Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (2): 224-233.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2022.02.007
• Molecular biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Zhen Wang1, Liuyan Yang1, Weizhong Pei2, Xin Li1, Zhen Yang1, Yongchun Zhang1( )
)
Received:2020-08-15
Online:2022-03-20
Published:2022-02-22
Contact:
Yongchun Zhang
E-mail:saasflower@163.com
About author:Wang Zhen(1986—),female,research associate,Ph.D,mainly engaged in flowering breeding and molecular biology.
Supported by:CLC Number:
Zhen Wang, Liuyan Yang, Weizhong Pei, Xin Li, Zhen Yang, Yongchun Zhang. Expression and Functional Analysis of FT Homologous Genes in Saffron(Crocus sativus L.)[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(2): 224-233.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://bbr.nefu.edu.cn/EN/10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2022.02.007
Table 1
Gene specific primers used to isolate complete FT coding sequences of saffron
名称 Name | 正向引物 Forward primer(5′—3′) | 反向引物 Reverse primer(5′—3′) |
|---|---|---|
| CsatFT1 | CCG | CG |
| CsatFT2 | GC | CCG |
| CsatFT3 | CCG | GG |
Table 2
Gene specific primers used for qRT-PCR analysis
名称 Name | 正向引物 Forward primer(5′—3′) | 反向引物 Reverse primer(5′—3′) |
|---|---|---|
| CsatGAPDH | ATAGCTTATTATTAGACGGA | CTCAAGGGAATCATGGGCT |
| CsatFT1 | AATGAGTAGGGATTCGCTGGTG | GCGGGTTACTTGGATTTGGA |
| CsatFT2 | AGAGTCCACGACCGTCGCTC | TAAATCCTTCTCCCACCGCA |
| CsatFT3 | GTTTATTACAACTGCCAGAGGGAG | AAGGCTTTGGAAGAATGATTTCAAG |
Table 3
Gene specific primers used for RT-PCR analysis
名称 Name | 正向引物 Forward primer(5′—3′) | 反向引物 Reverse primer(5′—3′) | 长度 Length /bp |
|---|---|---|---|
| NtEF1α | GAGGCACTTCCTGGTGACAAT | GGGCTCCTTCTCAATCTCCTTAC | 273 |
| AtEF1α | CAAGATGGATGCCACTACCC | AGTGGGAGACGAAGGGGCT | 255 |
| CsatFT1 | ATTCGCTGGTGCTCGGTAG | CCTCAGATGCGGGTTACTTG | 230 |
| CsatFT2 | GGTCGGAAATGGATGTGAG | CTCTCGTAGCACACAATCTCCTG | 222 |
| CsatFT3 | GAGATTGGTGGCTGTGACTAT | TGCTGGAACAGGATAAACACG | 218 |
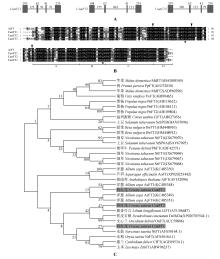
Fig.1
Gene structures and alignment of amino acid sequences and phylogenetic analysis of CsatFT homologs of saffronA.Gene structures of FT;Boxes indicate exons and lines indicate introns,the numbers represent their corresponding lengths(bp);B.Alignment of amino acid sequences of FT homologs;Boxes and asterisks represent the conserved residues;Triangles show the exon boundaries of FT of Arabidopsis.The four segments of the fourth exon are shown as A,B,C and D[25];C.Phylogenetic analysis of the FT homologs from different plant species.Grey boxes represent three FT genes of saffron,CsatFT1,CsatFT2 and CsatFT3
Table 4
Flowering phenotypes of representative T0 transgenic tobacco lines harboring FT homologs of saffron
