection of pEASY-T1-CbuGRAS1 in E.coli(1-6.PCR products of pEASY-T1-CbuGRAS1);C.PCR detection of pEASY-T1-CbuGRAS2 in E.coli(1-6.PCR products of pEASY-T1-CbuGRAS2);D.PCR detection of pEASY-T1-CbuGRAS9 in E.coli(1-6.PCR products of pEASY-T1-CbuGRAS9;E.PCR detection of pEASY-T1-CbuGRAS22 in E.coli(1-6.PCR products of pEASY-T1-CbuGRAS22);F.PCR detection of pEASY-T1-CbuGRAS9 in E.coli(1-6.PCR products of pEASY-T1-CbuGRAS9).

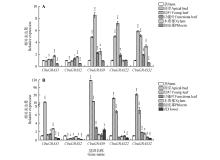
Fig.5
Tissue-specific expression analysis of CbuDELLAsA.Expression analysis of CbuDELLAs among different tissues in Catalpa bungei ‘Luoqiu No.1’;B.Expression analysis of CbuDELLAs among different tissues in Catalpa ‘Bairihua’;* represented P value was less than 0.05,** represented P value was less than 0.01,*** represented P value was less than 0.001.

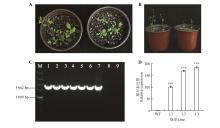
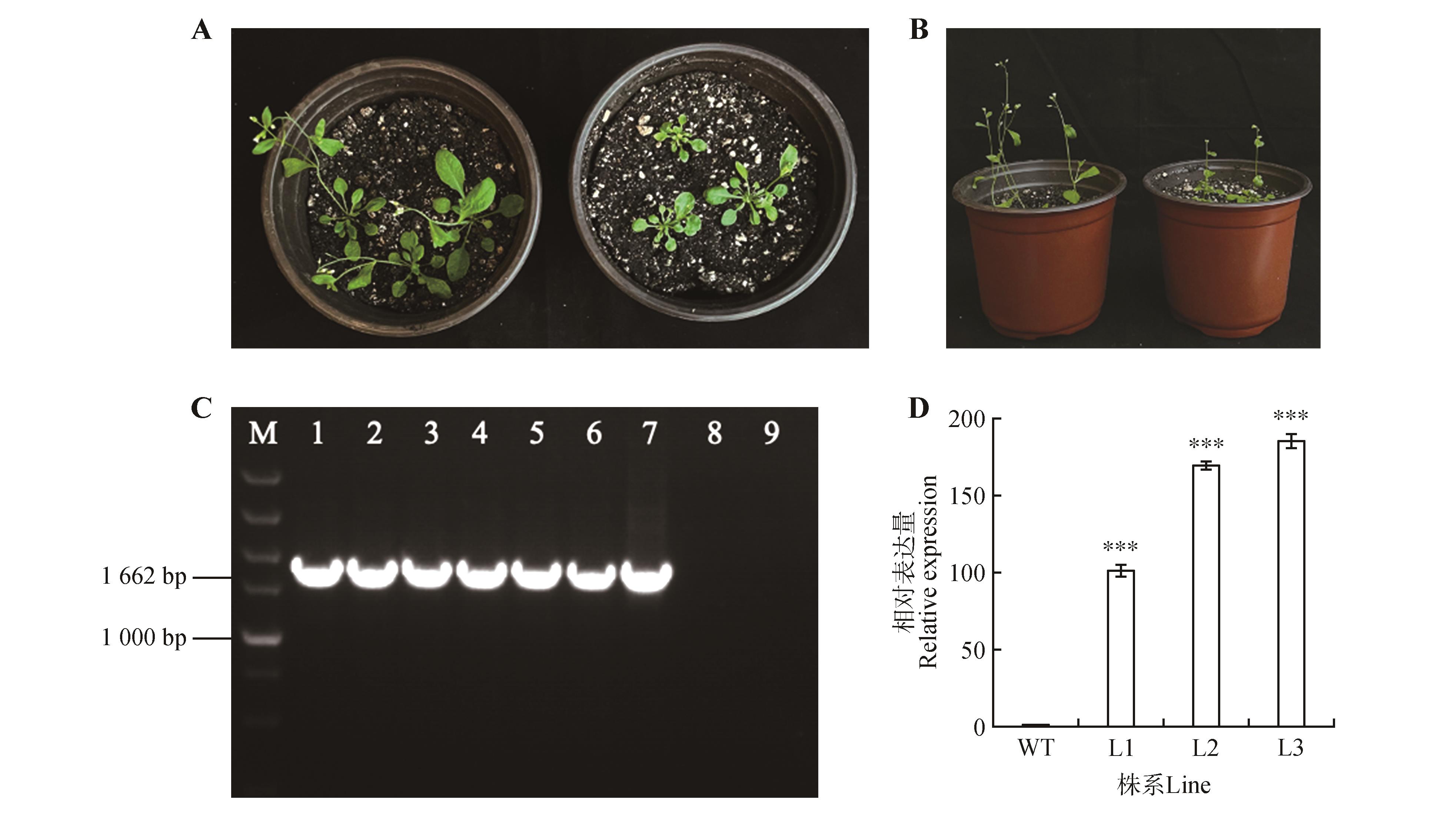
Fig.6
Phenotype observation and expression pattern analysis of heterologus transformation of CbuGRAS9A-B.The left side of wild-type Arabidopsis thaliana,the right side over-expression of CbuGRAS9Arabidopsis thaliana.After positive identification,three strains were selected and leaves were taken for qRT-PCR analysis;C.Detection of transgenic Arabidopsis DNA level(M.DL5000 DNA Marker;1-6.PCR products of transgenic lines;7.Positive control;8.Wild type Arabidopsis thalianas;9.ddH2O as a negative control);D.qRT-PCR detection of transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana(WT.Wild-type Arabidopsis thaliana;L1-L3.Transgenic Arabidopsisthaliana);*** represented P value was less than 0.001.
| 1 | 雍伟东,种康,许智宏,等.高等植物开花时间决定的基因调控研究[J].科学通报,2000,45(5):455-466. |
| YONG W D, ZHONG K, XU Z H,et al.The regulation of flowering time determination in higher plants[J].Chinese Science Bulletin,2000,45(5):455-466. | |
| 2 | 孙昌辉,邓晓建,方军,等.高等植物开花诱导研究进展[J].遗传,2007,29(10):1182-1190. |
| SUN C H, DENG X J, FANG J,et al.An overview of flowering transition in higher plants[J].Hereditas(Beijing),2007,29(10):1182-1190. | |
| 3 | IZAWA T.What is going on with the hormonal control of flowering in plants?[J].The Plant Journal,2021,105(2):431-445. |
| 4 | 周琴,张思思,包满珠,等.高等植物成花诱导的分子机理研究进展[J].分子植物育种,2018,16(11):3681-3692. |
| ZHOU Q, ZHANG S S, BAO M Z,et al.Research of molecular mechanisms of flowering induction in higher plants[J].Molecular Plant Breeding,2018,16(11):3681-3692. | |
| 5 | 杨小凤,李小蒙,廖万金.植物开花时间的遗传调控通路研究进展[J].生物多样性,2021,29(6):825-842. |
