Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (4): 647-656.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2022.04.014
• Physiology and Ecology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Bing GAO, Pengfei GAO, Weifang FAN, Zhenghong FENG, Jianhui WU( )
)
Received:2021-09-01
Online:2022-07-20
Published:2022-07-15
Contact:
Jianhui WU
E-mail:wujianhui660915@126.com
About author:GAO Bing(1998—),female,master,majoring in landscape plant germplasm resources.
Supported by:CLC Number:
Bing GAO, Pengfei GAO, Weifang FAN, Zhenghong FENG, Jianhui WU. Effects of Cadmium Stress on the Root Structure and Physiology of Symbiont of Potentilla sericea and Arbuscular Mycorrhizal fungi[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(4): 647-656.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://bbr.nefu.edu.cn/EN/10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2022.04.014
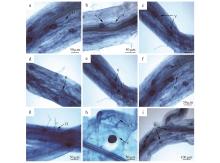
Fig.1
Microstructure of symbiosis of roots and mycorrhiza of P. sericeaa.Non-septal hyphae invade root component dendritic H(hypha);b.Non-septal hyphae H and vesicles V(vesicle);c.Abnormal vesicles V;d.Hypha invasion points H;e.Mycelium H has a bifurcated shape and swells at the top to form a vesicle V;f.It has been digested into a spotted arbuscular A (Arbuscular) and a septal hyphae H;g.Mycelial invasion point H;h.Witch branch A and round vesicle V;i.Irregular vesicle
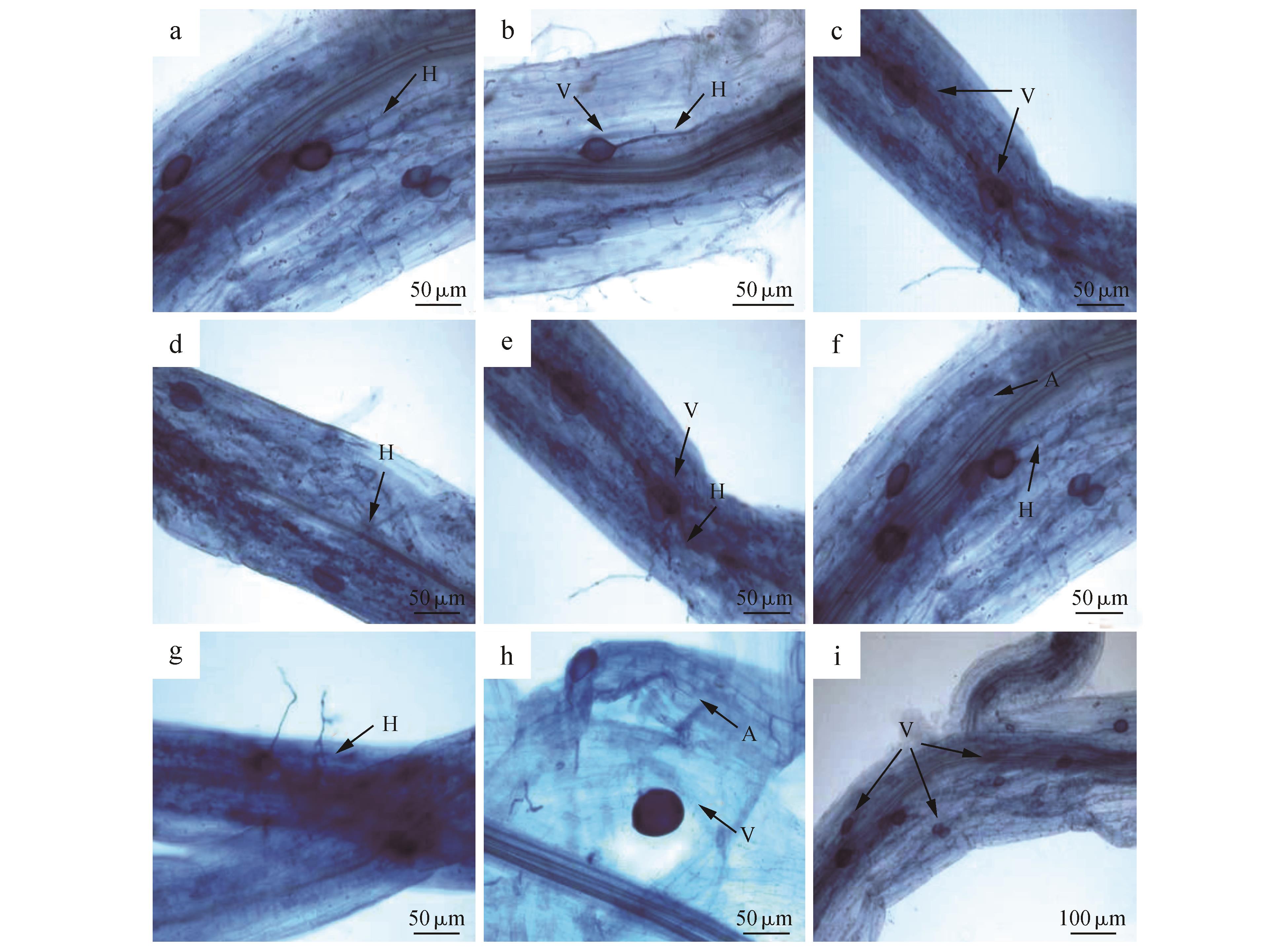
Table 1
Effect of AM fungi on the infection rate of P. sericea mycorrhiza under cadmium stress
接种菌株 Inoculated strain | 镉质量浓度 Cd mass concentration /(mg•L-1) | 菌根侵染率 Mycorrhizal colonization rate /% |
|---|---|---|
| F.mosseae | 0 | 100±0(a) |
| 5 | 98.70±0.03(a) | |
| 10 | 80.86±2.60(b) | |
| 15 | 66.33±1.27(a) | |
| 20 | 43.57±1.77(b) | |
| R. intraradices | 0 | 89.33±0.03(a) |
| 5 | 73.90±0.73(b) | |
| 10 | 58.19±1.48(a) | |
