Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (2): 207-217.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2023.02.006
• Physiology and Ecology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Tingting LI, Liu YANG, Xiaoxia LI, Yisong WANG, Xiuwei WANG( )
)
Received:2022-09-01
Online:2023-03-20
Published:2023-03-07
Contact:
Xiuwei WANG
E-mail:wxgreat@nefu.edu.cn
About author:LI Tingting(1993—),female,postgraduate,major in plant ecophysiology.
Supported by:CLC Number:
Tingting LI, Liu YANG, Xiaoxia LI, Yisong WANG, Xiuwei WANG. Different Nitrogen Forms on the Photosynthetic Characteristics and Growth of Fraxinus mandshurica and Quercus mongolica[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(2): 207-217.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://bbr.nefu.edu.cn/EN/10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2023.02.006
Table 1
Effects of different treatments and species types on seedling growth traits and photosynthetic parameters( P value)
指标 Index | 氮处理 Treatment | 树种 Species | 氮处理×树种 Treatment×Species |
|---|---|---|---|
最大净光合速率 Maximum net photosynthetic rate | * | ** | * |
气孔导度 Stomatal conductance | ** | 0.107 | 0.749 |
胞间CO2摩尔分数 Intercellular CO2 concentration | * | 0.942 | 0.111 |
蒸腾速率 Transpiration rate | 0.089 | * | 0.408 |
表观量子效率 Apparent photosynthetic quantum efficiency | 0.079 | 0.513 | ** |
光饱和点 Light saturation point | 0.840 | * | 0.057 |
叶氮质量分数 N Contects | *** | *** | *** |
株高 Plant height | * | 0.889 | 0.999 |
地径 Ground diameter | ** | *** | * |
光合氮素利用效率 Photosynthetic nitrogen utilization efficiency | *** | *** | *** |

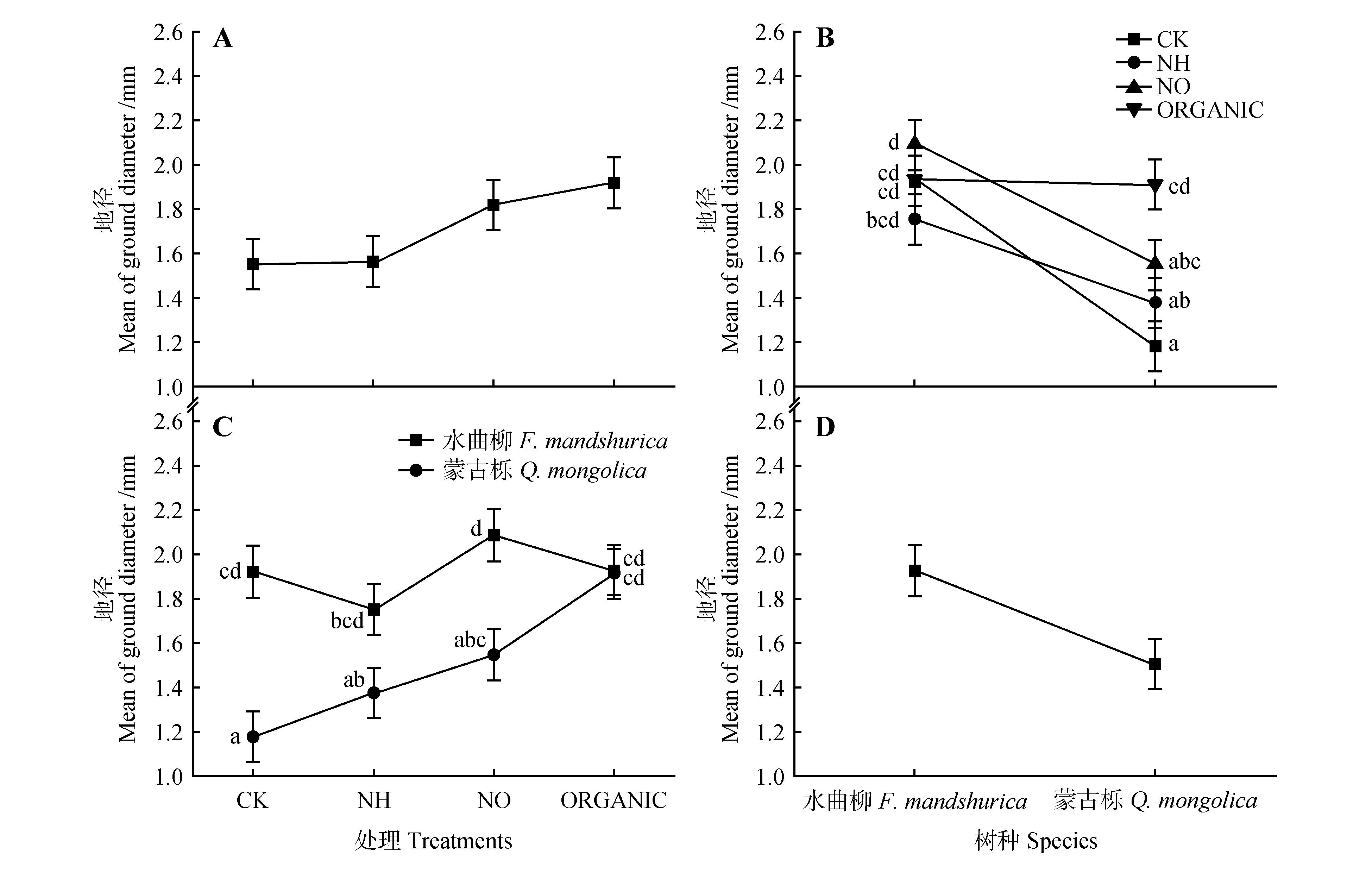
Fig.2
Effects of different nitrogen forms and tree species on ground diameter(A,D) and the interaction of different treatments and tree species on ground diameter(B,C)The parallel lines in the figure indicate that there is no significant interaction effect among the groups;The intersecting lines indicate that there is a significant interaction effect between the groups;the same as below
| 1 | WHITE P J, BROWN P H.Plant nutrition for sustainable development and global health[J].Annals of Botany,2010,105(7):1073-1080. |
| 2 | MAKINO A, SATO T, NAKANO H,et al.Leaf photosynthesis,plant growth and nitrogen allocation in rice under different irradiances[J].Planta,1997,203(3):390-398. |
| 3 | 张雷明,上官周平,毛明策,等.长期施氮对旱地小麦灌浆期叶绿素荧光参数的影响[J].应用生态学报,2003,14(5):695-698. |
| ZHANG L M, SHANGGUAN Z P, MAO M C,et al.Effects of long term application of nitrogen fertilizer on leaf chlorophyll fluorescence of upland winter wheat[J].Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2003,14(5):695-698. | |
| 4 | 贾维嘉,蒋伟,刘建,等.不同氮素形态对总状绿绒蒿幼苗生长与光合作用的影响[J].西部林业科学,2019,48(6):72-79. |