| YANG X F, LI X M, LIAO W J.Advances in the genetic regulating pathways of plant flowering time[J].Biodiversity Science,2021,29(6):825-842. | |
| 6 | FUKAZAWA J, OHASHI Y, TAKAHASHI R,et al.DELLA degradation by gibberellin promotes flowering via GAF1-TPR-dependent repression of floral repressors in Arabidopsis [J].The Plant Cell,2021,33(7):2258-2272. |
| 7 | YOSHIDA H, HIRANO K, SATO T,et al.DELLA protein functions as a transcriptional activator through the DNA binding of the indeterminate domain family proteins[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2014,111(21):7861-7866. |
| 8 | 高秀华,傅向东.赤霉素信号转导及其调控植物生长发育的研究进展[J].生物技术通报,2018,34(7):1-13. |
| GAO X H, FU X D.Research of gibberellin signal transduction and regulation of plants growth and development[J].Biotechnology Bulletin,2018,34(7):1-13. | |
| 9 | BAO S J, HUA C M, SHEN L S,et al.New insights into gibberellin signaling in regulating flowering in Arabidopsis [J].Journal of Integrative Plant Biology,2020,62(1):118-131. |
| 10 | GAO X H, HUANG X Z, XIAO S L,et al.Evolutionarily conserved DELLA-mediated gibberellin signaling in plants[J].Journal of Integrative Plant Biology,2008,50(7):825-834. |
| 11 | 赵春丽.苋菜AtGAI基因克隆及功能分析[D].福州:福建农林大学,2020. |
| ZHAO C L.Cloning and functional analysis of AtGAI from Amaranth [D].Fuzhou:Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University,2020. | |
| 12 | MURASE K, HIRANO Y, SUN T P,et al.Gibberellin-induced DELLA recognition by the gibberellin receptor GID1[J].Nature,2008,456(7221):459-463 |
| 13 | 李强,吴建明,梁和,等.高等植物赤霉素生物合成及其信号转导途径[J].生物技术通报,2014,(10):16-22. |
| LI Q, WU J M, LIANG H,et al.Biosynthesis and signal transduction pathways of gibberellin in higher plants[J].Biotechnology Bulletin,2014,(10):16-22. | |
| 14 | FUKAZAWA J, TERAMURA H, MURAKOSHI S,et al.DELLAs function as coactivators of GAI-ASSOCIATED FACTOR1 in regulation of gibberellin homeostasis and signaling in Arabidopsis [J].The Plant Cell,2014,26(7):2920-2938 |
| 15 | XUE H D, GAO X, HE P,et al.Origin,evolution,and molecular function of DELLA proteins in plants[J].The Crop Journal,2022,10(2) :287-299. |
| 16 | 岳川,曾建明,曹红利,等.高等植物赤霉素代谢及其信号转导通路[J].植物生理学报,2012,48(2):118-128. |
| YUE C, ZENG J M, CAO H L,et al.Metabolism and signal transduction pathways of gibberellin in higher plants[J].Plant Physiology Journal,2012,48(2):118-128. | |
| 17 | JIANG C F, FU X D.GA action:turning on de-DELLA repressing signaling[J].Current Opinion in Plant Biology,2007,10(5) :461-465. |
| 18 | CONTI L, NELIS S, ZHANG C J,et al.Small ubiquitin-like modifier protein SUMO enables plants to control growth independently of the phytohormone gibberellin[J].Developmental Cell,2014,28(1):102-110. |
