Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (5): 866-875.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2022.05.018
• Physiology and Ecology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Huan WANG1,2, Yunfei XU1,2, Yibo LIU1,2, Qinsong LIU1,2, Wenjuan XU1,2, Yun LONG1,2, Xiao XU1,3( )
)
Received:2021-12-06
Online:2022-09-20
Published:2022-09-15
Contact:
Xiao XU
E-mail:xuxiao_cwnu@163.com
About author:WANG Huan(1996—),female,master candidate,mainly engaged in plant ecology.
Supported by:CLC Number:
Huan WANG, Yunfei XU, Yibo LIU, Qinsong LIU, Wenjuan XU, Yun LONG, Xiao XU. Allelopathic Effects on Seed Germination and Seedling Growth of Brassica pekinensi, Caused by Water Extracts of Branches and Leaves from Davidia involucrata and Bothrocaryum controversum[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(5): 866-875.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://bbr.nefu.edu.cn/EN/10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2022.05.018
Table 1
Effects of water extracts from branches or leaves of D. involucrata on seed germination of cabbage
来源 Source | 质量浓度 Concentration /g·mL-1 | 发芽率 Germination percentage /% | 发芽指数 Germination index | 发芽速度指数 Germination speed index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
珙桐枝 Branches of D. involucrata | 0(CK) | 96.00±0.01ab | 65.53±1.40a | 731.40±12.24a |
| 0.025 | 93.00±0.01c | 64.00±1.62a | 714.20±14.45a | |
| 0.050 | 94.00±0.01bc | 64.33±1.39a | 721.00±12.59a | |
| 0.075 | 97.00±0.01a | 64.47±1.12a | 730.40±11.53a | |
| 0.100 | 97.33±0.01a | 63.87±1.07a | 729.60±10.42a | |
珙桐叶 Leaves of D. involucrata | 0(CK) | 96.00±0.01a | 65.53±1.40a | 731.40±12.24a |
| 0.025 | 96.33±0.01a | 65.23±1.82a | 731.90±16.44a | |
| 0.050 | 95.00±0.01ab | 50.86±1.19b | 613.10±10.84b | |
| 0.075 | 91.67±0.01b | 32.07±0.80c | 403.80±11.27c | |
| 0.100 | 84.00±0.02c | 22.29±0.80d | 283.10±11.02d |
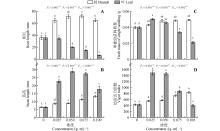
Fig.1
Effects of water extracts from branches and leaves of D. involucrata on the growth of cabbage seedlingsValues with the different letters on the bars indicate significant differences between mean values;o.Organ effect;c.Concentration effect;o×c.Organ effect and concentration effect are denoted as
Table 2
Effects of water extracts from branches and leaves of the B. controversum on seed germination of cabbage
来源 Source | 质量浓度 Concentration /(g·mL-1) | 发芽率 Germination percentage /% | 发芽指数 Germination index | 发芽速度指数 Germination speed index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
灯台树枝 B. controversum | 0(CK) | 96.00±0.01ab | 65.53±1.40a | 731.40±12.24a |
| 0.025 | 95.67±0.01ab | 64.28±2.40a | 722.20±18.15a | |