| JIA W J, JIANG W, LIU J,et al.Effects of different nitrogen forms on growth and photosynthesis of Meconopsis racemosa seedlings[J].Journal of West China Forestry Science,2019,48(6):72-79. | |
| 5 | 罗来超,苗艳芳,李生秀,等.氮素形态对小麦幼苗生长及根系生理特性的影响[J].河南科技大学学报(自然科学版),2013,34(4):81-84,1. |
| LUO L C, MIAO Y F, LI S X,et al. Effect of N forms on growth and root physiological characteristics of wheat seedling[J].Journal of Henan University of Science & Technology(Natural Science),2013,34(4):81-84,1. | |
| 6 | INOKUCHI R, KUMA K I, MIYATA T,et al.Nitrogen-assimilating enzymes in land plants and algae:phylogenic and physiological perspectives[J].Physiologia Plantarum,2002,116(1):1-11. |
| 7 | 张延春,陈治锋,龙怀玉,等.不同氮素形态及比例对烤烟长势、产量及部分品质因素的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2005,11(6):787-792. |
| ZHANG Y C, CHEN Z F, LONG H Y,et al.Effect of different nitrogen forms and their ratio on agronomical character,economic and quality of flue-cured tobacco[J].Plant Nutrition and Fertitizer Science,2005,11(6):787-792. | |
| 8 | 张彦东,范志强,王庆成,等.不同形态N素对水曲柳幼苗生长的影响[J].应用生态学报,2000,11(5):665-667. |
| ZHANG Y D, FAN Z Q, WANG Q C,et al.Effect of different nitrogen forms on growth of Fraxinus mandshurica seedlings[J].Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2000,11(5):665-667. | |
| 9 | 陈科屹,张会儒,雷相东.不同群落蒙古栎种群空间格局的地统计学分析[J].应用生态学报,2018,29(5):1542-1550. |
| CHEN K Y, ZHANG H R, LEI X D.Geostatistical analysis on the spatial pattern of Quercus mongolica population in different communities[J].Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2018,29(5):1542-1550. | |
| 10 | 葛文志,薛思雷,刘忠玲.水曲柳林分适宜立地条件研究进展[J].防护林科技,2015(4):56-57,67. |
| GE W Z, XUE S L, LIU Z L.Research progress on suitable site conditions for Fraxinus mandshurica [J].Protection Forest Science and Technology,2015(4):56-57,67. | |
| 11 | 薛思雷,王庆成,孙欣欣,等.遮荫对水曲柳和蒙古栎光合、生长和生物量分配的影响[J].植物研究,2012,32(3):354-359. |
| XUE S L, WANG Q C, SUN X X,et al.Effects of shading on the photosynthetic characteristics,growth,and biomass allocation in Fraxinus mandshurica and Quercus mongolica [J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2012,32(3):354-359. | |
| 12 | WANG G J, LIN F, HU J R,et al.Effects of nitrogen and soil microbe on growth and photosynthesis of Fraxinus mandschurica seedlings[J].Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2019,30(5):1445-1462. |
| 13 | 马立祥,赵甍,毛子军,等.不同氮素水平下增温及[CO2]升高综合作用对蒙古栎幼苗生物量及其分配的影响[J].植物生态学报,2010,34(3):279-288. |
| MA L X, ZHAO M, MAO Z J,et al.Effects of elevated temperature and [CO2] under different nitrogen regimes on biomass and its allocation in Quercus mongolica seedlings[J].Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology,2010,34(3):279-288. | |
