Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (5): 730-737.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2024.05.010
• Physiology and Ecology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xiting ZHANG1,2, Jianyu ZHANG3, Zhaoliang ZHONG4, Wenjie WANG5( )
)
Received:2024-04-22
Online:2024-09-20
Published:2024-09-23
Contact:
Wenjie WANG
E-mail:wwj225@nefu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Xiting ZHANG, Jianyu ZHANG, Zhaoliang ZHONG, Wenjie WANG. Characteristics of Plant Diversity in Chuona River Reserve, Daxing'anling Mountains[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(5): 730-737.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://bbr.nefu.edu.cn/EN/10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2024.05.010
Table 1
Stand structure in Chuona River Reserve
层次结构 Vertical structure | 指标 Index | 平均值 Mean | 中位数 Median | 标准误差 Standard error | 分布区间 Distribution interval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
乔木层 Arbor layer | 乔木树高TH/m | 15.29 | 15.41 | 0.29 | 10.78~19.07 |
| 乔木胸径TDBH/cm | 15.37 | 15.29 | 0.35 | 11.19~19.84 | |
| 乔木枝下高TCBH/m | 9.78 | 9.94 | 0.38 | 3.91~14.42 | |
| 郁闭度CD | 0.68 | 0.70 | 0.02 | 0.40~0.90 | |
| 乔木密度TD/(株·m-2) | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.01 | 0.05~0.21 | |
灌木层 Shrub layer | 灌木高度SH/m | 0.69 | 0.70 | 0.05 | 0.20~1.30 |
| 灌木地径SGD/cm | 1.13 | 1.11 | 0.05 | 0.51~1.77 | |
| 灌木冠幅 SCD/m2 | 0.25 | 0.22 | 0.04 | 0.13~1.14 | |
| 灌木盖度SC/% | 16.35 | 15.76 | 1.44 | 3.15~40.73 | |
| 灌木密度SD/(株·m-2) | 7.01 | 2.04 | 2.14 | 0.25~59.75 | |
草本层 Herb layer | 草本高度HH/cm | 28.98 | 27.00 | 1.35 | 17.40~49.83 |
| 草本盖度HC/% | 14.14 | 12.02 | 1.51 | 3.66~42.32 |
Table 2
Plant diversity in Chuona River Reserve
指标 Index | 平均值 Mean | 中位数 Median | 标准误差 Standard error | 25%中位数 25% median | 75%中位数 75% median | 最小50%区间 Minimum 50% range | 最大分布区间 Max interval | 分布区间 Distribution interval | 类型 Distribution type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
乔木丰富度T-R Tree richness | 3.97 | 4.00 | 0.20 | 3.00 | 5.00 | 3.00~4.00 | 5.00~65.00 | 2.00~7.00 | 多峰 Multimodal |
乔木Simpson指数T-D Tree Simpson index | 0.42 | 0.44 | 0.03 | 0.34 | 0.54 | 0.40~0.57 | 0.40~0.50 | 0.08~0.70 | 单峰 Unimodal |
乔木Shannon指数T-H′ Tree Shannon-Wiener index | 0.76 | 0.76 | 0.04 | 0.61 | 0.92 | 0.63~0.95 | 0.60~0.80 | 0.20~1.33 | 单峰 Unimodal |
乔木Pielou指数T-Ea Tree evenness index | 0.67 | 0.69 | 0.03 | 0.51 | 0.82 | 0.80~0.90 | 0.50~0.60 | 0.39~0.94 | 单峰 Unimodal |
灌木丰富度S-R Shrub richness | 2.66 | 3.00 | 0.19 | 2.00 | 3.00 | 2.00~3.00 | 3.00~4.00 | 1.00~5.00 | 单峰 Unimodal |
灌木Simpson指数S-D Shrub Simpson index | 0.35 | 0.46 | 0.04 | 0.10 | 0.53 | 0.42~0.57 | 0.40~0.50 | 0~0.66 | 多峰 Multimodal |
灌木Shannon指数S-H′ Shrub Shannon-Wiener index | 0.58 | 0.67 | 0.06 | 0.24 | 0.89 | 0.70~1.00 | 0.50~1.00 | 0~1.24 | 单峰 Unimodal |
