植物研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (1): 20-29.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2023.01.003
收稿日期:2021-12-18
出版日期:2023-01-20
发布日期:2022-12-23
通讯作者:
周存宇
E-mail:zhoucy@yangtzeu.edu.cn
作者简介:李腾(1995—),男,硕士研究生,主要从事湿地植物与生态修复方面的研究。
基金资助:
Teng LI1, Cunyu ZHOU1( ), Chaodong YANG1, Zhanfeng LIU2
), Chaodong YANG1, Zhanfeng LIU2
Received:2021-12-18
Online:2023-01-20
Published:2022-12-23
Contact:
Cunyu ZHOU
E-mail:zhoucy@yangtzeu.edu.cn
About author:LI Teng(1995—),male,master postgraduates,mainly engaged in the study of wetland plants and ecological restoration.
Supported by:摘要:
蜈蚣草(Pteris vittata)是多年生的超积累砷植物,并用于修复受重金属污染的土壤。利用光学显微镜和荧光显微镜来研究蜈蚣草的解剖结构及组织化学特征,以此明确该物种适应干旱岩生环境,以及具有离子超富集作用的特点。结果表明:(1)蜈蚣草孢子体的根状茎、不定根和叶的结构均为初生结构,不定根的结构由内而外包括维管柱、内皮层、皮层、木质化厚壁组织层和表皮。(2)根状茎结构由内而外包括网状中柱、内皮层、皮层、表皮外覆盖的角质层。(3)羽状复叶的总叶柄的结构由内而外包括维管束、内皮层、皮层、厚壁组织层、表皮外覆盖的角质层。叶片为异面叶,表皮内方具厚壁层,叶表皮具角质层,仅下表皮有气孔。(4)蜈蚣草根表皮、皮层与根毛的表面富含果胶,皮层木质化;黄连素离子通透性试验结果显示,根毛、根表皮和皮层滞留大量黄连素离子。综上,植物体的内皮层、木质化厚壁组织层、异面叶和厚的角质层结构说明蜈蚣草适应岩生环境,根具木质化皮层和富含果胶的组织化学特点,以及离子通透性试验表明其与离子超积累功能有关。
中图分类号:
李腾, 周存宇, 杨朝东, 刘占峰. 蜈蚣草的解剖结构与组织化学特征[J]. 植物研究, 2023, 43(1): 20-29.
Teng LI, Cunyu ZHOU, Chaodong YANG, Zhanfeng LIU. Anatomical and Histochemical Features of the Pteris vittata (Pteridaceae)[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(1): 20-29.

图1
蜈蚣草不定根的解剖结构(长度20~56 mm)A~C.距根尖10 mm处;D~F.距根尖20 mm处;G~H.距根尖30 mm处;A、D、G.硫酸氢黄连素-苯胺兰染色,置于紫外光下观察;B、E、H.苏丹红7B染色,明亮视野下观察;C、F.钌红染色,明亮视野下观察;A.原生木质部,内皮层(箭头),通道细胞,木质化皮层(*),皮层,表皮,根毛;B.原生木质部,内皮层(箭头),皮层,表皮,根毛;C.内皮层(箭头),皮层,表皮,根毛;D.原生木质部,内皮层(箭头),木质化皮层(*),皮层,表皮,根毛;E.后生木质部,内皮层(箭头),木质化增厚皮层(*),皮层,表皮,根毛;F.后生木质部,内皮层(箭头),皮层,表皮,根毛;G.后生木质部,内皮层(箭头),木质化皮层(*),皮层,表皮,根毛;H.后生木质部,内皮层(箭头),木质化增厚皮层(*),皮层,表皮,根毛;co.皮层;cu.角质层;h.根毛;hy.皮下层;mx.后生木质部;pa.栅栏组织;pc.通道细胞;px.原生木质部;rh.表皮;sp.海绵组织;vb.维管束;ve.叶脉
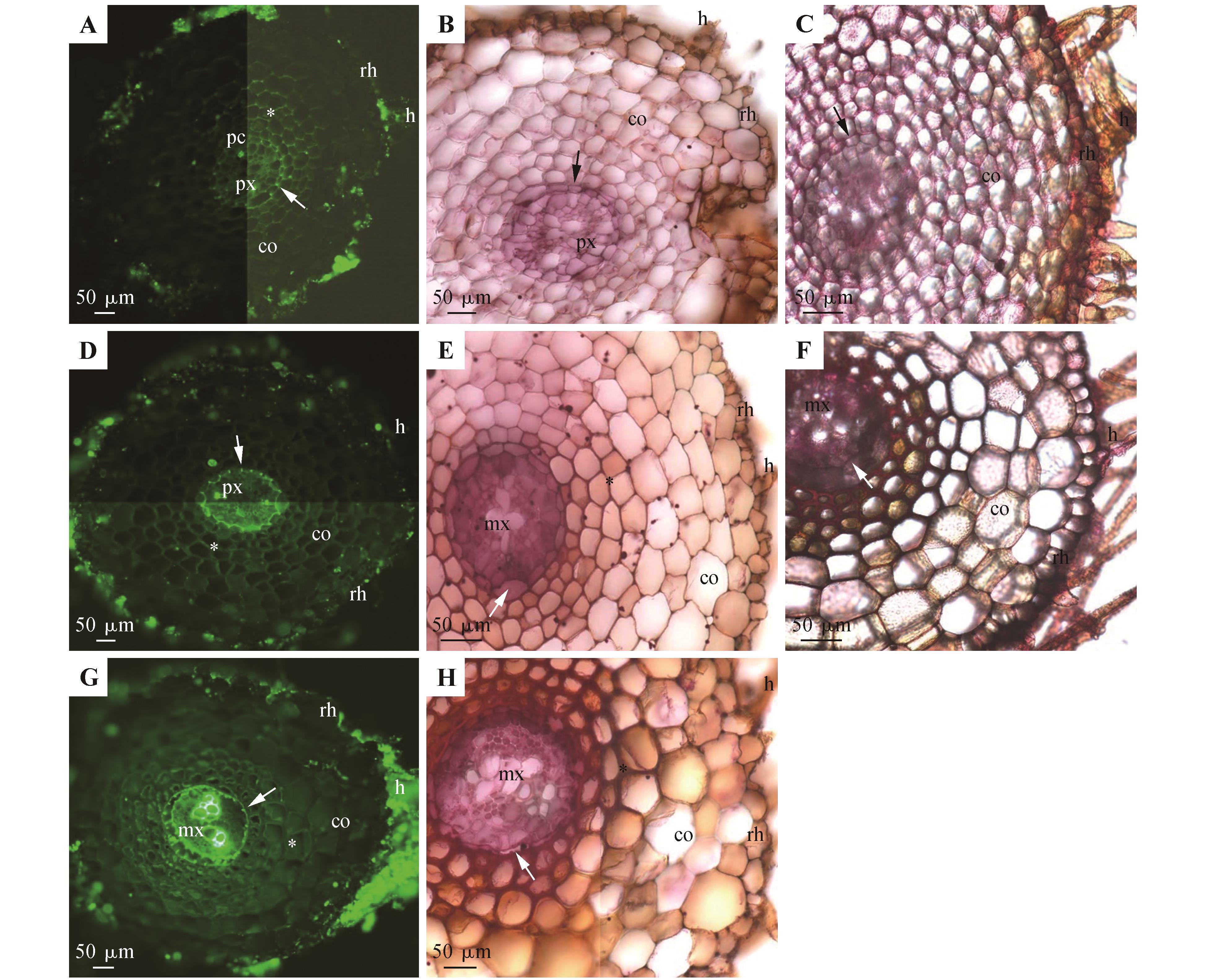
图2
蜈蚣草根的质外体通透性(长度20~50 mm)A~B.距根尖5 mm处;C~D.完整的根尖;E~H.距根尖10 mm处;I~L.距根尖20 mm处;A、E、L.未染色,明亮视野下观察;B、F、J.未染色,紫外光下自发荧光;C、G、K.用黄连素示踪剂处理并在紫外光下观察;D、H、L.用黄连素与KSCN溶液处理并在紫外光下观察;A.皮层,表皮,根毛;B.木质化增厚皮层(*);C.根尖显示出强烈的黄色荧光(箭头);黄连素染色下的根表皮表面和根毛(箭头);D.根尖显示出强烈的黄色荧光(箭头);黄连素与KSCN染色下的根表皮表面和根毛(箭头);E.木质化增厚皮层(*),皮层,表皮,根毛;F.原生木质部,木质化增厚皮层(*),根毛;G.原生木质部,木质化皮层(*),皮层;黄连素染色的根表皮和根毛;H.初生木质部,木质化增厚皮层(*),皮下层;硫氰酸黄连素染色的根表皮和根毛;I.木质化增厚皮层(*),皮层,表皮,根毛;J.原生木质部,内皮层(箭头),木质化增厚皮层(*);K.原生木质部,内皮层(箭头),木质化皮层(*),皮层;黄连素染色的根表皮和根毛;L.后生木质部,内皮层(箭头),木质化皮层(*),皮层;硫氰酸黄连素染色下的根表皮和根毛