| 15 | 43.36±0.83(a) | |
| 20 | 17.60±5.77(b) |
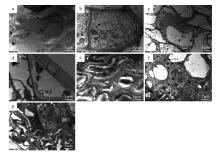
Fig.2
The ultrastructure of the root system of P. sericeaa.No inoculation,Cd0(×20 000);b.No inoculation,Cd5(×20 000);c.No inoculation,Cd10(×20 000);d.No inoculation,Cd20(×20 000);E.Inoculation,Cd5(×20 000);f.Inoculation,Cd10(×20 000);g.Inoculation,Cd20(×20 000);M.Mitochondria;W.Cell wall;S.Starch granules;V.Vacuoles
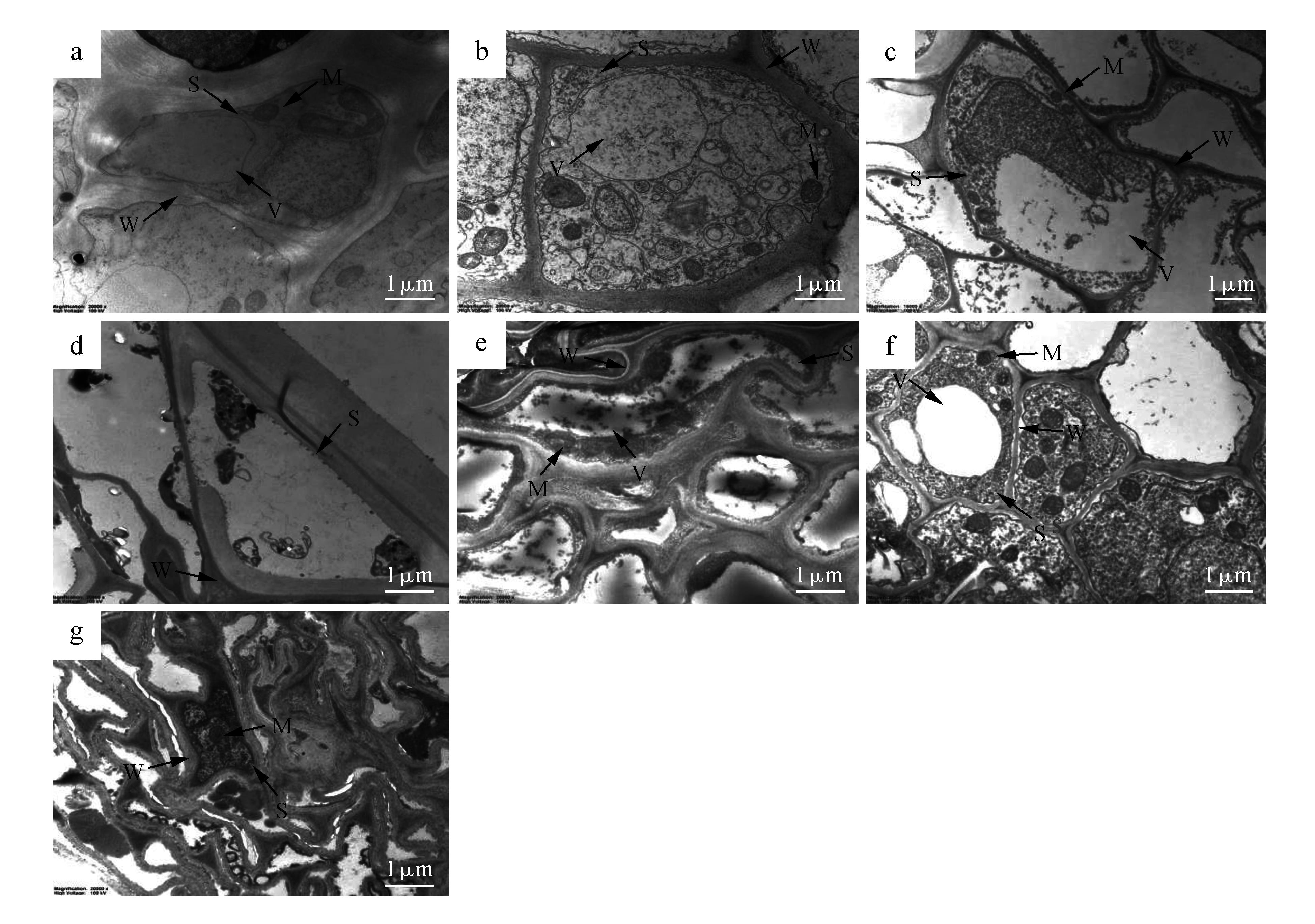

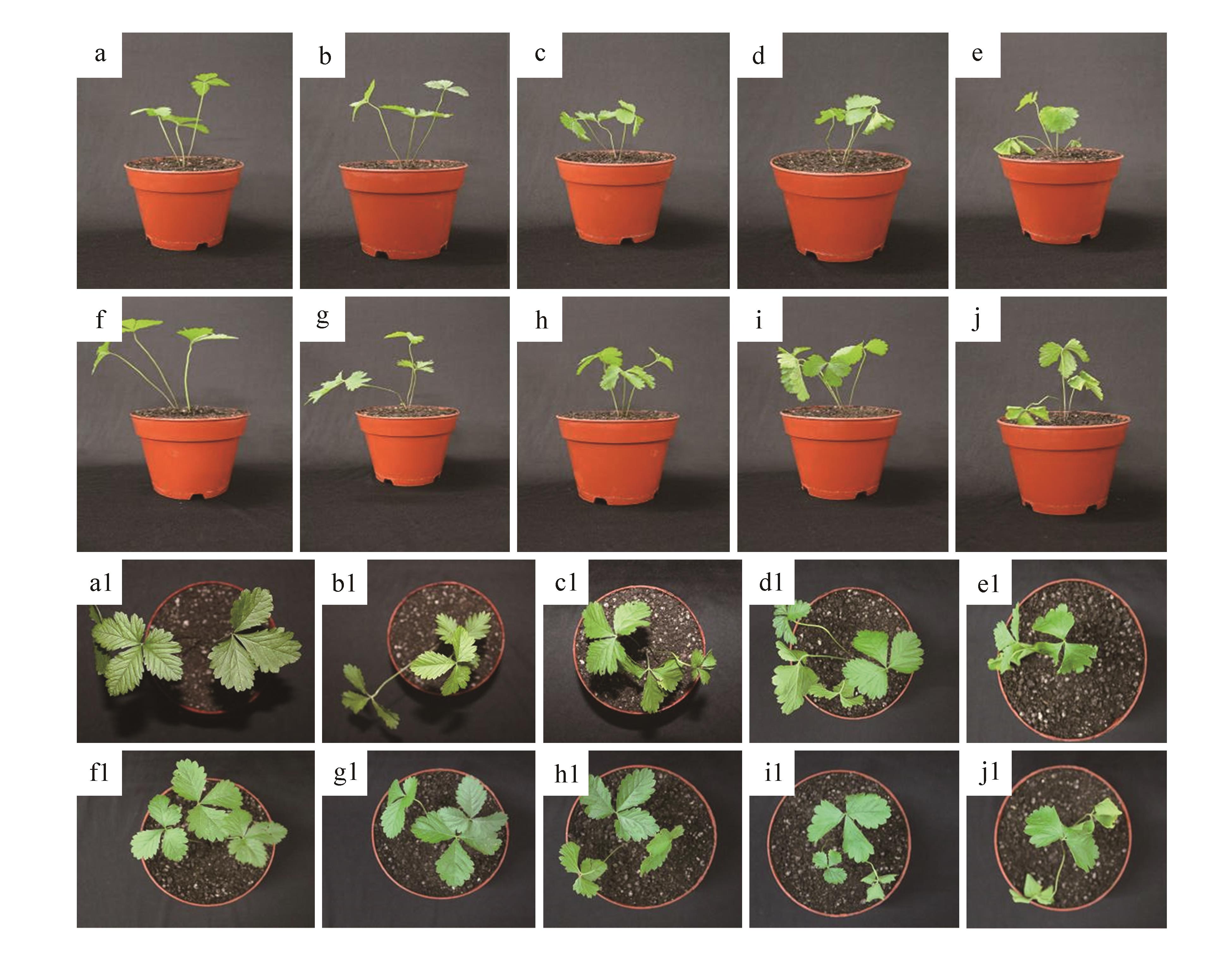
Fig.3
Growth index of Potentilla sericea L.- F.mosseae symbiont under cadmium stressa,a1.No inoculation,Cd0;b,b1.No inoculation,Cd5;c,c1.No inoculation,Cd10;d,d1.No inoculation,Cd15;e,e1.No inoculation,Cd20;f,f1.Inoculation,Cd0;g,g1.Inoculation,Cd5;h,h1.Inoculation,Cd10;i,i1.Inoculation,Cd15;j,j1.Inoculation,Cd20

| 1 | 张良,杨春雪.盐碱胁迫对星星草—丛枝菌根真菌共生体酶活性及游离氨基酸的影响[J].东北林业大学学报,2018,46(11):91-96. |
| ZHANG L, YANG C X.Enzyme activities and free amino acids of Puccinellia tenuiflora-Arbuscular mycorrhizal Symbiont under saline-alkali stress[J].Journal of Northeast Forestry University,2018,46(11):91-96. | |
| 2 | 刘芳,景戍旋,胡健,等.镉污染和接种丛枝菌根真菌对紫花苜蓿生长和氮吸收的影响[J].草业学报,2017,26(2):69-77. |
| LIU F, JING S X, HU J,et al.Effects of cadmium and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculation on the growth and nitrogen uptake of alfalfa(Medicago sativa)[J].Acta Prataculturae Sinica,2017,26(2):69-77. | |
| 3 | 陆爽,郭欢,王绍明,等.盐胁迫下AM真菌对紫花苜蓿生长及生理特征的影响[J].水土保持学报,2011,25(2):227-231. |
| LU S, GUO H, WANG S M,et al.Effects of AM fungi on growth and physiological characters of Medicago sativa L.under NaCl stress[J].Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2011,25(2):227-231. | |
| 4 | 杨海霞,刘润进,郭绍霞.AM真菌摩西球囊霉对盐胁迫条件下高羊茅生长特性的影响[J].草业学报,2014,23(4):195-203. |
| YANG H X, LIU R J, GUO S X.Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Glomus mosseae on the growth characteristics of Festuca arundinacea under salt stress conditions[J].Acta Prataculturae Sinica,2014,23(4):195-203. | |
