植物研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (4): 573-587.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2021.04.013
收稿日期:2020-06-02
出版日期:2021-07-20
发布日期:2021-03-24
通讯作者:
周兴文
E-mail:xingwenzhou2003@163.com
作者简介:李博(1981—),男,博士,副教授,主要从事植物资源利用研究。
基金资助:
Bo LI, He-Xia LIU, Qin LIU, Xing-Wen ZHOU( )
)
Received:2020-06-02
Online:2021-07-20
Published:2021-03-24
Contact:
Xing-Wen ZHOU
E-mail:xingwenzhou2003@163.com
About author:LI Bo(1981—),male,PhD,associate professor,mainly engaged in plant resources utilization research.
Supported by:摘要:
花瓣大小是影响金花茶(Camellia nitidissima)观赏价值的主要因素之一,但金花茶花瓣发育形成机制尚不清楚。将金花茶花瓣发育过程划分为幼蕾期(S1)、初蕾期(S2)、显色期(S3)、半开期(S4)、盛开期(S5)五个阶段,利用RNA-seq技术分析花发育过程中转录组的动态变化,以期对金花茶花瓣发育形成的转录机理进行初步探究。通过对金花茶花瓣发育过程中的差异表达基因进行富集分析和趋势分析,发现生长素转导途径所含差异表达基因数量最多,部分AUX1/LAX共转运体、AUX/IAA基因、SAUR等生长素应答基因在开花过程中明显上调,表明生长素是调控花瓣生长重要的调控因子。MYB、bHLH、锌指蛋白等转录因子、木葡聚糖内糖基转移酶/水解酶(XTH)、果胶酯酶(PE)、果胶裂解酶(PL)等部分下游功能基因,其中XTH显著富集于GO分类中的水解酶活性,表明它们可能对金花茶花瓣的生长起重要调控作用。此外,对FT、SOC1、AP3、PI、SEP3等开花调控关键基因在金花茶花瓣发育过程中的表达情况进行了分析,结果表明这些基因主要以中低表达为主。高表达基因进行KEGG富集分析结果表明,次生代谢物质合成伴随着金花茶花瓣的整个发育过程。这些结果为进一步揭示金花茶花瓣发育的转录调控机制奠定了理论基础。
中图分类号:
李博, 刘合霞, 刘秦, 周兴文. 金花茶花瓣转录组分析及花瓣发育调控基因挖掘[J]. 植物研究, 2021, 41(4): 573-587.
Bo LI, He-Xia LIU, Qin LIU, Xing-Wen ZHOU. Transcriptome Analysis of Petals and to Explore Related Genes in Petal Development of Camellia nitidissima[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(4): 573-587.

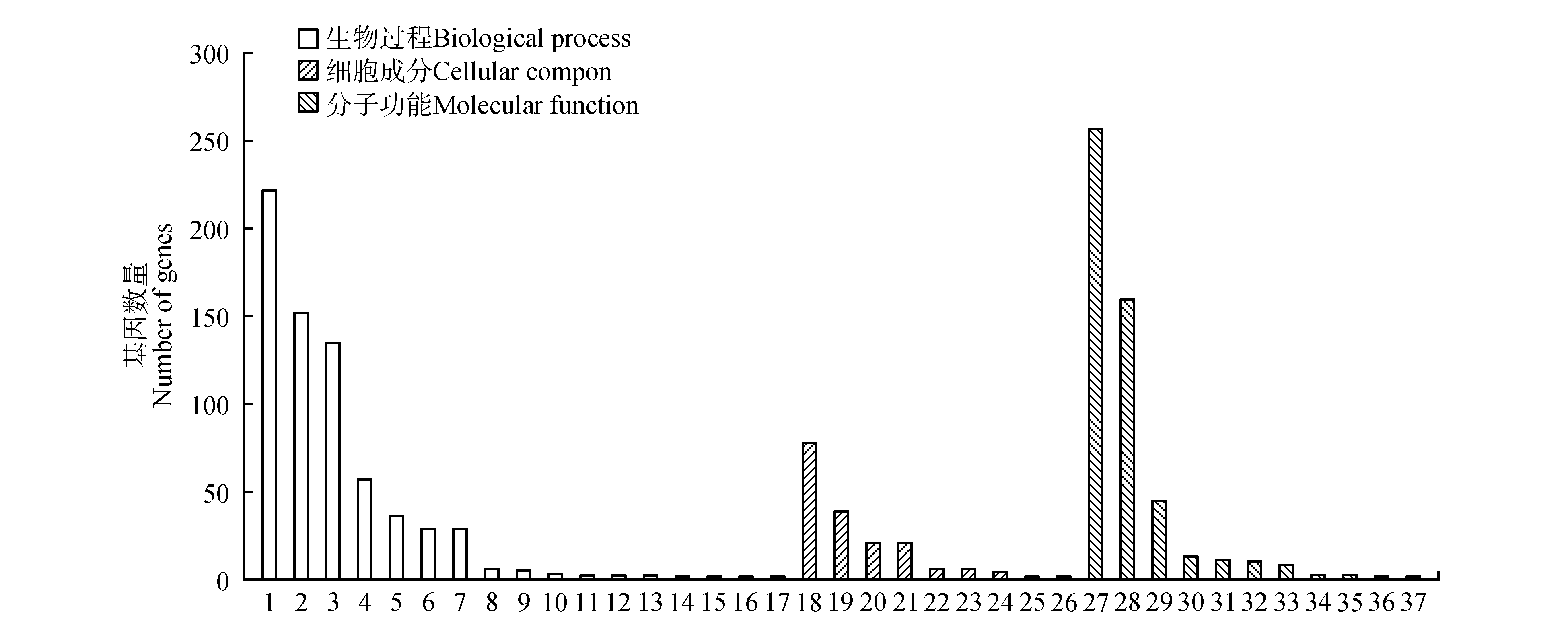
图3
金花茶差异表达基因的GO分类1.代谢进程;2.单有机体进程;3.细胞进程;4.定位;5.应激响应;6.生物过程调节;7.生物调节;8.信号传导;9.细胞成分组织或生物起源;10.有机体进程;11.生长;12.发育过程;13.有机体多细胞进程;14.免疫系统进程;15.生物进程的负调控;16.繁殖;17.繁殖进程;18.催化活性;19.结合;20.转运活性;21.分子功能调节因子;22.核酸结合转录因子活性;23.电子载体活性;24.抗氧化活性;25.信号转导活性;26.结构分子活性;27.营养库活性;28.分子转导活性;29.膜;30.膜部分;31.细胞;32.细胞部分;33.高分子配合物;34.细胞器;35.胞外区域部分;36.超分子纤维;37.细胞器部分
| 1 | 黄瑞斌,和太平,庄嘉,等.广西防城港市金花茶组植物资源及其保育对策[J].广西农业生物科学,2007,26(S1):32-37. |
| Huang R B,He T P,Zhuang J,et al.Plant resource and it’s conservational countermeasure of Sect.Chrysantha Chang in Fangchenggang[J].Journal of Guangxi Agricultural and Biological Science,2007,26(S1):32-37. | |
| 2 | 孔桂菊,袁胜涛,孙立.金花茶药理作用研究进展[J].时珍国医国药,2016,27(6):1459-1461. |
| Kong G J,Yuan S T,Sun L.Progress in pharmacological action research of Camellia nitidissima[J].Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research,2016,27(6):1459-1461. | |
| 3 | Dai L,Li J L,Liang X Q,et al.Flowers of Camellia nitidissima cause growth inhibition,cell-cycle dysregulation and apoptosis in a human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell line[J].Molecular Medicine Reports,2016,14(2):1117-1122. |