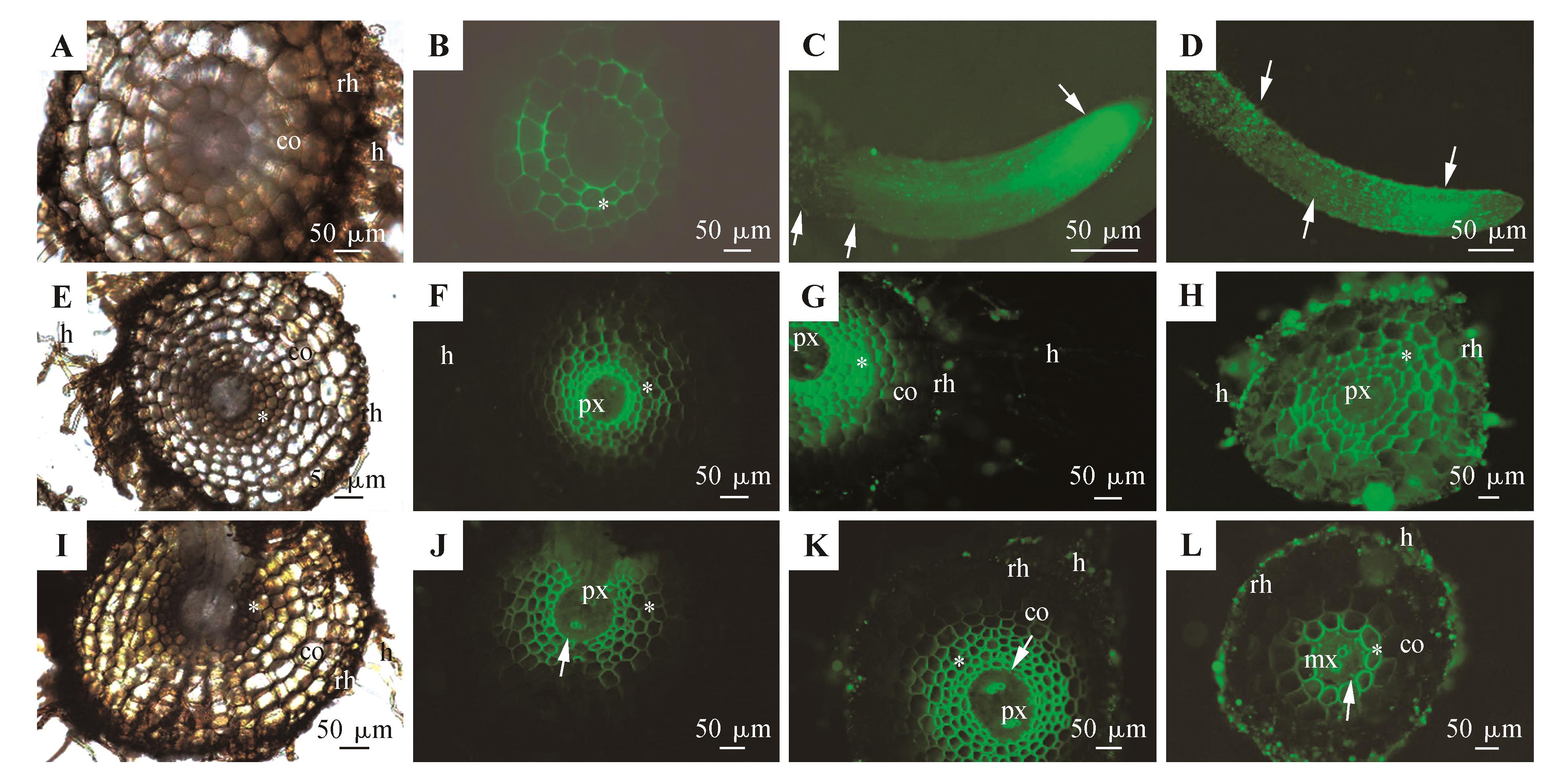
图4
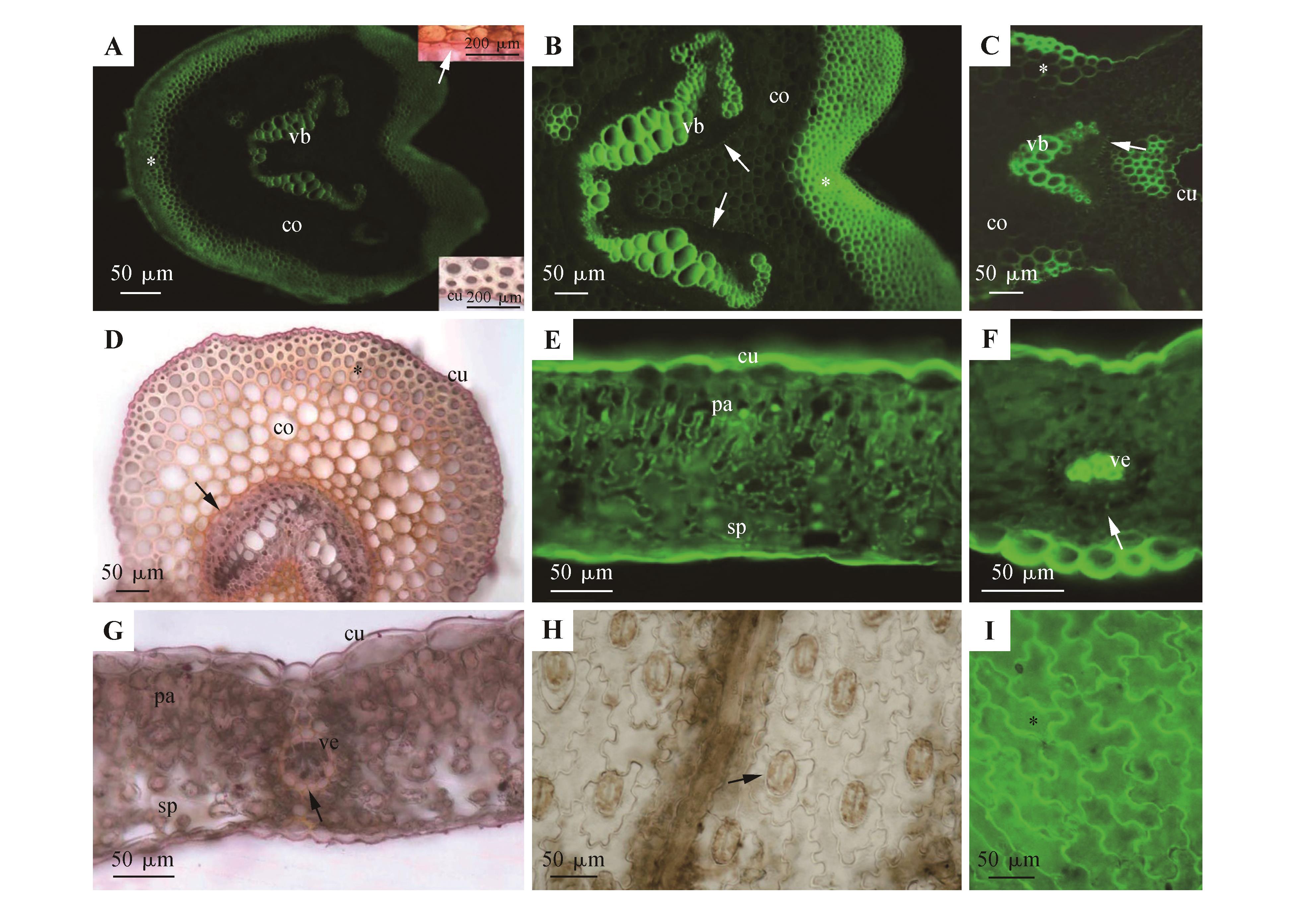
蜈蚣草成熟柄和叶的显微结构所有图片展示的均为硫酸氢黄连素-苯胺兰染色并置于紫外光下观察(除特殊说明);A.叶柄部分。维管束,皮层,外围厚壁组织层(*);上方插图展示了栓质化内皮层(箭头);下方插图展示了表皮表面的角质层;两张插图的样本均用苏丹红7B染色并再明亮视野下观察;B.图A中维管束,内皮层(箭头),皮层,外围厚壁组织层(*)的放大图;C.中央叶脉切面;维管束,内皮层(箭头),皮层,外围厚壁组织层(*),角质层;D.中央叶脉切面;维管束,内皮层(箭头),皮层,外围厚壁组织层(*),角质层。苏丹红7B染色并在明亮视野下观察;E.叶片部分,叶片正面向上;栅栏组织,海绵组织,角质层;F.叶片部分,叶片正面向上;细叶脉内皮层(箭头);G.叶片部分,叶片正面向上;栅栏组织,海绵组织,细叶脉,内皮层(箭头),角质层;苏丹7B染色,并在明亮视野下观察;H.叶片背面;气孔(箭头);无染色,在明亮视野下观察;I.叶片正面;表皮细胞(*)
| 1 | 张泽宏,吴小霞.5种蕨类植物叶片解剖结构及其对阴生环境的适应性研究[J].华中师范大学学报(自然科学版),2013,47(6):840-843. |
| ZHANG Z H, WU X X.Study on the anatomy structure of five species of fern leaves and its adaptability to sciophyte environment[J].Journal of Huazhong Normal University(Natural Sciences),2013,47(6):840-843. | |
| 2 | LOMBI E, ZHAO F J, FUHRMANN M,et al.Arsenic distribution and speciation in the fronds of the hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata [J].New Phytologist,2002,156(2):195-203. |
| 3 | CAILLE N, ZHAO F J, MCGRATH S P.Comparison of root absorption,translocation and tolerance of arsenic in the hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata and the nonhyperaccumulator Pteris tremula [J].New Phytologist,2005,165(3):755-761. |
| 4 | SU Y H, MCGRATH S P, ZHU Y G,et al.Highly efficient xylem transport of arsenite in the arsenic hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata [J].New Phytologist,2008,180(2):434-441. |
| 5 | WAGNER S, HOEFER C, PUSCHENREITER M,et al.Arsenic redox transformations and cycling in the rhizosphere of Pteris vittata and Pteris quadriaurita [J].Environmental and Experimental Botany,2020,177:104122. |
| 6 | ZHAO F J, DUNHAM S J, MCGRATH S P.Arsenic hyperaccumulation by different fern species[J].New Phytologist,2002,156(1):27-31. |
| 7 | DE OLIVEIRA L M, GRESS J, DE J,et al.Sulfate and chromate increased each other’s uptake and translocation in As-hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata [J].Chemosphere,2016,147:36-43. |
| 8 | SOURI Z, KARIMI N, SANDALIO L M.Arsenic hyperaccumulation strategies:an overview[J].Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology,2017,5:67. |