| 19 | ACHARD P, GENSCHIK P.Releasing the brakes of plant growth:how GAs shutdown DELLA proteins[J].Journal of Experimental Botany,2009,60(4):1085-1092. |
| 20 | GONÇALVES N M, FERNANDES T, NUNES C,et al.SUMOylation of rice DELLA SLR1 modulates transcriptional responses and improves yield under salt stress[J/OL].bioRxiv(2020-03-10)[2023-05-02].. |
| 21 | DAVIÈRE J M, ACHARD P.A pivotal role of DELLAs in regulating multiple hormone signals[J].Molecular Plant,2016,9(1):10-20. |
| 22 | 黄昊,宫铭,张金凤,等.珍珠黄杨矮化基因BsGAI2的克隆及功能分析[J].植物遗传资源学报,2018,19(1):150-156. |
| HUANG H, GUO M, ZHANG J F,et al.Cloning and function analysis on BsGAI2 gene from Buxus sinica var.parvifolia M.Cheng[J].Journal of Plant Genetic Resources,2018,19(1):150-156. | |
| 23 | 王智.楸树开花突变体“百日花”的分子调控机制[D].北京:中国林业科学研究院,2019. |
| WANG Z.The mechanism of the flowering mutant “Bai ri hua” in Catalpa bungei [D].Beijing:Chinese Academy of Forestry,2019. | |
| 24 | 麻文俊,杨桂娟,王军辉,等.楸树不同单株花性状变异分析[J].植物研究,2020,40(3):386-393. |
| MA W J, YANG J J, WANG J H,et al.Analysis of variation in flower traits of different individual of Catalpa bungei [J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2020,40(3):386-393. | |
| 25 | 赵鲲,王军辉,麻文俊,等.杂交新品种“百日花”楸树选育与栽培试验研究[J].安徽林业科技,2020,46(6):15-18. |
| ZHAO K, WANG J H, MA W J,et al.Research on the breeding and cultivation experiment of the hybrid variety “Bai ri hua” Catalpa bungei [J].Anhui Forestry Technology,2020,46(6):15-18. | |
| 26 | WANG Z, MA W J, ZHU T Q,et al.Multi-omics sequencing provides insight into floral transition in Catalpa bungei.C.A.Mey[J].BMC Genomics,2020,21(1):508. |
| 27 | WANG Z, ZHU T Q, MA W J,et al.Potential function of CbuSPL and gene encoding its interacting protein during flowering in Catalpa bungei [J].BMC Plant Biology,2020,20(1):105 |
| 28 | LANGMEAD B, SALZBERG S L.Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2[J].Nature Methods,2012,9(4):357-359. |
| 29 | WANG R, ZHANG Y, WANG C,et al.ThNAC12 from Tamarix hispida directly regulates ThPIP2;5 to enhance salt tolerance by modulating reactive oxygen species[J].Plant Physiology and Biochemistry,2021,163:27-35. |
| 30 | KECHIN A, BOYARSKIKH U, KEL A,et al.cutPrimers:a new tool for accurate cutting of primers from reads of targeted next generation sequencing[J].Journal of Computational Biology,2017,24(11):1138-1143. |
| 31 | QUINLAN A R, HALL I M.BEDTools:a flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features[J].Bioinformatics,2010,26(6):841-842. |