| 5 | 何红君.丛枝菌根真菌接种对Cd胁迫下芹菜生长、生理及富集特征的影响[J].东北农业科学,2020,45(3):70-75,102. |
| HE H J.Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculation on the growth,physiology and accumulation characteristics of celery(Apium graveolens L.) under cadmium stress[J].Journal of Northeast Agricultural Sciences,2020,45(3):70-75,102. | |
| 6 | JIA T T, WANG J, CHANG W,et al.Proteomics analysis of E. angustifolia seedlings inoculated with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi under salt stress[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2019,20(3):788. |
| 7 | 卢鑫,胡文友,黄标,等.丛枝菌根真菌对玉米和续断菊间作镉吸收和累积的影响[J].土壤,2017,49(1):111-117. |
| LU X, HU W Y, HUANG B,et al.Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi(AMF) on Cd absorption and accumulation in maize and Sonchus asper L. hill using intercropping system[J].Soils,2017,49(1):111-117. | |
| 8 | PHILLIPS J M, HAYMAN D S.Improved procedures for clearing roots and staining parasitic and vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi for rapid assessment of infection[J].Transactions of the British Mycological Society,1970,55(1):158-161,IN16-IN18. |
| 9 | 刘润进,陈应龙.菌根学[M].北京:科学出版社,2007. |
| LIU R J, CHEN Y L.Mycorrhizology[M].Beijing:Science Press,2007. | |
| 10 | 张静.铅、镉胁迫对绢毛委陵菜结构及生理特性的影响[D].哈尔滨: 东北林业大学,2016. |
| ZHANG J.Effects of Pb and Cd stress on structure and physiological characteristics of Potentilla sericea [D].Harbin: Northeast Forestry University,2016. | |
| 11 | 王学奎.植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M].2版.北京:高等教育出版社,2006:23-25. |
| WANG X K.Principles and techniques of plant physiological biochemical experiment[M].2nd ed.Beijing:Higher Education Press,2006:23-25. | |
| 12 | DICKSON S.The Arum-Paris continuum of mycorrhizal symbioses[J].New Phytologist,2004,163(1):187-200. |