灌木Pielou指数S-Ea Shrub evenness index | 0.73 | 0.78 | 0.04 | 0.61 | 0.91 | 0.73~1.00 | 0.90~1.00 | 0.38~1.00 | 单峰 Unimodal |
草本丰富度H-R Herb richness | 10.87 | 11.00 | 0.53 | 8.00 | 13.00 | 10.00~13.00 | 10.00~12.50 | 4.00~22.00 | 单峰 Unimodal |
草本Simpson指数H-D Herb Simpson index | 0.78 | 0.80 | 0.02 | 0.74 | 0.85 | 0.78~0.87 | 0.80~0.90 | 0.40~0.92 | 单峰 Unimodal |
草本Shannon指数H-H′ Herb Shannon-Wiener index | 1.89 | 1.94 | 0.06 | 1.72 | 2.14 | 1.75~2.10 | 1.75~2.00 | 0.89~2.66 | 单峰 Unimodal |
草本Pielou指数H-Ea Herb evenness index | 0.69 | 0.69 | 0.02 | 0.62 | 0.78 | 0.67~0.78 | 0.65~0.75 | 0.43~0.86 | 单峰 Unimodal |

Fig.2
Variance decomposition analysis among stand structure, site conditions and protection intensityTH.Tree height;TDBH.Tree diameter at breast height;TCBH.Tree clear branch height;SH.Shrub height;SGD.Shrub ground diameter;SCD.Shrub crown width;HH.Herb height;CD.Canopy density;SC.Shrub coverage;HC.Herb coverage;TD.Tree density;SD.Shrub density;SOC.Soil organic carbon;TN.Soil total nitrogen;TP.Soil total phosphorus;BD.Soil bulk density;MC.Soil moisture content;ASP.Aspect;LSP.Slope;PI. Protection intensity.
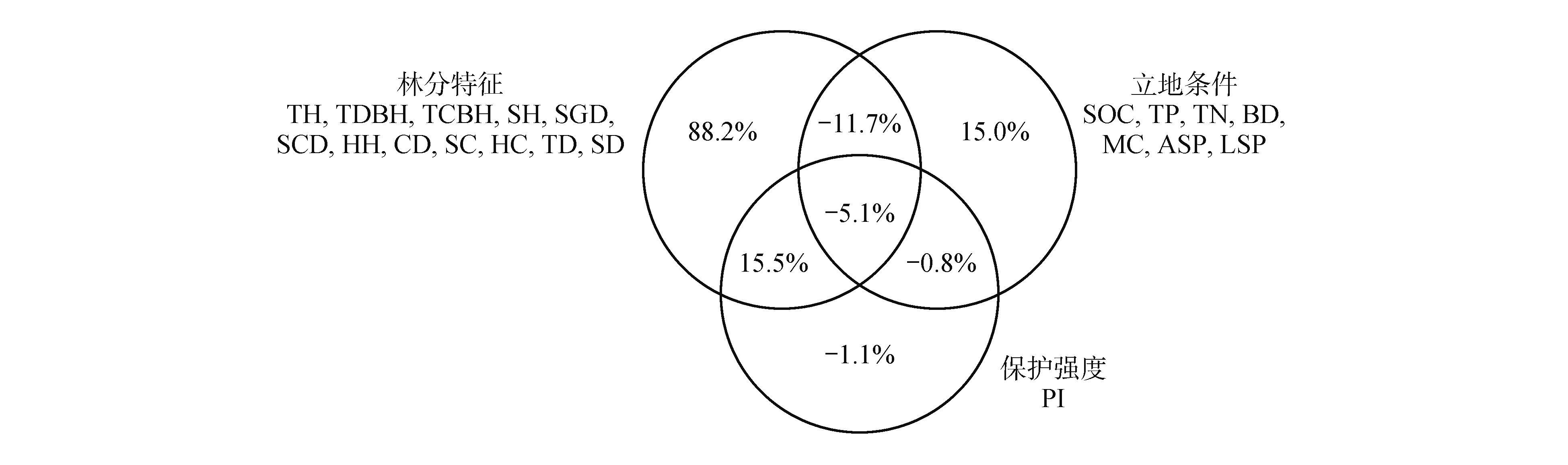
Table 3
Simple term effects and conditional term effects
简单效应 Simple term effects | 条件效应 Conditional term effects | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
项目 Item | 解释量 Explains/% | F | P | 项目 Item | 解释量 Explains/% | F | P |
| HC | 15.4 | 5.5 | 0.002 | HC | 15.4 | 5.5 | 0.002 |
| SD | 12.4 | 4.2 | 0.002 | SD | 11.7 | 4.6 | 0.006 |
| TH | 7.8 | 2.5 | 0.010 | TH | 8.1 | 3.5 | 0.004 |
| SH | 7.2 | 2.3 | 0.016 | BD | 4.6 | 2.2 | 0.038 |
| PI | 6.8 | 2.2 | 0.046 | HH | 4.8 | 2.1 | 0.052 |
| BD | 6.7 | 2.2 | 0.048 | SOC | 3.8 | 1.8 | 0.088 |
| TCBH | 6.0 | 1.9 | 0.080 | CD | 3.1 | 1.5 | 0.166 |
| SCD | 5.5 | 1.7 | 0.112 | TD | 3.4 | 1.7 | 0.122 |
| HH | 4.4 | 1.4 | 0.254 | SGD | 2.5 | 1.3 | 0.290 |
| TP | 4.3 | 1.3 | 0.278 | SH | 3.9 | 2.1 | 0.054 |
| SC | 4.0 | 1.3 | 0.254 | MC | 3.3 | 1.9 | 0.094 |
| ASP | 4.0 | 1.2 | 0.262 | SCD | 2.0 | 1.2 | 0.362 |
| SOC | 3.8 | 1.2 | 0.326 | ASP | 3.1 | 1.8 | 0.110 |
| CD | 3.5 | 1.1 | 0.364 | SLP | 2.5 | 1.5 | 0.204 |
| SGD | 3.0 | 0.9 | 0.440 | TP | 2.0 | 1.2 | 0.300 |
| MC | 2.6 | 0.8 | 0.580 | TDBH | 1.6 | 1.0 | 0.450 |
| TDBH | 2.1 | 0.6 | 0.706 | PI | 1.4 | 0.9 | 0.514 |
| TD | 2.1 | 0.6 | 0.722 | TN | 1.3 | 0.8 | 0.566 |
| TN | 2.0 | 0.6 | 0.706 | TCBH | 1.3 | 0.8 | 0.620 |
| SLP | 1.3 | 0.4 | 0.892 | SC | 0.1 | <0.1 | 1.000 |
| 1 | ZHENG L T, BARRY K E, GUERRERO-RAMÍREZ N R,et al.Effects of plant diversity on productivity strengthen over time due to trait-dependent shifts in species overyielding[J].Nature Communications,2024,15(1):2078. |