| 32 | KANEHISA M, GOTO S, KAWASHIMA S,et al.The KEGG databases at GenomeNet[J].Nucleic Acids Research,2002,30(1):42-46. |
| 33 | 于磊.水曲柳DELLA家族基因应答低温胁迫及参与被动休眠调控研究[D].哈尔滨:东北林业大学,2021. |
| YU L. DELLA family in Fraxinus mandshurica to low temperature stress and involvement in passive dormancy regulation[D].Harbin:Northeast Forestry University,2021. | |
| 34 | 蔡健宇,余婧,张景云,等.烟草DELLA基因家族的克隆与表达模式分析[J].烟草科技,2022,55(10):10-18. |
| CAI J Y, YU J, ZHANG J Y,et al.Expression pattern analysis of DELLA family in tobacco [J].Tobacco Science & Technology,2022,55(10):10-18. | |
| 35 | ZHONG G Y, YANG Y Z.Characterization of grape gibberellin Insensitive1 mutant alleles in transgenic Arabidopsis [J].Transgenic Research,2012,21(4):725-741. |
| 36 | 温玮.棉花DELLA蛋白的基因克隆与功能的初步鉴定[D].海口:海南大学,2010. |
| WEN W.Cloning and functional identification of DELLA protein in cotton[D].Haikou:Hainan University,2010. | |
| 37 | 张晶星,马彦广,王辉丽,等.油松JAZ基因家族特征及其与DELLA蛋白互作的功能域鉴定[J].北京林业大学学报,2022,44(12):12-22. |
| ZHANG J X, MA Y G, WANG H L,et al.Characterization of JAZ family of Pinus tabulaeformis and identification of functional domain interacting with DELLA Protein[J].Journal of Beijing Forestry University,2022,44(12):12-22. | |
| 38 | 周鹏,李钱峰,熊敏,等.DELLA蛋白介导的激素互作调控植物生长发育研究进展[J].植物生理学报,2020,56(4):661-671. |
| ZHOU P,LI Q F,XIONG M,Advances in DELLA protein-mediated phytohormonal crosstalk in regulation of plant growth and development[J].Plant Physiology Journal,2020,56(4):661-671. | |
| 39 | DAVIÈRE J M, ACHARD P.Gibberellin signaling in plants[J].Development,2013,140(6):1147-1151. |
| 40 | FENG S H, MARTINEZ C, GUSMAROLI G,et al.Coordinated regulation of Arabidopsis thaliana development by light and gibberellins[J].Nature,2008,451(7177):475-479. |
| 41 | CAO D N, CHENG H, WU W,et al.Gibberellin mobilizes distinct DELLA-dependent transcriptomes to regulate seed germination and floral development in Arabidopsis [J].Plant Physiology,2006,142(2):509-525. |
| 42 | MOURADOV A, CREMER F, COUPLAND G.Control of flowering time:interacting pathways as a basis for diversity[J].The Plant Cell,2002,14():S111-S130. |
| 43 | FUKAZAWA J, MIYAMOTO C, ANDO H,et al.DELLA-GAF1 complex is involved in tissue-specific expression and gibberellin feedback regulation of GA20ox1 in Arabidopsis [J].Plant Molecular Biology,2021,107(3):147-158. |
| 44 | SUN T P.The molecular mechanism and evolution of the GA-GID1-DELLA signaling module in plants[J].Current Biology,2011,21(9):R338-R345. |