| 13 | ZUBEK S, BŁASZKOWSKI J, BUCHWALD W.Fungal root endophyte associations of medicinal plants[J].Nova Hedwigia,2012,94(3/4):525-540. |
| 14 | 郭贵华,刘海艳,李刚华,等.ABA缓解水稻孕穗期干旱胁迫生理特性的分析[J].中国农业科学,2014,47(22):4380-4391. |
| GUO G H, LIU H Y, LI G H,et al.Analysis of physiological characteristics about ABA alleviating rice booting stage drought stress[J].Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2014,47(22):4380-4391. | |
| 15 | 冯岚,严岩,闫兴成,等.乙草胺胁迫下水位对湿地芦苇生长及土壤酶活性的影响[J].森林工程,2021,37(2): 24-29. |
| FENG L, YAN Y, YAN X C,et al.Effects of water levels on wetland reed growth and soil enzyme activities under acetochlor stress[J].Forest Engineering,2021,37(2):24-29. | |
| 16 | 朱生翠.根际真菌对植物吸收重金属镉的强化作用研究[D].株洲:湖南工业大学,2014. |
| ZHU S C.The strengthen effect of rhizosphere fungi on phytoextraction of soils contaminated with cadmium[D].Zhuzhou:Hunan University of Technology,2014 | |
| 17 | 王晔,李航,汤宇,等.浙江镜湖湿地3种菌根植物根部真菌群落多样性及对金属元素富集能力的研究[J].植物研究,2019,39(6):883-889. |
| WANG Y, LI H, TANG Y,et al.Fungal community and their metal accumulation ability of three mycorrhizal plants in Jinghu wetland,Zhejing[J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2019,39(6):883-889. | |
| 18 | 孙红.丛枝菌根真菌对Cd胁迫下柳枝稷生长和能源品质的影响及机理研究[D].北京:中国农业大学,2018. |
| SUN H.The mechanism of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in improving Cd tolerance and bioenergy quality for switchgrass[D].Beijing:China Agricultural University,2018. | |
| 19 | 屈雁朋,房玉林,刘延琳,等.镉胁迫下接种AM真菌对葡萄次生代谢酶活性的影响[J].西北林学院学报,2009,24(5):101-105. |
| QU Y P, FANG Y L, LIU Y L,et al.Effects of AM fungal on the secondary metabolites of grape under cadmium stress[J].Journal of Northwest Forestry University,2009,24(5):101-105. | |
| 20 | BAXTER I, HOSMANI P S,RUS A,et al.Root suberin forms an extracellular barrier that affects water relations and mineral nutrition in Arabidopsis[J].PLoS Genetics,2009,5(5):e1000492. |