数量 No. | 开花时主杆叶片数量 No. leaves on main stem at flowering | 现蕾时植株高度 Plant height at first flower bud /cm | 从移栽到现蕾的时间 Time between transformed plantlet regeneration and first flower bud /d | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wt | 6 | 13.70±1.34a | 29.10±1.86b | 68.10±1.86a |
| 35S::CsatFT1 | 25 | 13.20±1.40a | 32.00±3.20a | 59.90±3.21c |
| 35S::CsatFT2 | 20 | 13.10±1.20a | 32.30±2.91a | 61.80±3.79b |
| 35S::CsatFT3 | 25 | 12.50±1.35a | 28.90±2.85b | 59.50±2.37c |
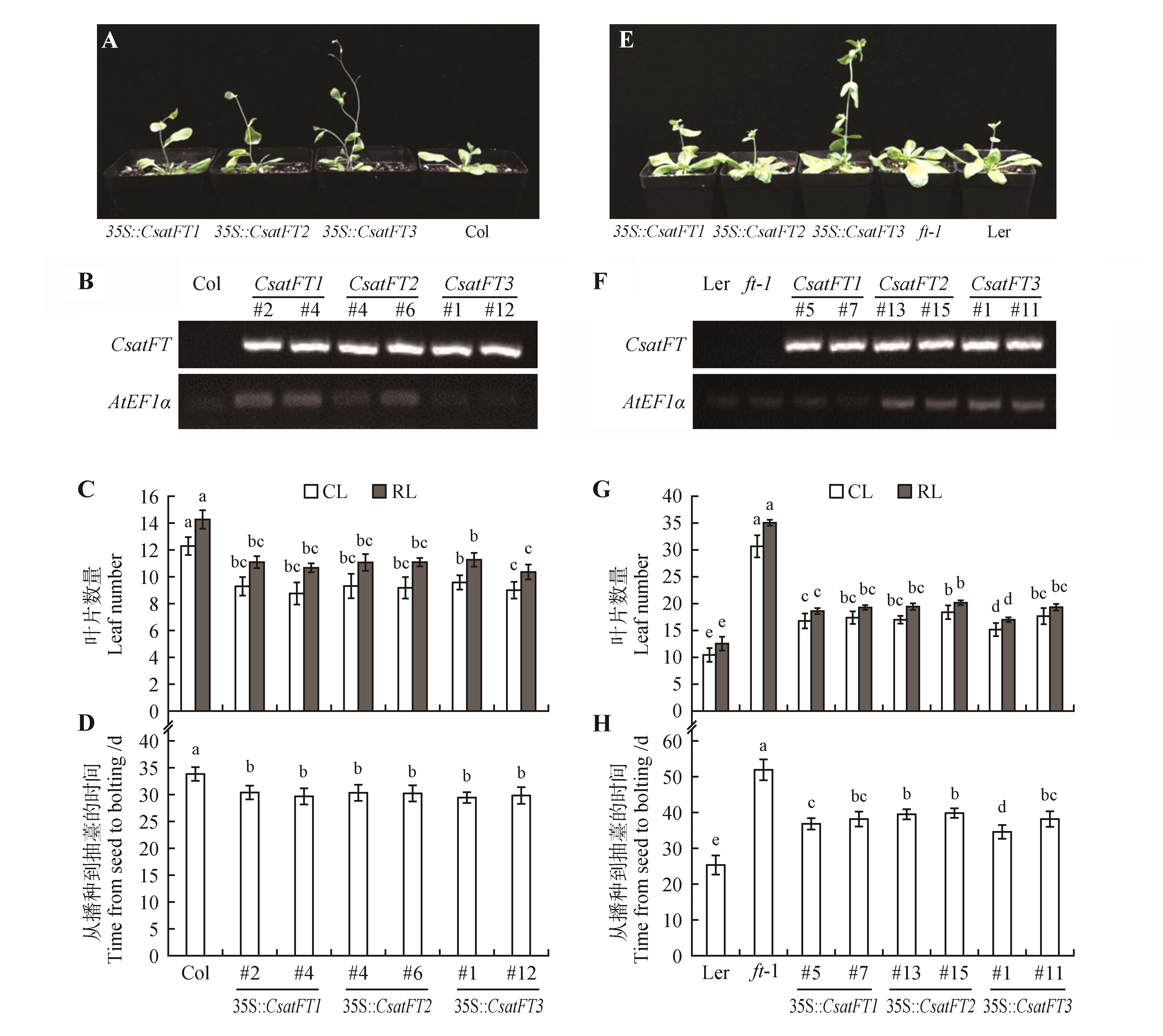
Fig.4
Phenotypic analysis of ectopically expressing CsatFT homologs of saffron in the Col and ft-1 mutantsA. 30-day-old 35S::CsatFT1,35S::CsatFT2,35S::CsatFT3,Col Arabidopsis;B. RT-PCR analysis to conform the transgenic lines;C. Leaf number of wild-type Col and transgenic Arabidopsis plants under LD(16 h-light/8 h-dark) conditions;D. Time from seed to bolting of wild-type Col and transgenic Arabidopsis plants under LD(16 h-light/8 h-dark) conditions;E. Phenotype of ectopically expressing FT homologs of saffron in ft-1 mutant;F. RT-PCR analysis to conform the transgenic lines;G. Leaf number of wild-type Ler,ft-1 and transgenic Arabidopsis plants under LD(16 h-light/8 h-dark) conditions;H. Time from seed to bolting of wild-type Ler,ft-1 and transgenic Arabidopsis plants under LD(16 h-light/8 h-dark) conditions;CL.Cauline leaves;RL.Rosette leaves;The common letters within the same figures are not significantly different at P=0.05
| 1 | Amasino R.Seasonal and developmental timing of flowering[J].The Plant Journal,2010,61(6):1001-1013. |
| 2 | Fornara F,De Montaigu A,Coupland G.SnapShot:control of flowering in Arabidopsis[J].Cell,2010,141:550.e1-550.e2. |
| 3 | Corbesier L,Vincent C,Jang S,et al.FT protein movement contributes to long-distance signaling in floral induction of Arabidopsis[J].Science,2007,316(5827):1030-1033. |
| 4 | Tamaki S,Matsuo S,Wong H L,et al.Hd3a protein is a mobile flowering signal in rice[J].Science,2007,316(5827):1033-1036. |
| 5 | Abe M,Kobayashi Y,Yamamoto S,et al.FD,a bZIP protein mediating signals from the floral pathway integrator FT at the shoot apex[J].Science,2005,309(5737):1052-1056. |
| 6 | Wigge P A,Kim M C,Jaeger K E,et al.Integration of spatial and temporal information during floral induction in Arabidopsis[J].Science,2005,309(5737):1056-1059. |
| 7 | Carmona M J,Calonje M,Martínez-Zapater J M.The FT/TFL1 gene family in grapevine[J].Plant Molecular Biology,2007,63(5):637-650. |
| 8 | Danilevskaya O N,Meng X,Hou Z L,et al.A genomic and expression compendium of the expanded PEBP gene family from maize[J].Plant Physiology,2008,146(1):250-264. |
| 9 | Sato H,Heang D,Sassa H,et al.Identification and characterization of FT/TFL1 gene family in cucumber[J].Breeding Science,2009,59(1):3-11. |
| 10 | Kotoda N,Hayashi H,Suzuki M,et al.Molecular characterization of FLOWERING LOCUS T-like genes of apple (Malus × domestica Borkh.)[J].Plant and Cell Physiology,2010,51(4):561-575. |