| 2 | ZUPPINGER-DINGLEY D, SCHMID B, PETERMANN J S,et al.Selection for niche differentiation in plant communities increases biodiversity effects[J].Nature,2014, 515(7525):108-111. |
| 3 | LIU D, WANG T, PEÑUELAS J,et al.Drought resistance enhanced by tree species diversity in global forests[J].Nature Geoscience,2022,15(10):800-804. |
| 4 | SCHNABEL F, LIU X J, KUNZ M,et al.Species richness stabilizes productivity via asynchrony and drought-tolerance diversity in a large-scale tree biodiversity experiment[J].Science Advances,2021,7(51):eabk1643. |
| 5 | 覃海宁,赵莉娜.中国高等植物濒危状况评估[J].生物多样性,2017,25(7):689-695. |
| QIN H N, ZHAO L N.Evaluating the threat status of higher plants in China[J].Biodiversity Science,2017,25(7):689-695. | |
| 6 | 张喜亭,张建宇,李斯雯,等.大兴安岭双河保护区植物多样性和群落结构特征分析[J].北京林业大学学报,2021,43(7):79-87. |
| ZHANG X T, ZHANG J Y, LI S W,et al.Characteristics of plant diversity and community structure in Shuanghe Nature Reserve in Daxing'anling area of northeastern China[J].Journal of Beijing Forestry University,2021,43(7):79-87. | |
| 7 | 杜寿康,唐国勇,刘云根,等.不同立地环境下金沙江干热河谷各区段植物多样性[J].浙江农林大学学报,2022,39(4):742-749. |
| DU S K, TANG G Y, LIU Y G,et al.Plant diversity in various sections of Jinsha River dry-hot valley under different site environments[J].Journal of Zhejiang A & F University,2022,39(4):742-749. | |
| 8 | MA M J, BASKIN C C, YU K L,et al.Wetland drying indirectly influences plant community and seed bank diversity through soil pH[J].Ecological Indicators,2017,80:186-195. |
| 9 | 佘丹琦,张喜亭,肖路,等.小兴安岭凉水国家级自然保护区植物beta多样性及其影响因素[J].生物多样性,2022,30(3):21274. |
| SHE D Q, ZHANG X T, XIAO L,et al.Plant beta diversity and its influence factors in the Liangshui National Nature Reserve in the central region of the Xiaoxing’an Mountains[J].Biodiversity Science,2022,30(3):21274. | |
| 10 | 刘杰,罗亚皇,李德铢,等.青藏高原及毗邻区植物多样性演化与维持机制:进展及展望[J].生物多样性,2017,25(2):163-174. |
| LIU J, LUO Y H, LI D Z,et al.Evolution and maintenance mechanisms of plant diversity in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and adjacent regions:retrospect and prospect[J].Biodiversity Science,2017,25(2):163-174. | |
| 11 | 庄凯勋,王淑芳,侯武才.大兴安岭东部林区自然保护区林火问题的探讨[J].森林防火,2005(4):9-12. |
| ZHUANG K X, WANG S F, HOU W C.Discussion on forest fire issues in the nature reserve of the eastern region of the Daxing’an Mountains[J].Journal of Wildland Fire Science,2005(4):9-12. | |
| 12 | 马克平,刘玉明.生物群落多样性的测度方法Ⅰ α多样性的测度方法(下)[J].生物多样性,1994,2(4):231-239. |
| MA K P, LIU Y M.Measurement of biotic community diversity I α diversity(Part 2)[J].Biodiversity Science,1994,2(4):231-239. | |
| 13 | WANG Q, WANG W J, HE X Y,et al.Urbanization-induced glomalin changes and their associations with land-use configuration,forest characteristics,and soil properties in Changchun,Northeast China[J].Journal of Soils and Sediments,2019,19(5):2433-2444. |
| 14 | 孙玉成,张喜亭,季倩如,等.大兴安岭泰加林植物多样性特征调查与分析[J].林业资源管理,2022(6):124-130. |