| 21 | 陈良华,胡相伟,杨万勤,等.接种丛枝菌根真菌对雌雄美洲黑杨吸收铅镉的影响[J].环境科学学报,2017,37(1):308-317. |
| CHEN L H, HU X W, YANG W Q,et al.Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizae fungi inoculation on absorption of Pb and Cd in females and males of Populus deltoides when exposed to Pb and Cd pollution[J].Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2017,37(1):308-317. | |
| 22 | ABDELHAMEED R E, METWALLY R A.Alleviation of cadmium stress by arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis[J].International Journal of Phytoremediation,2019,21(7):663-671. |
| 23 | 高璿濛,王玉丹,杨春雪.松嫩盐碱草地蒲公英根围AM真菌侵染特性及种类多样性[J].中国农业大学学报,2019,24(5):90-97. |
| GAO X M, WANG Y D, YANG C X.Mycorrhizal fungal infection characteristics and the diversity of Taraxacum mongolicum rhizosphere in Songnen saline-alkaline grassland[J].Journal of China Agricultural University,2019,24(5):90-97. | |
| 24 | 关萍,金恺,袁蕴宁,等.镉胁迫对两种蔊菜生长的影响及其在植物体内的积累和转运特性[J].沈阳农业大学学报,2020,51(6):714-720. |
| GUAN P, JIN K, YUAN Y N,et al.Effects of cadmium stress on growth of two species of Rorippa and the characteristics of accumulation and translocation to cd in plants[J].Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University,2020,51(6):714-720. | |
| 25 | 柳检,罗立强.芹菜根细胞的超微结构与铅形态特征分析[J].分析化学,2018,46(9):1479-1485. |
| LIU J, LUO L Q.Analysis of ultrastructure of root cell and lead speciation in celery[J].Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry,2018,46(9):1479-1485. | |
| 26 | 李春烨,丁国华,刘保东.重金属影响植物细胞超微结构和功能的研究进展[J].中国农学通报,2013,29(18):114-118. |
| LI C Y, DING G H, LIU B D.Research progress of heavy metal affecting plant cell ultrastructure and function[J].Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin,2013,29(18):114-118. | |
| 27 | 胡金朝,郑爱珍.重金属胁迫对植物细胞超微结构的损伤[J].商丘师范学院学报,2005,21(5):126-128,134. |
| HU J Z, ZHENG A Z.The damage of heavy metal stress on plant cell ultrastructure[J].Journal of Shangqiu Teachers College,2005,21(5):126-128,134. | |