| 9 | WYLIE R B.Variations in leaf structure among ‘Adiantum pedatum plants growing in a rock cavern[J].American Journal of Botany,1949,36(3):282-287. |
| 10 | SRIDHAR B B M, HAN F X, DIEHL S V,et al.Effect of phytoaccumulation of arsenic and chromium on structural and ultrastructural changes of brake fern(Pteris vittata) [J].Brazilian Journal of Plant Physiology,2011,23(4):285-293. |
| 11 | MARTÍNEZ O G, VILTE I.The structure of petioles in Pteris(Pteridaceae)[J].American Fern Journal,2012,102(1):1-10. |
| 12 | ZHANG G M, LIAO W B, DING M Y,et al.Flora of China:Vol.2/3:Pteridaceae[M].Beijing:Science Press,2013:169-256. |
| 13 | NEIRA D A, ANDRADA A R, DE LOS ÁNGELES PÁEZ V,et al.Anatomical,histochemical and cytogenetic features of Doryopteris triphylla(Pteridaceae)[J].American Journal of Plant Sciences,2017,8(4):907-920. |
| 14 | SÂRBU A, SMARANDACHE D, MARINESCU A T,et al.Anatomical-histological observations conducted on aquatic ferns in the Danube Delta[J].Journal of Plant Development,2017,24:3-21. |
| 15 | WETZEL M L R, SYLVESTRE LDA S, BARROS C F,et al.Vegetative anatomy of Aspleniaceae Newman from Brazilian Atlantic rainforest and its application in taxonomy[J].Flora,2017,233:118-126. |
| 16 | GAAFAR A A, ALI S I, FARIED A M,et al.An insight into chemical content,biological effect and morphological features of Pteris vittata L.,rarely growing in Egypt[J].Research Journal of Chemistry and Environment,2018,22(10):47-55. |
| 17 | WU D, LI L B, MA X B,et al.Morphological and anatomical adaptations to dry,shady environments in Adiantum reniforme var.sinense(Pteridaceae)[J].PeerJ,2020,8:e9937. |
| 18 | KATO M, IMAICHI R.Morphological diversity and evolution of vegetative organs in pteridophytes[J].Evolution and Diversification of Land Plants,1997,27-43. |
| 19 | LI X, FANG Y H, YANG J,et al.Overview of the morphology,anatomy,and ontogeny of Adiantum capillus-veneris:an experimental system to study the development of ferns[J].Journal of Systematics and Evolution,2013,51(5):499-510. |
| 20 | VASCO A, MORAN R C, AMBROSE B A.The evolution,morphology,and development of fern leaves[J].Frontiers in Plant Science,2013,4:345. |