| 45 | 岳溶榕.梨单性结实相关DELLA基因的功能分析[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2019. |
| YUE R R.Functional analysis of DELLA related to parthenocarpy in Pear[D].Yangling:Northwest A&F University,2019. | |
| 46 | YU S, GALVÃO V C, ZHANG Y C,et al.Gibberellin regulates the Arabidopsis floral transition through miR156-targeted SQUAMOSA promoter binding-like transcription factors[J].The Plant Cell,2012,24(8):3320-3332. |
| 47 | 段怡红,阎媛媛,陈丽婷,等.陆地棉开花时间相关基因GhMYB44的克隆与功能验证[J].中国农业科技导报,2020,22(12):29-38. |
| DUAN Y H, YAN Y Y, CHEN L T,et al.Cloning and functional verification of flowering time related gene GhMYB44 in cotton[J].Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology,2020,22(12):29-38. | |
| 48 | 李巍.水稻MYB21-like基因Os01g45090和Os05g49310的功能研究[D].哈尔滨:东北林业大学,2015. |
| LI W.Functional studies on the MYB21-like genes Os01g45090 and Os05g49310 in rice[D].Harbin:Northeast Forestry University,2015. | |
| 49 | 冯震.陆地棉开花相关基因GhAP1互作基因筛选及其功能鉴定[D].北京:中国农业科学院,2021. |
| FENG Z.Functional identification of GhAP1 interaction genes related to flowering in cotton [D].Beijing:Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences,2021. |
| [1] | Shixian LIAO, Yuting WANG, Liben DONG, Yongmei GU, Fenglin JIA, Tingbo JIANG, Boru ZHOU. Function Analysis of the Transcription Factor PsnbZIP1 of Populus simonii×P. nigra in Response to Salt Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(2): 288-299. |
| [2] | Denggao LI, Rui LIN, Qinghui MU, Na ZHOU, Yanru ZHANG, Wei BAI. Identification and Analysis of the Potato StCRKs Gene Family and Expression Patterns in Response to Stress Signals [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(6): 1033-1043. |
| [3] | He CHENG, Shuanghui TIAN, Yang ZHANG, Cong LIU, De’an XIA, Zhigang WEI. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analysis of nsLTP Gene Family in Populus trichocarpa [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(3): 412-423. |
| [4] | Yuning Yang, Hao Dong, Shiwei Dong, Nairui Wang, Yue Song, Hanguo Zhang, Shujuan Li. Cloning and Expression Analysis of Transcription Factor LobHLH34 from Larix olgensis [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(1): 112-120. |
| [5] | Jiaming Zhao, Erqin Fan, Yi Liu, Zhi Wang, Junhui Wang, Guanzheng Qu. Cloning and Bioinformatics Analysis of CbuATX1,CbuATX1-like and CbuATX2 Genes from Catalpa bungei [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(1): 47-61. |