| 28 | 姜艺,黄琳丽.镉胁迫对植物的影响探究[J].南方农业,2020,14(30):138-139. |
| JIANG Y, HUANG L L.Research on the effects of Cadmium stress on plants[J].South China Agriculture,2020,14(30):138-139. | |
| 29 | 高芳,林英杰,张佳蕾,等.镉胁迫对花生生理特性、产量和品质的影响[J].作物学报,2011,37(12):2269-2276. |
| GAO F, LIN Y J, ZHANG J L,et al.Effects of cadmium stresses on physiological characteristics,pod yield,and seed quality of peanut[J].Acta Agronomica Sinica,2011,37(12):2269-2276. | |
| 30 | 滕振宁,方宝华,刘洋,等.镉对不同品种水稻光合作用的影响[J].中国农业气象,2016,37(5):538-544. |
| TENG Z N, FANG B H, LIU Y,et al.Effects of Cd on photosynthesis of different rice varieties[J].Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology,2016,37(5):538-544. | |
| 31 | 吴建慧,刘俊学,张静,等.绢毛委陵菜叶片超微结构及生理特性对镉的响应[J].草地学报,2016,24(6):1278-1282. |
| WU J H, LIU J X, ZHANG J,et al.The response of Potentilla sericea ultrastructure and physiological characteristics to cadmium stress[J].Acta Agrestia Sinica,2016,24(6):1278-1282. |
| [1] | Xin’ai ZHONG, Shiqi MENG, Wanting Zhou, Qi YAO, Qiong ZHANG, Wang XING, Dali LIU. Identification of Glutathione S-transferase Gene Family in Sugar Beet and the Response to Cadmium Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(5): 790-801. |
| [2] | Jin-Yu LIU, Sheng-Wei LIN, Jing-Yu PAN, Qin ZHANG. Different Improved Soil Substrates on the Growth and Physiological Characters of Seedlingsfrom Trollius chinensis Bunge [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(6): 928-937. |
| [3] | Hong-Yi ZHAO, Jue-Lan GUAN, Xue-Yuan ZHANG, Qing LIANG, Jian ZHANG, Hong-Ling HU. Photosynthetic Characteristics of Sassafras tzumu under Cadmium Stress in Soil [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(4): 506-513. |
| [4] | SONG Zi-Wen, LIU Huan-Zhen, MA Xiao-Yu, SUN Guo-Yu, YI Jia-Xin, ZHANG Chun-Hua, YOU Yuan-Xiang, WANG De-Qiu, LI Kai-Long. Effects of Cadmium Stress on Growth,Physiology and Biochemistry of Different Ploidy of Populus ussuriensis [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(5): 728-734. |