| 0.050 | 94.00±0.02b | 65.81±1.59a | 730.10±15.81a | |
| 0.075 | 98.00±0.01a | 64.12±1.67a | 722.10±15.29a | |
| 0.100 | 93.00±0.01b | 60.17±1.32a | 683.50±13.95a | |
灯台树叶 B. controversum | 0(CK) | 0.96±0.01a | 65.53±1.40a | 731.40±12.24a |
| 0.025 | 79.67±0.02b | 20.12±0.73b | 255.40±9.28b | |
| 0.050 | 6.00±0.01c | 0.57±0.14c | 6.20±1.76c | |
| 0.075 | 0.67±0.00d | 0.07±0.051c | 0.70±0.59c | |
| 0.100 | 0d | 0c | 0c |
Table 3
Effects of the mixed water extracts with the branches and leaves of D. involucrata, B. controversum and D. involucrata & B. controversum on the germination of cabbage seeds
来源 Source | 质量浓度 Concentration /g·mL-1 | 发芽率 Germination percentage/% | 发芽指数 Germination index | 发芽速度指数 Germination speed index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
枝+叶(珙桐) Branch & Leaf(D. involucrata) | 0(CK) | 99.00±0.01a | 60.99±1.10a | 713.40±8.42a |
| 0.025 | 93.33±0.01b | 46.50±1.04b | 579.90±12.18b | |
| 0.050 | 88.67±0.01b | 42.02±0.96c | 539.80±11.54b | |
| 0.075 | 81.33±0.02c | 36.42±1.10d | 478.30±13.86c | |
| 0.100 | 72.00±0.02d | 27.55±1.67e | 364.20±12.14d | |
枝+叶(灯台树) Branch & Leaf(B. controversum) | 0(CK) | 99.00±0.01a | 60.99±1.10a | 713.40±8.42a |
| 0.025 | 94.67±0.01a | 46.14±0.90b | 586.60±10.31b | |
| 0.050 | 82.00±0.01b | 25.97±0.83c | 344.50±11.40c | |
| 0.075 | 28.00±0.03c | 6.72±1.06d | 87.60±14.24d | |
| 0.100 | 7.00±0.02d | 1.17±0.44e | 14.30±5.74e | |
枝+叶(珙桐+灯台树) Branch & Leaf (D. involucrata+B. controversum) | 0(CK) | 99.00±0.01a | 60.99±1.10a | 713.40±8.42a |
| 0.025 | 98.00±0.01a | 56.55±1.21b | 678.20±10.62a | |
| 0.050 | 85.00±0.01b | 35.82±1.07c | 473.50±14.32b | |
| 0.075 | 49.67±0.02c | 16.07±0.91d | 215.50±12.52c | |
| 0.100 | 29.33±0.04d | 8.51±1.10e | 112.80±16.02d |
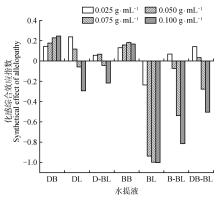
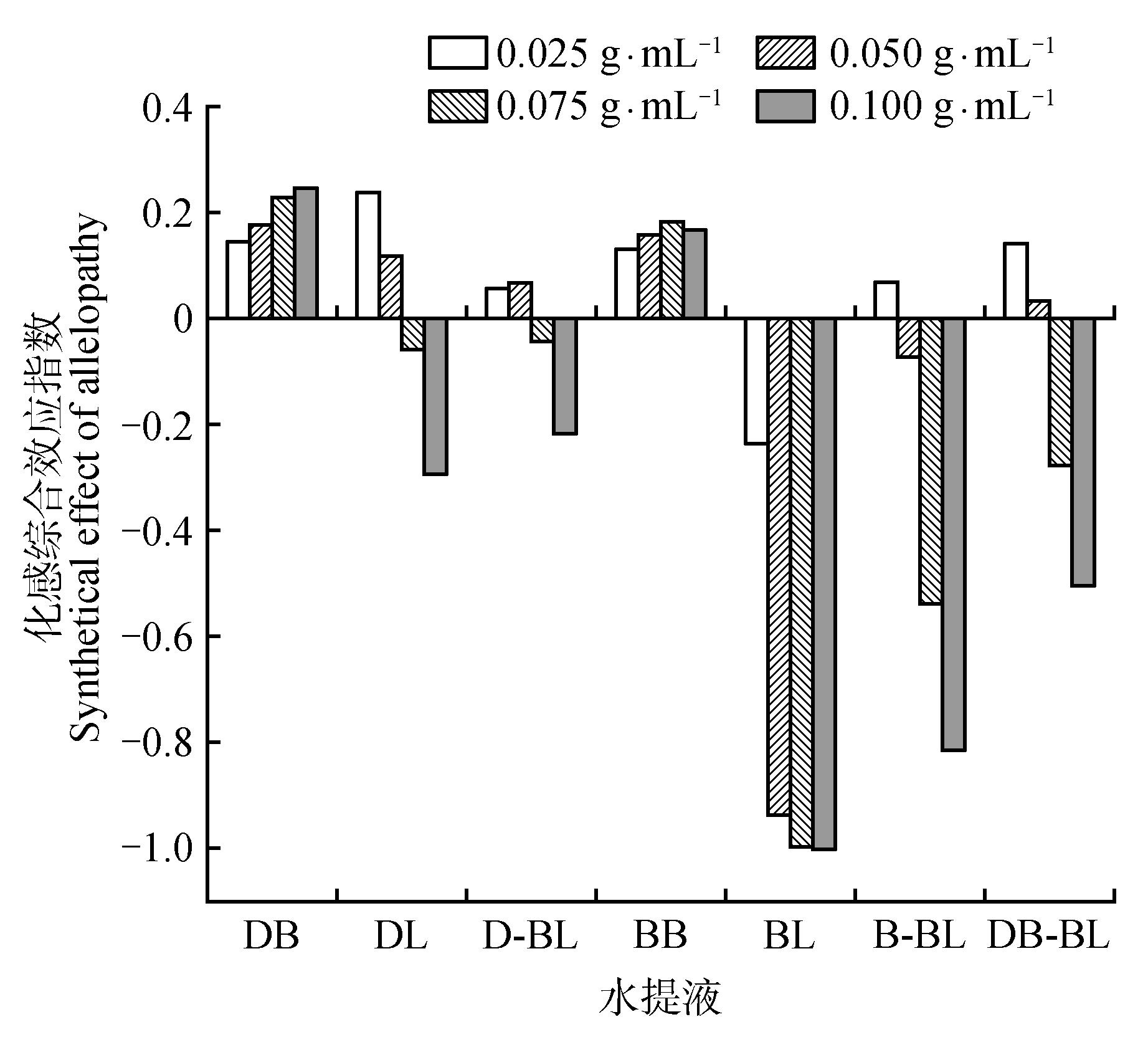
Fig.4
The synthetical allelopathic effect index of various concentrations of different water extracts on seed germination and seedling growth of cabbageDB.Branches of D. involucrate;DL.Leaves of D. involucrate;D-BL.Branches and leaves of D. involucrate;BB.Branches of B. controversum;BL.Leaves of B. controversum;B-BL.Branches and leaves of B. controversum;DB-BL.Branches and leaves of D. involucrata,B. controversum
| 1 | RICE E L.Allelopathy[M].2nd ed.Orlando:Academic Press,1984. |
| 2 | BONANOMI G, SICUREZZA M G, CAPORASO S,et al.Phytotoxicity dynamics of decaying plant materials[J].New Phytologist,2006,169(3):571-578. |
| 3 | FAROOQ M, JABRAN K, CHEEMA Z A,et al.The role of allelopathy in agricultural pest management[J].Pest Management Science,2011,67(5):493-506. |
| 4 | 孔垂华,徐涛,胡飞,等.环境胁迫下植物的化感作用及其诱导机制[J].生态学报,2000,20(5):849-854. |