| 4 | Wang W X,Liu H Y,Wang Z N,et al.Phytochemicals from Camellia nitidissima Chi inhibited the formation of advanced glycation end-products by scavenging methylglyoxal[J].Food Chemistry,2016,205:204-211. |
| 5 | He D Y,Li X Y,Sai X,et al.Camellia nitidissima C.W.Chi:a review of botany,chemistry,and pharmacology[J].Phytochemistry Reviews,2017,17(2):327-349. |
| 6 | Fenster C B,Armbruster W S,Wilson P,et al.Pollination syndromes and floral specialization[J].Annual Review of Ecology Evolution & Systematics,2004,35:375-403. |
| 7 | Stuurman J,Hoballah M E,Broger L,et al.Dissection of floral pollination syndromes in petunia[J].Genetics,2004,168(3):1585-1599. |
| 8 | Nishihara M,Nakatsuka T.Genetic engineering of flavonoid pigments to modify flower color in floricultural plants[J].Biotechnology Letters,2011,33(3):433-441. |
| 9 | Irish V F.The Arabidopsis petal:a model for plant organogenesis[J].Trends in Plant Science,2008,13(8):430-436. |
| 10 | Abraham M C,Metheetrairut C,Irish V F.Natural variation identifies multiple loci controlling petal shape and size in Arabidopsis thaliana[J].PLoS One,2013,8(2):e56743. |
| 11 | Schmid M,Davison T S,Henz S R,et al.A gene expression map of Arabidopsis thaliana development[J].Nature Genetics,2005,37(5):501-506. |
| 12 | Han Y,Wan H H,Cheng T R,et al.Comparative RNA-seq analysis of transcriptome dynamics during petal development in Rosa chinensis[J].Scientific Reports,2017,7(1):43382. |
| 13 | Wang J J,Wang H B,Ding L,et al.Transcriptomic and hormone analyses reveal mechanisms underlying petal elongation in Chrysanthemum morifolium ‘Jinba’[J].Plant Molecular Biology,2017,93(6):593-606. |
| 14 | Zhou X W,Li J Y,Zhu Y L,et al.De novo assembly of the Camellia nitidissima Transcriptome reveals key genes of flower pigment biosynthesis[J].Frontiers in Plant Science,2017,8:1545. |
| 15 | Grabherr M G,Haas B J,Yassour M,et al.Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome[J].Nature Biotechnology,2011,29(7):644-652. |
| 16 | Li B,Dewey C N.RSEM:accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome[J].BMC Bioinformatics,2011,12(1):323. |
| 17 | Trapnell C,Williams B A,Pertea G,et al.Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation[J].Nature Biotechnology,2010,28(5):511-515. |
| 18 | Anders S,Huber W.Differential expression analysis for sequence count data[J].Genome Biology,2010,11(10):R106. |
| 19 | Young M D,Wakefield M J,Smyth G K,et al.Gene ontology analysis for RNA-seq:accounting for selection bias[J].Genome Biology,2010,11(2):R14. |
| 20 | Mao X Z,Cai T,Olyarchuk J G,et al.Automated genome annotation and pathway identification using the KEGG Orthology(KO) as a controlled vocabulary[J].Bioinformatics,2005,21(19):3787-3793. |