| 21 | PLACKETT A R G, DI STILIO V S, LANGDALE J A.Ferns:the missing link in shoot evolution and development[J].Frontiers in Plant Science,2015,6:972. |
| 22 | HARRISON C J, MORRIS J L.The origin and early evolution of vascular plant shoots and leaves[J].Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B-Biological Sciences,2018,373(1739):20160496. |
| 23 | HUIET L, LI F W, KAO T T,et al.A worldwide phylogeny of Adiantum(Pteridaceae) reveals remarkable convergent evolution in leaf blade architecture[J].TAXON,2018,67(3):488-502. |
| 24 | CHAPPLE C C S, PETERSON R L.Root structure in the fern Platycerium bifurcatum(Cav.) C.Chr.(Polypodiaceae)[J].Botanical Gazette,1987,148(2):180-187. |
| 25 | DAMUS M, PETERSON R L, ENSTONE D E,et al.Modifications of cortical cell walls in roots of seedless vascular plants[J].Botanica Acta,1997,110(2):190-195. |
| 26 | SCHNEIDER H.Root anatomy of Aspleniaceae and the implications for systematics of this fern family[J].Fern Gazette,1997,15:160-168. |
| 27 | HOSE E, CLARKSON D T, STEUDLE E,et al.The exodermis:a variable apoplastic barrier[J].Journal of Experimental Botany,2001,52(365):2245-2264. |
| 28 | ALBERSHEIM P, DARVILL A, ROBERTS K,et al.Plant cell walls:from chemistry to biology[M].New York:Garland Science,2011. |
| 29 | JOCA T A C, DE OLIVEIRA D C, ZOTZ G,et al.The velamen of epiphytic orchids:variation in structure and correlations with nutrient absorption[J].Flora,2017,230:66-74. |
| 30 | JOCA T A C, DE OLIVEIRA D C, ZOTZ G,et al.Chemical composition of cell walls in velamentous roots of epiphytic Orchidaceae[J].Protoplasma,2020,257(1):103-118. |
| 31 | RIBEIRO M L R C, SANTOS M G, MORAES M G.Leaf anatomy of two Anemia Sw.species(Schizaeaceae-Pteridophyte) from a rocky outcrop in Niterói,Rio de Janeiro,Brazil[J].Revista Brasileira de Botânica,2007,30(4):695-702. |
| 32 | DE LOS ÁNGELES LAGORIA M, AVILA G, NEIRA D A,et al.Morphoanatomical and histochemical characteristics of the epiphytic fern Pleopeltis macrocarpa(Polypodiaceae)[J].Brazilian Journal of Botany,2018,41(3):739-750. |
| 33 | MAHLEY J N, PITTERMANN J, NICK R,et al.Geometry,allometry and biomechanics of fern leaf petioles:their significance for the evolution of functional and ecological diversity within the Pteridaceae[J].Frontiers in Plant Science,2018,9:197. |