| KONG C H, XU T, HU F,et al.Allelopathy under environmental stress and its induced mechanism[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2000,20(5):849-854. | |
| 5 | 刘忠玲,王庆成,郝龙飞.白桦、落叶松不同器官水浸液对种子萌发和播种苗生长的种间化感作用[J].应用生态学报,2011,22(12):3138-3144. |
| LIU Z L, WANG Q C, HAO L F.Interspecific allelopathic effect of different organs’ aqueous extracts of Betula platyphylla and Larix olgensis on their seed germination and seedling growth[J].Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2011,22(12):3138-3144. | |
| 6 | 鲍红春,郝丽珍,张凤兰,等.沙芥水浸提液对白菜种子萌发和幼苗生长的化感作用[J].植物生理学报,2015,51(7):1109-1116. |
| BAO H C, HAO L Z, ZHANG F L,et al.Allelopathic effects of aqueous extracts of Pugionium cornutum on seed germination and seedling growth of cabbage[J].Plant Physiology Journal,2015,51(7):1109-1116. | |
| 7 | 陈黎,刘成功,万志兵,等.南方红豆杉种子不同部位浸提液对小白菜的化感作用[J].东北林业大学学报,2020,48(7):90-97. |
| CHEN L, LIU C G, WAN Z B,et al.Allelopathic effect of extracts from different parts of Taxus chinensis var. mairei seeds on cabbage[J].Journal of Northeast Forestry University,2020,48(7):90-97. | |
| 8 | LIU J Y, XU G, YIN L Z,et al.Invasive plants exert disproportionately negative allelopathic effects on the growth and physiology of the earthworm Eisenia fetida [J].Science of the Total Environment,2020,747:141534. |
| 9 | 梁玲,江洁蓓,张腾驹,等.不同色彩珙桐苞片与叶片的生理特性研究[J].植物研究,2020,40(4):505-513. |
| LIANG L, JIANG J B, ZHANG T J,et al.Physiological characteristics of Davidia involucrata bracts and leaves with different colors[J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2020,40(4):505-513. | |
| 10 | 张桂芳.野生珙桐伴生植物群落特征研究[D].雅安:四川农业大学,2018. |
| ZHANG G F.Characteristics of associated plant communities of Davidia involucrata [D].Ya’an:Sichuan Agricultural University,2018. | |
| 11 | LIU Q S, FENG Z Q, XU W J,et al.Exogenous melatonin-stimulated transcriptomic alterations of Davidia involucrata seedlings under drought stress[J].Trees,2021,35(3):1025-1038. |
| 12 | LIU Q S, VETUKURI R R, XU W J,et al.Transcriptomic responses of dove tree (Davidia involucrata Baill.) to heat stress at the seedling stage[J].Forests,2019,10(8):656. |
| 13 | 刘婷婷,刘沁松,徐文娟,等.珙桐(Davidia involucrata Baill.)苞片功能性状及性状间关系对海拔的响应[J].生态学杂志,2020,39(3):794-802. |
| LIU T T, LIU Q S, XU W J,et al.Altitudinal changes of functional traits and relationships among traits of bracts in dove tree (Davidia involucrata Baill.) [J].Chinese Journal of Ecology,2020,39(3):794-802. | |
| 14 | JOSE S, GILLESPIE A R, PALLARDY S G.Interspecific interactions in temperate agroforestry[J].Agroforestry Systems,2004,61(1):237-255. |