| 21 | Jason E,Bar-Joseph Z.STEM:a tool for the analysis of short time series gene expression data[J].BMC Bioinformatics,2006,7(1):191. |
| 22 | 张欢,杨英杰,李鼎立,等.杜梨根茎叶特异表达基因的RNA-Seq分析[J].园艺学报,2018,45(10):1881-1894. |
| Zhang H,Yang Y J,Li D L,et al.RNA-Seq analysis of the tissue-specific expressed genes of Pyrusbetulaefolia in root,stem and leaf[J].Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2018,45(10):1881-1894. | |
| 23 | Livak K J,Schmittgen T D.Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-△△CT method[J].Methods,2001,25(4):402-408. |
| 24 | Powell A E,Lenhard M.Control of organ size in plants[J].Current Biology,2012,22(9):R360-R367. |
| 25 | Winship L J,Obermeyer G,Geitmann A,et al.Under pressure,cell walls set the pace[J].Trends in Plant Science,2010,15(7):363-369. |
| 26 | Buchanan B B,Gruissem W,Jones R L.Biochemistry and molecular biology of plants[M].New Jersey:Wiley,2002:85-86. |
| 27 | Cosgrove D J.Growth of the plant cell wall[J].Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology,2005,6(11):850-861. |
| 28 | Rose J K,Braam J,Fry S C,et al.The XTH family of enzymes involved in xyloglucan endotransglucosylation and endohydrolysis:current perspectives and a new unifying nomenclature[J].Plant & Cell Physiology,2002,43(12):1421-1435. |
| 29 | Lang X A,Li N,Li L F,et al.Integrated metabolome and transcriptome analysis uncovers the role of anthocyanin metabolism in Michelia maudiae[J].International Journal of Genomics,2019,2019:4393905. |
| 30 | Li H,Li J R,Dong Y M,et al.Time-series transcriptome provides insights into the gene regulation network involved in the volatile terpenoid metabolism during the flower development of lavender[J].BMC Plant Biology,2019,19:313. |
| 31 | Rothenberg D O,Yang H J,Chen M B,et al.Metabolome and transcriptome sequencing analysis reveals anthocyanin metabolism in pink flowers of anthocyanin-rich tea(Camellia sinensis)[J].Molecules,2019,24(6):1064. |
| 32 | Yue J Y,Zhu C X,Zhou Y,et al.Transcriptome analysis of differentially expressed unigenes involved in flavonoid biosynthesis during flower development of Chrysanthemum morifolium ‘Chuju’[J].Scientific Reports,2018,8(1):13414. |
| 33 | Singh A P,Tripathi S K,Nath P,et al.Petal abscission in rose is associated with the differential expression of two ethylene-responsive xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase genes,RbXTH1 and RbXTH2[J].Journal of Experimental Botany,2011,62(14):5091-5103. |