| 14 | 张韫.土壤·水·植物理化分析教程[M].北京:中国林业出版社,2011:53-58. |
| ZHANG Y.Soil·water·plant physicochemical analysis Course[M].Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House,2011:53-58. | |
| 15 | THORNLEY J H M.Mathematical models in plant physiology[M].London:Academic Press,1976. |
| 16 | FIELD C, MERINO J, MOONEY H A.Compromises between water-use efficiency and nitrogen-use efficiency in five species of California evergreens[J].Oecologia,1983,60(3):384-389. |
| 17 | 何惠川,何丙辉,刘玉民,等.重庆地区8个薄壳山核桃品种叶片光合生理测定分析[J].中南林业科技大学学报,2022,42(1):86-93. |
| HE H C, HE B H, LIU Y M,et al.Analysis of leaf photosynthetic physiology of 8 pecan varieties in Chongqing[J].Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology,2022,42(1):86-93. | |
| 18 | HOTHORN T, BRETZ F, WESTFALL P.Simultaneous inference in general parametric models[J].Biometrical Journal,2008,50(3):346-363. |
| 19 | 顾红梅,邓光华,翁贤权,等.丝栗栲幼苗对不同氮含量及形态的营养响应[J].江西农业大学学报,2016,38(2):312-318. |
| GU H M, DENG G H, WENG X Q,et al.Growth response of Castanopsis fargesii seedlings to nitrogen nutrition[J].Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis,2016,38(2):312-318. | |
| 20 | 李海霞,邢亚娟,李正华,等.不同氮素形态对蒙古栎幼苗生长及生理特性的影响[J].森林工程,2021,37(2):35-40. |
| LI H X, XING Y J, LI Z H,et al.Effects of different nitrate form on the growth and physiological characteristics for Quercus mongolica seedlings[J].Forest Engineering,2021,37(2):35-40. | |
| 21 | 任海燕,田磊,朱毅,等.氮水添加改变内蒙古典型草原两种优势植物的氮吸收偏好[J].科学通报,2022,67(13):1459-1468. |
| REN H Y, TIAN L, ZHU Y,et al.Nitrogen and water addition alter nitrogen uptake preferences of two dominant plant species in a typical Inner Mongolian steppe[J].Chinese Science Bulletin,2022,67(13):1459-1468. | |
| 22 | 范志强.氮磷营养及氮形态对水曲柳幼苗生长和生理的影响机制[D].哈尔滨:东北林业大学,2004. |
| FAN Z Q.Effects of nitrogen,phosphorus and nitrogen forms on growth and physiological traits of Fraxinus mandshurica seedlings[D].Harbin:Northeast Forestry University,2004. | |
| 23 | PHILLIPS R P, BRZOSTEK E, MIDGLEY M G.The mycorrhizal-associated nutrient economy:a new framework for predicting carbon-nutrient couplings in temperate forests[J].New Phytologist,2013,199(1):41-51. |
| 24 | EASTMAN B A, ADAMS M B, BRZOSTEK E R,et al.Altered plant carbon partitioning enhanced forest ecosystem carbon storage after 25 years of nitrogen additions[J].New Phytologist,2021,230(4):1435-1448. |
| 25 | 杨建华,王芳,张军辉,等.长期施氮与减水处理对红松和蒙古栎根际磷浓度的影响[J].生态学杂志,2015,34(10):2699-2704. |
| YANG J H, WANG F, ZHANG J H,et al.Influence of long-term nitrogen fertilization and precipitation reduction on rhizospheric phosphorus concentration of Pinus koraiensis and Quercus mongolica [J].Chinese Journal of Ecology,2015,34(10):2699-2704. | |