| [6] | Shu-Ping PENG, Cheng-Ming DONG, Yun-Hao ZHU. Cloning and Expression Analysis of Two Key Genes of Jasmonic Acid Synthesis in Response to Endophytic Infection from Rehmannia glutinosa [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(2): 294-301. |
| [7] | Wen-Lin WANG, Hai-Sheng CHEN, Shu-Fang ZHENG, Song-Le FAN, Li-Feng WANG, Qiu-Jin TAN, Zhen-Shi QIN, Xi-Yun HUANG, Peng HE, Xiu-hua TANG, Peng XU. Cloning,Structure and Function Analysis of MiMYB2 Gene from Macadamia integrifolia [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(6): 913-922. |
| [8] | QIAO Bin-Jie, WANG De-Qiu, GAO Hai-Yan, LI Zhao-Min, GE Li-Li, DING Wen-Ya, ZHAO Xi-Yang. Photosynthetic and Stomatal Morphological Variation of Poplar Clones in Seedling Stage under Drought Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(2): 177-188. |
| [9] | WANG Qi, XU Zhi-Ru, CHEN Jin-Yuan, ZHANG Shuang, HUANG Jia-Huan, LIU Guan-Jun. Identification and Expression Analysis of Heavy Metal-associated Isoprenylated Plant Proteins(HIPPs) Genes in Populus [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2019, 39(6): 935-946. |
| [10] | BAI Xiao-Ming, DONG Shi-Wei, YANG Yu-Ning, SONG Yue, ZHANG Han-Guo, LI Shu-Juan. Cloning and Expression Analysis of Catalase Gene(LoCAT1) from Larix olgensis [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2019, 39(4): 539-546. |
| [11] | SUN Xiao-Sha, WANG Sui, ZHAO Xi-Yang, QU Guan-Zheng. Cloning and Bioinformatics Analysis 4CL3/4CL5 Gene of Populus alba×P.glandulosa [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2019, 39(4): 547-556. |
| [12] | WANG Heng-Tao, SHAO Wan-Xuan, XU Shu-Hao, ZENG Fan-Suo. Cloning and Expression Pattern Analysis of MUR5 Gene in Fraxinus mandshurica [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2018, 38(6): 913-920. |
| [13] | GONG Dao-Yong, HU Shang-Lian, CAO Ying, LU Xue-Qin, ZHANG Qing-Bo. Cloning and Bioinformatics Analysis of Two bZIP Genes of Bambusa emeiensis and Their Induced Expression under Abiotic Stresses [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2018, 38(2): 268-277. |
| [14] | SUN Shuang, ZHAO Xing-Tang, LIANG Nan-Song, LIU Ying, YU Lei, LIU Chun-Hao, QIN Jun-Qi, ZHAN Ya-Guang. Expression Patterns of FmABI5 Gene Induced by Abiotic Stress and Signal in Fraxinus mandshurica [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2017, 37(3): 453-460. |
| [15] | LI Hui-Ping, LI Bang-Yong, HU Shang-Lian, CAO Ying. Cloning and Expression Analysis of Two NAC Transcription Factors in Bambusa emeiensis [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2016, 36(6): 895-901. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||