| 11 | Navarro C,Abelenda J A,Cruz-Oró E,et al.Control of flowering and storage organ formation in potato by FLOWERING LOCUS T[J].Nature,2011,478(7367):119-122. |
| 12 | Hsu C Y,Liu Y X,Luthe D S,et al.Poplar FT2 shortens the juvenile phase and promotes seasonal flowering[J].The Plant Cell,2006,18(8):1846-1861. |
| 13 | Hsu C Y,Adams J P,Kim H,et al.FLOWERING LOCUS T duplication coordinates reproductive and vegetative growth in perennial poplar[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2011,108(26):10756-10761. |
| 14 | Leeggangers H A C F,Rosilio-Brami T,Bigas-Nadal J,et al.Tulipa gesneriana and Lilium longiflorum PEBP genes and their putative roles in flowering time control[J].Plant and Cell Physiology,2018,59(1):90-106. |
| 15 | 王桢,周琳,杨贞,等.番红花子球茎膨大过程中主要营养物质和植物激素的动态变化[J].植物生理学报,2019,55(9):1306-1314. |
| Wang Z,Zhou L,Yang Z,et al.Study on replacement corm enlargement of Crocus sativus and the dynamic changes in major nutriments and phytohormones during the vegetative development[J].Plant Physiology Journal,2019,55(9):1306-1314. | |
| 16 | 王桢,李心,李青竹,等.不同温度调控下西红花花芽分化进程及内源激素动态变化[J].西北农林科技大学学报:自然科学版,2021,49(4):102-112. |
| Wang Z,Li X,Li Q Z,et al.Process of floral bud differentiation and dynamic changes of endogenous hormones under different temperatures in saffron(Crocus sativus L.)[J].Journal of Northwest A&F University:Natural Science Edition,2021,49(4):102-112. | |
| 17 | Tsaftaris A S,Pasentsis K,Polidoros A N.Isolation of a differentially spliced C-type flower specific AG-like MADS-box gene from Crocus sativus and characterization of its expression[J].Biologia Plantarum,2005,49(4):499-504. |
| 18 | Tsaftaris A S,Polidoros A N,Pasentsis K,et al.Cloning,structural characterization,and phylogenetic analysis of flower MADS-box genes from crocus(Crocus sativus L.)[J].The Scientific World Journal,2007,7:1047-1062. |
| 19 | Tsaftaris A,Pasentsis K,Argiriou A.Cloning and characterization of FLOWERING LOCUS T-like genes from the perennial geophyte saffron crocus(Crocus sativus)[J].Plant Molecular Biology Reporter,2013,31(6):1558-1568. |
| 20 | 王桢.蔷薇科和矮牵牛开花基因FT/TFL1和SOC1功能的保守性与分化性研究[D].武汉:华中农业大学,2017. |
| Wang Z.Research of conserved and diverse functions of flowering related genes FT/TFL1 and SOC1 in rosacese and petunia[D].Wuhan:Huazhong Agricultural University,2017. | |
| 21 | Schmittgen T D,Livak K J.Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method[J].Nature Protocols,2008,3(6):1101-1108. |
| 22 | Tamura K,Peterson D,Peterson N,et al.MEGA5:molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood,evolutionary distance,and maximum parsimony methods[J].Molecular Biology and Evolution,2011,28(10):2731-2739. |
| 23 | Li X F,Jia L Y,Xu J,et al.FT-like NFT1 gene may play a role in flower transition induced by heat accumulation in Narcissus tazetta var.chinensis[J].Plant and Cell Physiology,2013,54(2):270-281. |