| 15 | XU Y, CHENG H F, KONG C H,et al.Intra-specific kin recognition contributes to inter-specific allelopathy:a case study of allelopathic rice interference with paddy weeds[J].Plant,Cell & Environment,2021,44(12):3479-3491. |
| 16 | 黄志群,廖利平,汪思龙,等.杉木根桩和周围土壤酚含量的变化及其化感效应[J].应用生态学报,2000,11(2):190-192. |
| HUANG Z Q, LIAO L P, WANG S L,et al.Dynamics of phenolics content of Chinese fir stump-roots and the rhizosphere soil and it’s allelopathy[J].Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2000,11(2):190-192. | |
| 17 | HUANG Z Q, LIAO L P, WANG S L,et al.Allelopathy of phenolics from decomposing stump-roots in replant Chinese fir woodland[J].Journal of Chemical Ecology,2000,26(9):2211-2219. |
| 18 | HUANG Z Q, TERRY H, WANG S L,et al.Autotoxicity of Chinese fir on seed germination and seedling growth[J].Allelopathy Journal,2002,9(2):187-193. |
| 19 | 杨立学.落叶松水浸液对胡桃楸种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响[J].应用生态学报,2006,17(6):1145-1147. |
| YANG L X.Effects of Larix gmelini aqueous extracts on seed germination and seedling growth of Juglans mandshurica [J].Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2006,17(6):1145-1147. | |
| 20 | 徐云飞,刘沁松,徐文娟,等.天然珙桐种群结构与动态特征在高低纬度地区的差异[J].植物研究,2020,40(6):855-866. |
| XU Y F, LIU Q S, XU W J,et al.Differences in population structure and dynamic characteristics of Davidia involucrata Baill.between high and low latitude regions[J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2020,40(6):855-866. | |
| 21 | 李金鑫,叶俊伟,刘大会.巴茅草水浸提液3种作物种子萌发及幼苗生长的化感作用[J].应用生态学报,2020,31(7):2219-2226. |
| LI J X, YE J W, LIU D H.Allelopathic effects of Miscanthus floridulus on seed germination and seedling growth of three crops[J].Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2020,31(7):2219-2226. | |
| 22 | 慕小倩,罗玛霞,段琦梅,等.10种菊科植物水提液对小麦幼苗生长的影响[J].西北植物学报,2003,23(11):2013-2016. |
| MU X Q, LUO M X, DUAN Q M,et al.Effects of water extracts from ten plants of Compositae against wheat seedling[J].Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica,2003,23(11):2013-2016. | |
| 23 | 高玉莲,李睿光,常静,等.油菜对3种作物种子萌发和幼苗生长的化感作用[J].应用生态学报,2020,31(12):4153-4160. |
| GAO Y L, LI R G, CHANG J,et al.Allelopathy of rape on seed germination and seedling growth of three crops[J].Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2020,31(12):4153-4160. | |
| 24 | BRUCE WILLIAMSON G, RICHARDSON D.Bioassays for allelopathy:measuring treatment responses with independent controls[J].Journal of Chemical Ecology,1988,14(1):181-187. |
| 25 | IQBAL Z, FURUBAYASHI A, FUJII Y.Allelopathic effect of leaf debris,leaf aqueous extract and rhizosphere soil of Ophiopogon japonicus Ker-Gawler on the growth of plants[J].Weed Biology and Management,2004,4(1):43-48. |