| 34 | PALACIOS-RÍOS M, GALÁN J M G Y, PRADA C,et al.Structure of the petioles and costae of Mexican and central American species of Pteris (Polypodiopsida,Pteridaceae) [J].Phytotaxa,2019,401(2):101-116. |
| 35 | HOLTTUM R E, OGURA Y.Comparative anatomy of vegetative organs of the pteridophytes[J].Kew Bulletin,1973,28(3):538. |
| 36 | LERSTEN N R.Occurrence of endodermis with a casparian strip in stem and leaf[J].The Botanical Review,1997,63(3):265-272. |
| 37 | ENSTONE D E, PETERSON C A, MA F S.Root endodermis and exodermis:structure,function,and responses to the environment[J].Journal of Plant Growth Regulation,2002,21(4):335-351. |
| 38 | HERNÁNDEZ-HERNÁNDEZ V, TERRAZAS T, MEHLTRETER K,et al.Studies of petiolar anatomy in ferns:structural diversity and systematic significance of the circumendodermal band[J].Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society,2012,169(4):596-610. |
| 39 | GELDNER N.The endodermis[J].Annual Review of Plant Biology,2013,64:531-558. |
| 40 | XIANG J Q, MING J J, YIN H Q,et al.Anatomy and histochemistry of the roots and shoots in the aquatic selenium hyperaccumulator Cardamine hupingshanensis(Brassicaceae)[J].Open Life Sciences,2019,14:318-326. |
| 41 | YANG C D, ZHANG X, ZHOU C Y,et al.Root and stem anatomy and histochemistry of four grasses from the Jianghan Floodplain along the Yangtze River,China[J].Flora,2011,206(7):653-661. |
| 42 | YANG C D, ZHANG X, LI J K,et al.Anatomy and histochemistry of roots and shoots in wild rice(Zizania latifolia Griseb.) [J].Journal of Botany,2014:181727. |
| 43 | YANG C D, YANG X L, ZHANG X,et al.Anatomical structures of alligator weed (Alternanthera philoxeroides) suggest it is well adapted to the aquatic-terrestrial transition zone[J].Flora,2019,253:27-34. |
| 44 | YANG C D, ZHANG X, WANG T,et al.Phenotypic plasticity in the structure of fine adventitious Metasequoia glyptostroboides roots allows adaptation to aquatic and terrestrial environments[J].Plants-Basel,2019,8(11):501. |
| 45 | YANG C D, ZHANG X, ZHANG F,et al.Structure and ion physiology of Brasenia schreberi glandular trichomes in vivo[J].PeerJ,2019,7:e7288. |