| 26 | FUNK J L, CORNWELL W K.Leaf traits within communities:context may affect the mapping of traits to function[J].Ecology,2013,94(9):1893-1897. |
| 27 | BARKER D H, VANIER C, NAUMBURG E,et al.Enhanced monsoon precipitation and nitrogen deposition affect leaf traits and photosynthesis differently in spring and summer in the desert shrub Larrea tridentata[J].New Phytologist,2006,169(4):799-808. |
| 28 | 郑淑霞,上官周平.不同功能型植物光合特性及其与叶氮含量、比叶重的关系[J].生态学报,2007,27(1):171-181. |
| ZHENG S X, SHANGGUAN Z P.Photosynthetic characteristics and their relationships with leaf nitrogen content and leaf mass per area in different plant functional types[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2007,27(1):171-181. | |
| 29 | 王庆伟,于大炮,代力民,等.全球气候变化下植物水分利用效率研究进展[J].应用生态学报,2010,21(12):3255-3265. |
| WANG Q W, YU D P, DAI L M,et al.Research progress in water use efficiency of plants under global climate change[J].Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2010,21(12):3255-3265. | |
| 30 | ALLEN M F, SWENSON W, QUEREJETA J I,et al.Ecology of mycorrhizae:a conceptual framework for complex interactions among plants and fungi[J].Annual Review of Phytopathology,2003,41:271-303. |
| [1] | Mengshuo LI, Yingze LIU, Huan LU, Sheng QIANG. Photosynthetic Capacity Differentiation and Gene Transcription in Different Geographical Populations of Arabidopsis thaliana under Common Garden conditions [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(1): 90-99. |
| [2] | Xiwu DU, Jun QIN, Kang YE, Yonghong HU, Yiwei TAO, Yongzheng PENG, Yanxiang SHEN, Yan LIANG, Li ZENG. Effects of Flooding Stress on Photosynthetic Characteristics of Yulania stellata and Its Cultivars [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(3): 483-491. |
| [3] | Dan WANG, Ya-Qi LI, Ji-Wei SUN, Jiang-Fei LI, Shi CHEN, Yu-Lan XU, Nian-Hui CAI. The Allometry Growth of Pinus yunnanensis Seedlings from Different Families [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(6): 965-973. |
| [4] | Dong ZHANG, Yan LIU, Han ZHANG, Zi-Jian ZHANG, Yang WANG, Mei-Cen LIU. Response of Photosynthesis and Leaf Morphological Characteristics to Drought Stress in Glycyrrhiza uralensis [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(3): 449-457. |
| [5] | Fang WANG, Zhi-Min LU, Jun WANG, Shi-Kai ZHANG, Yu-Xi LI, Shao-Chen LI, Jian-Qiu ZHANG, Yu-Chun YANG. Photosynthetic and Stomatal Characteristics of Pinus koraiensis and P.sibirica under Low Temperature Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(2): 205-212. |
| [6] | ZHAO Chun-Jian, LI Yu-Zheng, GUAN Jia-Jing, SU Wei-Ran, TIAN Yao, WANG Ting-Ting, LI Shen, LI Chun-Ying. Effect of Interplanting Taxus cuspidata with Ficus carica on Growth of Two Plants and Activities of Soil Enzymes [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(5): 679-685. |