| 34 | Becnel J,Natarajan M,Kipp A,et al.Developmental expression patterns of Arabidopsis XTH genes reported by transgenes and genevestigator[J].Plant Molecular Biology,2006,61(3):451-467. |
| 35 | Kurasawa K,Matsui A,Yokoyama R,et al.The AtXTH28 gene,a xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase,is involved in automatic self-pollination in Arabidopsis thaliana[J].Plant & Cell Physiology,2009,50(2):413-422. |
| 36 | Ariizumi T,Amagai M,Shibata D,et al.Comparative study of promoter activity of three anther-specific genes encoding lipid transfer protein,xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase and polygalacturonase in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana[J].Plant Cell Reports,2002,21(1):90-96. |
| 37 | Harada T,Torii Y,Morita S,et al.Cloning,characterization,and expression of xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase and expansin genes associated with petal growth and development during carnation flower opening[J].Journal of Experimental Botany,2011,62(2):815-823. |
| 38 | Santner A,Estelle M.Recent advances and emerging trends in plant hormone signalling[J].Nature,2009,459(7250):1071-1078. |
| 39 | Han Y,Yong X,Yu J Y,et al.Identification of candidate adaxial-abaxial-related genes regulating petal expansion during flower opening in Rosa chinensis “Old Blush”[J].Frontiers in Plant Science,2019,10:1098. |
| 40 | Swarup K,Benková E,Swarup R,et al.The auxin influx carrier LAX3 promotes lateral root emergence[J].Nature Cell Biology,2008,10(8):946-954. |
| 41 | Stepanova A N,Robertson-Hoyt J,Yun J,et al.TAA1-Mediated auxin biosynthesis is essential for hormone crosstalk and plant development[J].Cell,2008,133(1):177-191. |
| 42 | Riechmann J L,Ratcliffe O J.A genomic perspective on plant transcription factors[J].Current Opinion in Plant Biology,2000,3(5):423-434. |
| 43 | Zhang Y F,Cao G Y,Qu L J,et al.Characterization of Arabidopsis MYB transcription factor gene AtMYB17 and its possible regulation by LEAFY and AGL15[J].Journal of Genetics and Genomics,2009,36(2):99-107. |
| 44 | Pastore J J,Limpuangthip A,Yamaguchi N,et al.Late meristem IDENTITY2 acts together with leafy to activate APETALA1[J].Development,2011,138(15):3189-3198. |
| 45 | Lee D K,Geisler M,Springer P S.LATERAL ORGAN FUSION1 and LATERAL ORGAN FUSION2 function in lateral organ separation and axillary meristem formation in Arabidopsis[J].Development,2009,136(14):2423-2432. |
| 46 | Szécsi J,Joly C,Bordji K,et al.BIGPETALp,a bHLH transcription factor is involved in the control of Arabidopsis petal size[J].The EMBO Journal,2006,25(16):3912-3920. |
| 47 | 张璐,杜相革.植物水孔蛋白研究进展[J].植物科学学报,2014,32(3):304-314. |