| 26 | SONG L Y, LIN R, WU Z J,et al.Chemically diverse secondary metabolites from Davidia involucrate (dove tree) [J].Journal of Chemistry,2016,9806102. |
| 27 | 段志航.糖胶树、大叶糖胶树和灯台树三种植物化学成分的研究[D].昆明:云南师范大学,2019. |
| DUAN Z H.Studies on the chemical constituents of Alstonia scholaris,Alstonia macrophylla and Bothrocaryum controversum [D].Kunming:Yunnan Normal University,2019. | |
| 28 | 王璞,赵秀琴.几种化感物质对棉花种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响[J].中国农业大学学报,2001,6(3):26-31. |
| WANG P, ZHAO X Q.Effect of allelochemicals on cotton seed germination and seedling growth[J].Journal of China Agricultural University,2001,6(3):26-31. | |
| 29 | SUZUKI K, SHIMIZU T, KAWABATA J,et al.New 3,5,4’-trihydroxystilbene(resveratrol) oligomers from Carex fedia Nees var. miyabei(Franchet) T.Koyama(Cyperaceae)[J].Agricultural and Biological Chemistry,1987,51(4):1003-1008. |
| 30 | 姚树宽,李凤兰,彭丽娜,等.假苍耳不同部位水浸提液对五种十字花科植物化感作用的研究[J].草业学报,2018,27(9):56-66. |
| YAO S K, LI F L, PENG L N,et al.A study of the allelopathic effect of extracts from different parts of Iva xanthiifolia on five Brassicaceae species[J].Acta Prataculturae Sinica,2018,27(9):56-66. | |
| 31 | 杨立学.落叶松水提物对胡桃楸化感作用的生物测定[J].东北林业大学学报,2006,34(2):15-17. |
| YANG L X.Bioassay of allelopathical activity of larch(Larix gmelini) aqueous extracts against Juglans mandshurica [J].Journal of Northeast Forestry University,2006,34(2):15-17. | |
| 32 | BLUM U.Effects of microbial utilization of phenolic acids and their phenolic acid breakdown products on allelopathic interactions[J].Journal of Chemical Ecology,1998,24(4):685-708. |
| [1] | Lei XU, Xiao XU, Qinsong LIU. Effects of Exogenous Salicylic Acid on Antioxidant System and Gene Expression of Davidia involucrata Seedlings under Salt Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(4): 572-581. |
| [2] | Chunjing JIAO, Mingyue LI, Peng ZHANG. Effects of Exogenous Hormones Soaking and Osmotic Treatment on Thermal Dormancy of Seeds of Fraxinus mandshurica [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(3): 370-378. |
| [3] | Yingying TANG, Chuanchao GUO, Dang SHI, Nanlin JIANG, Zheng XU, Liqiang LIU. Effects of Pulp and Buried Depth on Seed Germination and Seedling Growth of Armeniaca vulgaris [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(2): 251-260. |
| [4] | Jian-Xin LIU, Rui-Rui LIU, Xiu-Li LIU, Hai-Yan JIA, Ting BU, Na LI. Effect of Soaking Seeds with NaHS on Seed Germination Characteristics of Naked Oat under Saline-Alkali Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(6): 870-877. |
| [5] | Yue ZHANG, Quan-Ling ZHANG, Zhi HONG, KAN Zi-Han, Zhao-Yue CHU, Ye TAO. Intraspecific and Interspecific Allelopathy of Invasive Plants Plantago virgica and Daucus carota [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(3): 441-448. |