| SUN Y C, ZHANG X T, JI Q R,et al.Survey and analysis of Taiga forest plant diversity features in Daxing’anling Mts[J].Forest Resources Management,2022(6):124-130. | |
| 15 | 张建宇.大兴安岭森林植物多样性、群落结构特征及耦合关系分析[D].哈尔滨:东北林业大学,2018. |
| ZHANG J Y.Characteristics of plant diversity and community structure in Daxing'anling forests and association analysis[D].Harbin:Northeast Forestry University,2018. | |
| 16 | 张云.黑龙江省绰纳河湿地自然资源现状分析[J].现代化农业,2014(7):29-30. |
| ZHANG Y.Analysis of the current situation of Natural Resources in Chuona River Wetland in Heilongjiang Province[J].Modernizing Agriculture,2014(7):29-30. | |
| 17 | 张建宇,王文杰,杜红居,等.大兴安岭呼中地区3种林分的群落特征、物种多样性差异及其耦合关系[J].生态学报,2018,38(13):4684-4693. |
| ZHANG J Y, WANG W J, DU H J,et al.Differences in community characteristics,species diversity,and their coupling associations among three forest types in the Huzhong area,Daxing’anling Mountains[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2018,38(13):4684-4693. | |
| 18 | 拓行行,李玉华,俞瀚林,等.宁南山区华北落叶松林下草本层群落特征及其影响因素[J].生态学杂志,2023,42(10):2449-2458. |
| TUO H H, LI Y H, YU H L,et al.Community characteristics and influencing factors of herbaceous layer under Larix gmelinii var.principis-rupprechtii forests in a south mountainous area of Ningxia[J].Chinese Journal of Ecology,2023,42(10):2449-2458. | |
| 19 | 姜倪皓,张诗函.楚雄市西郊云南松林下草本优势种种间联结及环境解释[J].生态环境学报,2021,30(11):2109-2120. |
| JIANG N H, ZHANG S H.Interspecific association and environmental interpretation of dominant herbaceous species in Pinus yunnanensis forest in the western suburbs of Chuxiong City[J].Ecology and Environmental Sciences,2021,30(11):2109-2120. | |
| 20 | XU W H, XIAO Y, ZHANG J J,et al.Strengthening protected areas for biodiversity and ecosystem services in China[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2017,114(7):1601-1606. |
| [1] | Xi ZHEN, Xuyang LIU, Wenjie LI, Feng ZHANG, Yue SU, Yao XIAO, Jie ZHANG, Tao WAN. Characteristics of Apocynum venetum Community and Its Relationship to Climatic Factors [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(3): 448-458. |
| [2] | Zhiwen ZHANG, Hongchao BAI, Zheng LIU, Wenguang LI, Gang YANG, Baojiang ZHENG. Species Diversity and Distribution Pattern of Wild Ribes in Northeast China [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(2): 192-199. |
| [3] | Yanli WEN, Rong LI. Diversity Pattern and Conservation of Monocotyledon in Yunnan,China [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(2): 200-209. |
| [4] | Yuqi MA, Yuhui LI, Lin LIN, Yue SHEN, Yufeng GU, Faguo WANG. Phyto-community Characteristics of the Dependent Environment of Dipteris shenzhenensis [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(1): 34-44. |