| [7] | LIU Ting-Yan, HAO Long-Fei, WANG Qing-Cheng, BAI Shu-Lan. Effects of Different Planting Densities on Cultivating Quality of Padus maackii Seedlings [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2019, 39(6): 863-868. |
| [8] | JI Li, HAN Jiao, WANG Fang, WANG Jun, SONG Di, ZHANG Li-Jie, QI Yong-Hui, YANG Yu-Chun. Effects of Drought Stress on Photosynthetic and Physiological Characteristics of Juglans mandshurica Seedlings in Different Soil Substrates [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2019, 39(5): 722-732. |
| [9] | LI Zhan-Jun, ZHANG Hou-Liang, GUO Xing, FAN Rui-Hong, MA Ke, LIU Ji-Yun, YANG Feng-Jian. Effects of Different Improvement Measures on Soil Structure and Element Composition,Photosynthesis and Growth of Poplar Leaves in Severe Saline-alkali Soils of Songnen Plain [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2019, 39(5): 733-739. |
| [10] | LI Rong-Yu, QIU Guo-Yu, SHEN Xiao-Xue, CHAI Min-Wei. Effects of Ammonium Nitrogen on Physiological and Ecological Characteristics of Kandelia obovata under Cadmium Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2018, 38(5): 653-660. |
| [11] | ZHANG Qiang, LIU Yi, WU Xiao-Min, SHU Liang-Zuo, SONG Yun-Xian, CHEN Chu, LONG Min-Hui. Preliminary Study on the Effects of Two Different Nitrogen Forms on Flavonoids Accumulation and Related Molecular Mechanism in Medicinal Plant Tetrastigma hemsleyanum [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2018, 38(3): 367-376. |
| [12] | LIU Zhao-Ying, JIANG Chuan-Ying, ZHAI Tong-Tong, CHANG Yuan, YAO Zhi-Hong, LIU Zhi-Hua, ZHANG Rong-Shu. Effects of Trichoderma asperellum Combined Application on Growth and Photosynthesis Characteristics of Populus davidiana×P.alba var. pyramidlis [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2018, 38(1): 64-74. |
| [13] | ZHANG Ming, LIU Fu-De, AN Shu-Qing, CAO Xue-Zhang. Leaf Traits of the Saplings of Later Successional Stage Tropical Montane Rain Forest in Hainan Island [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2017, 37(6): 907-914. |
| [14] | WANG Ke;DIAO Jian;YANG Rui;HU Yan-Bo*;SUN Guang-Yu. Effects of Leaf-spraying Nitrate on Stomatal Dynamics and Photosynthesis of Syringa oblata Lindl. Leaves [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2015, 35(6): 843-847. |
| [15] | ZHANG Qiang1,2;GUO Chuan-You1;ZHANG Xing-Wang1;BAI Kun-Dong2*;JIANG De-Bing3. Photosynthesis and Antioxidant Defense Strategies in Overwintering Plants of Tsuga chinensis and Cyclobalanopsis stewardiana [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2015, 35(2): 200-207. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||