| [5] | WU Jian-Hui, FAN Wei-Fang, NIU Zhe, ZHANG Jing, GAO Peng-Fei, LI Wen. Effects of Exogenous Methyl Jasmonate on Photosynthesis and Physiological Characteristics of Scutellaria regeliana under Drought Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(3): 360-367. |
| [6] | MA Yue-Hua, GUO Xiao-Rui, YANG Nan, ZHANG Ye, TANG Zhong-Hua, WANG Hong-Zheng. Physiological Mechanisms in Astragalus membranaceus Seedlings Responding to Cadmium Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2019, 39(4): 497-504. |
| [7] | FAN Qing;LÜXiu-Jun;YANG Liu;YANG Ying-Li*. Effects of Cd Stress on the Seed Germination,Seedling Growth and Activities of Antioxidant Enzymes in Petunia hybrida [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2010, 30(6): 685-691. |
| [8] | ZHANG Qing-Qing;XU Hai-Liang;YE Mao;LI Ji-Mei;YANG Hong-Mei;NIU Jun-Yong. Variation of Physiological Indexes of the Populus euphraticn’ Leaves under Different Groundwater Depth [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2009, 29(4): 453-459. |
| [9] | CHEN Shu-Ming;JIANG Ying-Shu;WANG Qiu-Yu*. Primary Studies on Physiological Response of Two Varieties of Cerasus humilis to NaHCO3 Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2009, 29(2): 209-215. |
| [10] | HE Yue-Jun;ZHONG Zhang-Cheng;*;LIU Jin-Chun;LIU Ji-Ming. Photosynthetic Characteristics of Broussonetia papyrifera Seedlings Inoculated AM Fungus in Limestone Soil Substratum [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2008, 28(4): 452-457. |
| [11] | YOU Ji-hong, LU Jing-mei, YANG Wen-jie. EFFECTS OF CALCIUM ON CHILLING RESISTANCE OF RADISHSEEDINGS AND SOME PHYSIOLOGICAL INDEXES [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2001, 21(3): 409-412. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||