| 46 | YANG C D, ZHANG X, SEAGO J L,Jr.,et al.Anatomical and histochemical features of Brasenia schreberi(Cabombaceae) shoots[J].Flora,2020,263:151524. |
| 47 | ZHANG X, HU L J, YANG C D,et al.Structural features of Phalaris arundinacea in the Jianghan Floodplain of the Yangtze River,China[J].Flora,2017,229:100-106. |
| 48 | ZHANG X, YANG C D, SEAGO J L,Jr..Anatomical and histochemical traits of roots and stems of Artemisia lavandulaefolia and A.selengensis(Asteraceae) in the Jianghan Floodplain,China[J].Flora,2018,239:87-97. |
| 49 | SEAGO J L Jr.Revisiting the occurrence and evidence of endodermis in angiosperm shoots[J].Flora,2020,273:151709. |
| 50 | PECKOVÁ E, TYLOVÁ E, SOUKUP A.Tracing root permeability:comparison of tracer methods[J].Biologia Plantarum,2016,60(4):695-705. |
| 51 | LÓPEZ-PÉREZ L, FERNÁNDEZ-GARCÍA N, OLMOS E,et al.The phi thickening in roots of broccoli plants:an acclimation mechanism to salinity?[J].International Journal of Plant Sciences,2007,168(8):1141-1149. |
| 52 | FERNANDEZ-GARCIA N, LOPEZ-PEREZ L, HERNANDEZ M,et al.Role of phi cells and the endodermis under salt stress in Brassica oleracea [J].New Phytologist,2009,181(2):347-360. |
| 53 | ALEAMOTUA M, MCCURDY D W, COLLINGS D A.Phi thickenings in roots:novel secondary wall structures responsive to biotic and abiotic stresses[J].Journal of Experimental Botany,2019,70(18):4631-4642. |
| 54 | KOVÁČ J,LUX A, SOUKUP M,et al.A new insight on structural and some functional aspects of peri-endodermal thickenings,a specific layer in Noccaea caerulescens roots[J].Annals of Botany,2020,126(3):423-434. |
| 55 | RUZIN S E.Plant microtechnique and microscopy[M].New York:Oxford University Press,1999. |
| 56 | BRUNDRETT M C, KENDRICK B, PETERSON C A.Efficient lipid staining in plant material with Sudan red 7B or fluoral yellow 088 in polyethylene glycol-glycerol[J].Biotechnic & Histochemistry,1991,66(3):111-116. |
| 57 | BRUNDRETT M C, ENSTONE D E, PETERSON C A.A berberine-aniline blue fluorescent staining procedure for suberin,lignin,and callose in plant tissue[J].Protoplasma,1988,146:133-142. |
| 58 | SEAGO J L Jr, PETERSON C A, ENSTONE D E,et al.Development of the endodermis and hypodermis of Typha glauca Godr. and Typha angustifolia L.roots[J].Canadian Journal of Botany,1999,77(1):122-134. |