| Zhang L,Du X G.Recent advances in plant aquaporins[J].Plant Science Journal,2014,32(3):304-314. | |
| 48 | Ma N,Xue J Q,Li Y H,et al.Rh-PIP2;1,a Rose aquaporin gene,is involved in ethylene-regulated petal expansion[J].Plant Physiology,2008,148(2):894-907. |
| 49 | 雍伟东,谭克辉,许智宏,等.高等植物开花时间决定的基因调控研究[J].科学通报,2000,45(5):455-466. |
| Yong W D,Chong K,Xu Z H,et al.Gene control of flowering time in higher plants[J].Chinese Science Bulletin,2000,45(18):1633-1642. | |
| 50 | Blümel M,Dally N,Jung C.Flowering time regulation in crops-what did we learn from Arabidopsis?[J].Current Opinion in Biotechnology,2015,32:121-129. |
| 51 | Bouchée F,Lobet G,Tocquin P,et al.FLOR-ID:an interactive database of flowering-time gene networks in Arabidopsis thaliana[J].Nucleic Acids Research,2016,44(D1):D1167-D1171. |
| 52 | Wang S,Huang H J,Han R,et al.BpAP1 directly regulates BpDEF to promote male inflorescence formation in Betula platyphylla × B.pendula[J].Tree Physiology,2019,39(6):1046-1060. |
| 53 | Agrawal G K,Abe K,Yamazaki M,et al.Conservation of the E function for floral organ identity in rice revealed by the analysis of tissue culture induced loss of function mutants of the OsMADS1 gene[J].Plant Molecular Biology,2005,59(1):125-135. |
| 54 | Theissen G.Development of floral organ identity:stories from the MADS house[J].Current Opinion in Plant Biology,2001,4(1):75-85. |
| 55 | Favaro R,Pinyopich A,Battaglia R,et al.MADS-box protein complexes control carpel and ovule development in Arabidopsis[J].The Plant Cell,2003,15(11):2603-2611. |
| 56 | Sablowski R W M,Meyerowitz E M.A homolog of NO APICAL MERISTEM is an immediate target of the floral homeotic genes APETALA3/PISTILLATA[J].Cell,1998,92(1):93-103. |
| 57 | Ma H,Depamphilis C.The ABCs of floral evolution[J].Cell,2000,101(1):5-8. |
| 58 | Fei Y,Liu Z X.Isolation and characterization of the PISTILLATA Ortholog gene from Cymbidium faberi Rolfe[J].Agronomy,2019,9(8):425. |
| [1] | 朱栗琼, 覃冬梅, 招礼军, 邓斌胜, 刘晟源, 蒋昌杰. 6种野生金花茶叶表皮微形态特征及其系统学意义[J]. 植物研究, 2021, 41(6): 841-850. |
| [2] | 朱利利, 杜庆鑫, 何凤, 庆军, 杜红岩. 杜仲雄花芽2个发育时期转录组分析[J]. 植物研究, 2020, 40(2): 284-292. |
| [3] | 李辛雷, 王佳童, 孙振元, 王洁, 殷恒福, 范正琪, 李纪元. 崇左金花茶花朵和叶片类黄酮UPLC-Q-TOF-MS分析[J]. 植物研究, 2019, 39(3): 365-371. |
| [4] | 周兴文;李纪元;朱宇林. 金花茶查尔酮合成酶基因CnCHS的克隆及遗传转化研究[J]. 植物研究, 2015, 35(3): 327-332. |
| [5] | 周兴文;李纪元*;殷恒福;范正琪;李辛雷. 金花茶FLS基因的克隆及其植物表达载体的构建[J]. 植物研究, 2013, 33(1): 58-65. |
| [6] | 柴胜丰;韦霄*;史艳财;王满莲;邹蓉;唐辉. 强光胁迫对濒危植物金花茶幼苗生长和叶绿素荧光参数的影响[J]. 植物研究, 2012, 32(2): 159-164. |
| [7] | 韦 霄;王满莲;蒋运生;唐 辉;陈宗游;曹洪麟*. 显脉金花茶的光合生理特性研究[J]. 植物研究, 2007, 27(4): 434-438. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||