| [5] | Mingyang CONG, Yongkun LI, Wenjing YANG, Puqing CHEN. Bryophyte Diversity of Underground Forests in Craters of Jingpohu Global Geopark [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(3): 361-369. |
| [6] | Fengling YIN, Minxia LIU, Cheng LIU, Mingxing WANG, Ke XI. Effects of Single-household and Multi-household Management on Soil Physicochemical Properties and Plant Diversity in Alpine Meadow [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(2): 261-271. |
| [7] | Min WANG, Run-Hui ZHOU, Fei-Yan YU, Hong-Jun DONG, Cong-Lin CHEN, Jing YU, Jian-Feng HAO. Dynamic Changes of Undergrowth Species Diversity and Biomass of Eucalyptus robusta Plantations at Different Ages [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(4): 496-505. |
| [8] | CONG Ming-Yang, TANG Lu-Yan, LI Jin-Jiang, ZHANG Mei-Ping, CHEN Bao-Zheng, XU Yue-Yue. Species Diversity of Bryophytes in Miyagi Relics of Shangjing Longquanfu,Parhai State,China [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2019, 39(2): 229-238. |
| [9] | ZHANG Xiao-Yue, QI Jin-Qiu, ZHANG Liu-Hua, WANG Mei-Zhen, LI Ting-Ting, YU Shun-Yao, HAO Jian-Feng. Effects of Human Disturbance on Species Diversity and Soil Physical and Chemical Properties of Revetment Forest in Wenjiang Section of the Jinma River [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2019, 39(1): 78-86. |
| [10] | DUAN Yi-Zhong, DU Zhong-Yu, KANG Fu-Ren. Community Characteristics of Endangered Plant of Ammopiptanthus mongolicus to Environmental Factors in Northwest Arid Area of China [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2018, 38(6): 834-842. |
| [11] | WU Ping-Ping. Species Diversity of Carpinus cordata Communities in Lishan Nature Reserve,Shanxi Province [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2018, 38(2): 195-200. |
| [12] | HAN Shu-Ting, TIAN Gui-Quan, HAN Shu-Mei. Species Diversity of Ground Bryophyte Communities in Different Vegetation in Daqinggou National Nature Reserve [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2017, 37(5): 664-672. |
| [13] | CONG Ming-Yang, CAO Di, CHEN Guo-Ping, CHEN Bao-Zheng, SUN Feng-Bin. Vertical Characteristics of Plant Diversity in Transition Between Mount. Yan and Mount. Taihang [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2017, 37(5): 673-681. |
| [14] | HONG Xia, TIAN Gui-Quan, WU Ri-Gumala. Species Diversity of Ground Bryophyte Communities in Junger Loess Hill-Cully Region in Inner Mongolia [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2016, 36(5): 712-720. |
| [15] | DU Jing-Qi, ZHANG Qiao-Xian, TIAN Xiao-Dong, WANG Yue, XU Xin-Yun, SONG Li, YUAN Zi-Qiang. Relationships between Vegetation Distribution, Species Diversity of Subalpine Meadow and Soil Chemical Factors in the Yundingshan, China [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2016, 36(3): 444-451. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||