| 59 | PETERSON R L, PETERSON C A, MELVILLE L H.Teaching plant anatomy through creative laboratory exercises[M].Ottawa:NRC Press,2008:164. |
| 60 | MEYER C J, SEAGO J L,Jr., PETERSON C A.Environmental effects on the maturation of the endodermis and multiseriate exodermis of Iris germanica roots[J].Annals of Botany,2009,103(5):687-702. |
| 61 | MEYER C J, PETERSON C A.Casparian bands occur in the periderm of Pelargonium hortorum stem and root[J].Annals of Botany,2011,107(4):591-598. |
| 62 | FAHN A.Plant Anatomy[M].4th ed.Oxford:Pergamon Press,1990. |
| 63 | EVERT R F.Esau’s plant anatomy:meristems,cells,and tissues of the plant body:their structure,function,and development[M].3rd ed.Hoboken:Wiley-Interscience,2006. |
| 64 | CRANG R, LYONS-SOBASKI S, WISE R.Microscopy and imaging:a concept-based approach to the structure of seed plants[M].Plant Anatomy,2018. |
| 65 | LUNA M L, GANEM M A, GROSSI M A,et al.Root anatomy of 37 species of Asplenium(Aspleniaceae) from Argentina:contributions to the systematics and phylogeny of the genus[J].Flora,2020,272:151706. |
| 66 | BONDADA B, TU C, MA L.Surface structure and anatomical aspects of Chinese brake fern(Pteris vittata; Pteridaceae) [J].Brittonia,2006,58:217-228. |
| 67 | LEROUX O, BAGNIEWSKA-ZADWORNA A, RAMBE S K,et al.Non-lignified helical cell wall thickenings in root cortical cells of Aspleniaceae(Polypodiales):histology and taxonomical significance[J].Annals of Botany,2011,107(2):195-207. |
| 68 | HERNÁNDEZ M A, TERÁN L, MATA M,et al.Helical cell wall thickenings in root cortical cells of Polypodiaceae species from Northwestern Argentina[J].American Fern Journal,2013,103(4):225-240. |
| 69 | FENG S M, NING K, LUAN D,et al.Chemical composition and antioxidant capacities analysis of different parts of Brasenia schreberi [J].Journal of Food Processing and Preservation,2019,43(8):e14014. |
| 70 | TAO Q, LIU Y K, LI M,et al.Cd-induced difference in root characteristics along root apex contributes to variation in Cd uptake and accumulation between two contrasting ecotypes of Sedum alfredii [J].Chemosphere,2020,243:125290. |