| 24 | Lee R,Baldwin S,Kenel F,et al.FLOWERING LOCUS T genes control onion bulb formation and flowering[J].Nature Communications,2013,4:2884. |
| 25 | Ahn J H,Miller D,Winter V J,et al.A divergent external loop confers antagonistic activity on floral regulators FT and TFL1[J].The EMBO Journal,2006,25(3):605-614. |
| 26 | Hiraoka K,Yamaguchi A,Abe M,et al.The florigen genes FT and TSF modulate lateral shoot outgrowth in Arabidopsis thaliana[J].Plant and Cell Physiology,2013,54(3):352-368. |
| 27 | Kinoshita T,Ono N,Hayashi Y,et al.FLOWERING LOCUS T regulates stomatal opening[J].Current Biology,2011,21(14):1232-1238. |
| 28 | Pin P A,Benlloch R,Bonnet D,et al.An antagonistic pair of FT homologs mediates the control of flowering time in sugar beet[J].Science,2010,330(6009):1397-1400. |
| 29 | Harig L,Beinecke F A,Oltmanns J,et al.Proteins from the FLOWERING LOCUS T-like subclade of the PEBP family act antagonistically to regulate floral initiation in tobacco[J].The Plant Journal,2012,72(6):908-921. |
| 30 | Heller W P,Ying Z T,Davenport T L,et al.Identification of members of the Dimocarpus longan flowering locus T gene family with divergent functions in flowering[J].Tropical Plant Biology,2014,7(1):19-29. |
| 31 | Hanzawa Y,Money T,Bradley D.A single amino acid converts a repressor to an activator of flowering[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2005,102(21):7748-7753. |
| 32 | Wang Z,Yang R G,Devisetty U K,et al.The divergence of flowering time modulated by FT/TFL1 is independent to their interaction and binding activities[J].Frontiers in Plant Science,2017,8:697. |
| 33 | Takada S,Goto K.TERMINAL FLOWER2,an Arabidopsis homolog of HETEROCHROMATIN PROTEIN1,counteracts the activation of Flowering Locus T by CONSTANS in the vascular tissues of leaves to regulate flowering time[J].The Plant Cell,2003,15(12):2856-2865. |
| [1] | WU Qi-Yao;WEI Chuan-Bao*;LI Jin-Hua. Prokaryotic Expression of TFMV,FVY and LMoV CP Gene,Antiserum Preparation and Virus Detection [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2013, 33(1): 73-79. |
| [2] | GAO Bin;ZHANG Hai-Yan;FAN Hai*. Expression,Purification and Immunoreactivity of Hygromycin-B-Phosphotransferase [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2011, 31(1): 56-60. |
| [3] | CHEN Peng-Fei;LIU Xue-Mei;*;SONG Fu-Nan;SONG Xing-Shun;LIU Ni;JIN Wei-Wei;LIU Wei. Cloning and Sequence Analysis of Full-length cDNA of Actin Gene from Birch(Betula platyphylla Suk.) [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2009, 29(3): 339-345. |
| [4] | MA Chun-Quan;ZHANG Ying;CUI Ying;WANG Bing;WANG Yu-Ting;LIU Jin-Ling;WANG Hong-Jian;LI Hai-Ying*. Construction of cDNA Library in Florescence and Screening Specifically Expressed Genes in Sugar Beet M14 [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2008, 28(4): 408-411. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||