| [6] | Yun-Fei XU, Qin-Song LIU, Wen-Juan XU, Jun-Feng TANG, Ting-Fa DONG, Bao-Zhen YANG, Xiao XU. Differences in Population Structure and Dynamic Characteristics of Davidia involucrata Baill. Between High and Low Latitude Regions [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(6): 855-866. |
| [7] | LU Yan, YAN Yue, CUI Cheng-Cheng, ZHANG Peng. Effects of Primary Dormancy-released Status and Drying Treatment on Germination of Fraxinus mandshurica Seeds [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(4): 490-495. |
| [8] | LIANG Ling, JIANG Jie-Bei, ZHANG Teng-Ju, Lü Jia-Yao, CHEN Xiao-Hong. Physiological Characteristics of Davidia involucrata Bracts and Leaves with Different Colors [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(4): 505-513. |
| [9] | YANG He, ZHANG Nan, LIU Zi-Guang, LIN Jian-Hui, SUN Shi-Chen, LIU Sheng-Yi, CEN Xi, WU Juan. Expression and Function of BoNR8 lncRNA in Cabbage under Cold Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(3): 441-446. |
| [10] | XIAO Zhi-Peng, YIN Chong-Min, GUO Lian-Jin, WU Yuan-Rong, HU Jin-Ping, LIU Yan-Yan, ZHONG You-Chun, XUE Ping-Ping. Effect of Light Quality on Seed Germination and Seeding Growth of Emmenopterys henryi [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(2): 189-195. |
| [11] | LIU Jian-Xin, OU Xiao-Bin, WANG Jin-Cheng. Cytosolic Ca2+ Involved in Seed Germination of Naked Oat Enhanced by Exogenous H2S under Saline-Alkali Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(1): 58-65. |
| [12] | ZHANG Teng-Ju, CHEN Xiao-Hong, LIU Jing, KANG Xi-Kun. Relationship between Anatomical Structures and Heat Resistance of Davidia involucrata Natural Populations in Sichuan Province [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2019, 39(2): 208-221. |
| [13] | YANG Nan, NIE Jiang-Li, XIN Wei, XIA Xu, LANG Yu-Jie, PEI Yi. Effects of EMS on Seed Germination of Anemarrhena asphodeloides in the Simulated Environment [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2019, 39(2): 246-251. |
| [14] | ZHAO Xiao-Ju, ZHANG Li-Xia, MAN Xiu-Ling. Effects of Exogenous NO on Seed Germination and Physiological Metabolism in Catharanthus roseus Seedling under NaCl Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2018, 38(5): 669-674. |
| [15] | LI Chun-Ying, ZHANG Jing-Jing, ZHAO Chun-Jian, JIANG Hong-Wei, REN Xue-Ting, SU Wei-Ran, GUAN Jia-Jing, LI Yu-Zheng. Effects of 3-methyl-1-butanol on Seed Germination and Seedling Growth of Maize and Wheat [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2018, 38(5): 785-789. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||