| 71 | WARDLAW C W.Experimental and analytical studies of Pteridophytes:IV.Stelar morphology:experimental observations on the relation between leaf development and stelar morphology in species of Dryopteris and Onoclea [J].Annals of Botany,1944,8(4):387-388. |
| 72 | SRIVASTAVA A, CHANDRA S.Structure and organization of the rhizome vascular system of four Polypodium species[J].American Fern Journal,2009,99(3):182-193. |
| 73 | DEROIN T, RAKOTONDRAINIBE F.Comparative rhizome anatomy of some species of Ceradenia L.E.Bishop and Zygophlebia L.E.Bishop(Polypodiaceae,formerly Grammitidaceae) from Madagascar[J].Modern Phytomorphology,2015,7:5-12. |
| 74 | BECARI-VIANA I, SCHWARTSBURD P B.Morpho-anatomical studies and evolutionary interpretations of the rhizomes of extant Dennstaedtiaceae[J].American Fern Journal,2017,107(3):105-123. |
| 75 | NORAINI T,DAMANHURI.Taxonomic value of the stipe anatomy in Davallia(Davalliaceae) in Peninsular Malaysia[J].Malayan Nature Journal,2014,65(65):130-144. |
| 76 | NORAINI T, AMIRUL-AIMAN A J, JAMAN R,et al.Systematic significance of stipe anatomy in peninsular Malaysian Blechnum L.(Blechnaceae) species[J].Malaysian Applied Biology,2014,43(2):119-128. |
| 77 | 袁王俊,张维瑞,尚富德.黄连营养器官解剖结构与其阴生环境相关性研究[J].河南大学学报(自然科学版),2007,37(2):184-186. |
| YUAN W J, ZHANG W R, SHANG F D.Study on the anatomical structure of vegetative organs of Coptis chinensis and its pertinence to sciophyte conditions[J].Journal of Henan University(Natural Science),2007,37(2):184-186. | |
| 78 | DEMATTEIS B, SOLIS S M, YESILYURT J C,et al.Comparative anatomy in four Cheilanthoid ferns[J].Boletin de la Sociedad Argentina de Botanica,2019,54(2):203-214. |
| 79 | SHAH S N, AHMAD M, ZAFAR M,et al.Leaf micromorphological adaptations of resurrection ferns in Northern Pakistan[J].Flora,2019,255:1-10. |
| 80 | OLADIPO O T, PHILIP T V, BAMIGBOYE R A,et al.Morphology and anatomy of three species of Asplenium L.at Obafemi Awolowo University Ile-Ife,Nigeria[J].Ife Journal of Science,2020,22(1):65-73. |
| [1] | 周敏, 蒋丹, 刘玥秀, 王小蓉, 汤浩茹, 陈清. P119驱动amiRNA介导的PL基因沉默对草莓果实硬度的影响[J]. 植物研究, 2019, 39(3): 441-449. |
| [2] | 孟庆焕1;祖元刚1;王化2;王洪政1;姜涛3;吴薇薇1;钟晨1;段喜华1*. 酶法辅助乙醇优选牡丹种皮总黄酮[J]. 植物研究, 2015, 35(4): 628-631. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||